In brief: A new collider concept would take quantum theories to an extreme
The approach could advance our understanding of fundamental forces under extreme conditions with applications from astrophysics to fusion research.
By Manuel Gnida
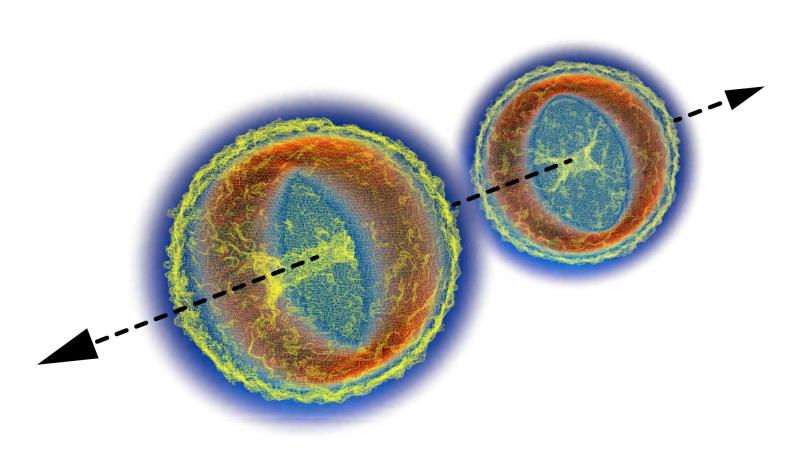
A new idea for smashing beams of elementary particles into one another could reveal how light and matter interact under extreme conditions that may exist on the surfaces of exotic astrophysical objects, in powerful cosmic light bursts and star explosions, in next-generation particle colliders and in hot, dense fusion plasma.
Most such interactions in nature are very successfully described by a theory known as quantum electrodynamics (QED). However, the current form of the theory doesn’t help predict phenomena in extremely large electromagnetic fields. In a recent paper in Physical Review Letters, researchers from the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and their colleagues have suggested a new particle collider concept that would allow us to study these extreme effects.
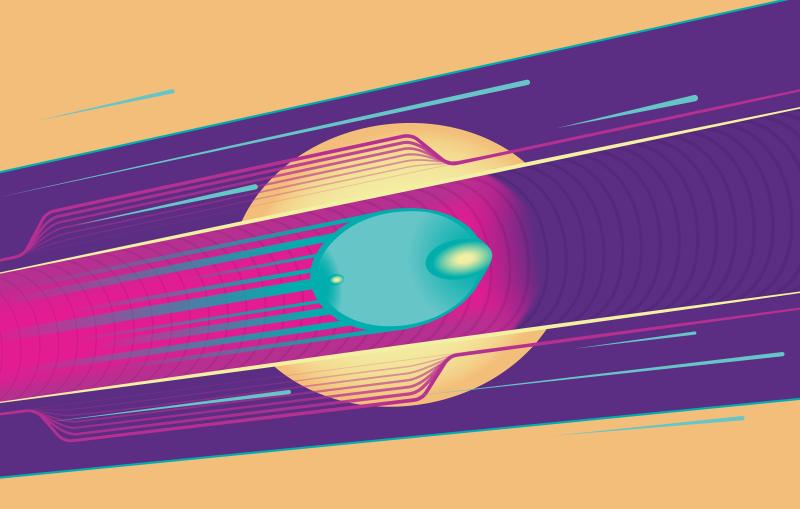
Extreme fields sap energy from colliding particle beams – an unwanted loss that is typically mitigated by bundling particles into relatively long, flat bunches and keeping the electromagnetic field strength in check. Instead, the new study suggests making particle bunches so short that they wouldn’t have enough time to lose energy. Such a collider would provide an opportunity to study intriguing effects associated with extreme fields, including the collision of photons emerging from the particle beams.
The study was a collaboration of researchers at SLAC; Princeton University; University of Lisbon, Portugal; University of Düsseldorf, Germany; and National Research Nuclear University MEPhI, Russia. Parts of this project were funded through a DOE Office of Science Early Career Research Program award. A workshop on exploring extreme-field QED and the physics phenomena it creates will be held at SLAC in late summer.
Citation: Vitaly Yakimenko et al., Physical Review Letters, 16 May 2019 (10.1103/PhysRevLett.122.190404)
Contact
For questions or comments, contact the SLAC Office of Communications at communications@slac.stanford.edu.
SLAC is a vibrant multiprogram laboratory that explores how the universe works at the biggest, smallest and fastest scales and invents powerful tools used by scientists around the globe. With research spanning particle physics, astrophysics and cosmology, materials, chemistry, bio and energy sciences and scientific computing, we help solve real-world problems and advance the interests of the nation.
SLAC is operated by Stanford University for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit energy.gov/science.