SLAC topics
Matter in extreme conditions
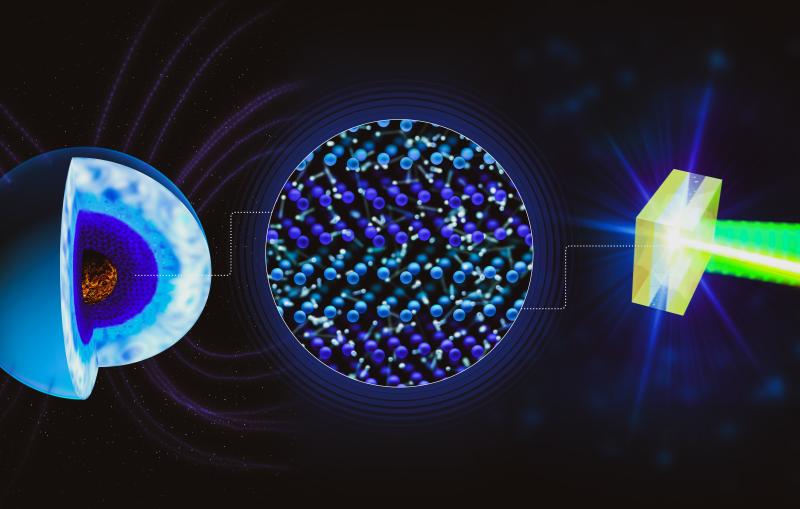
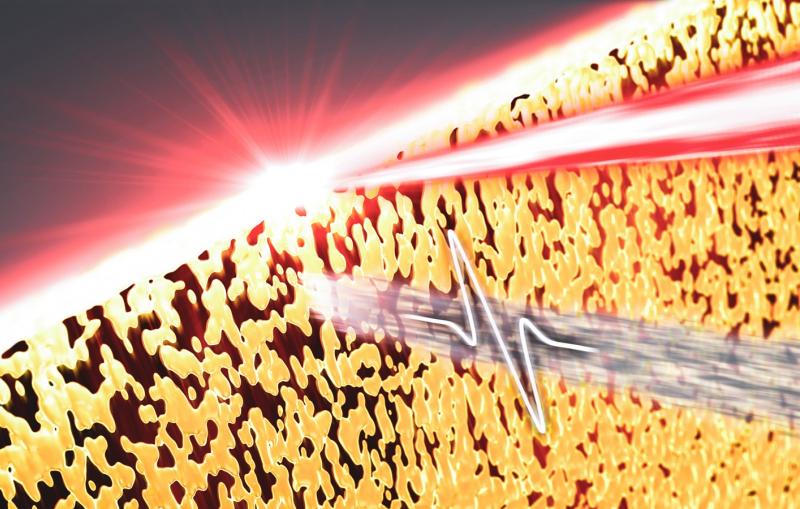
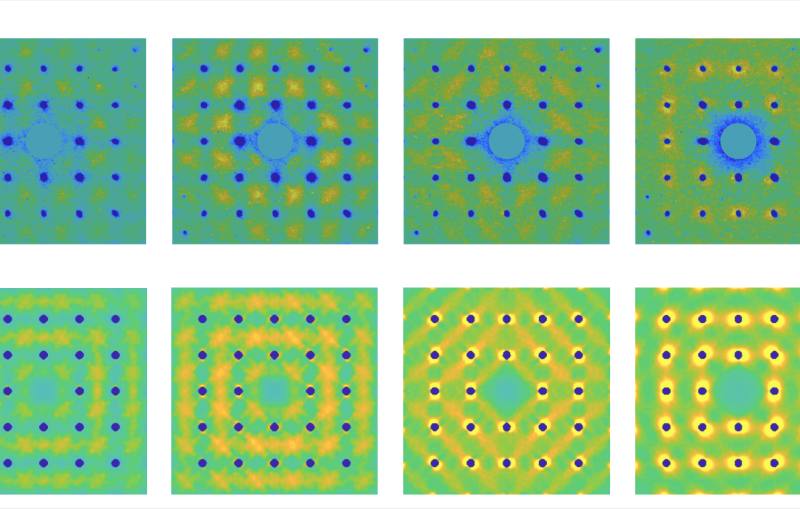
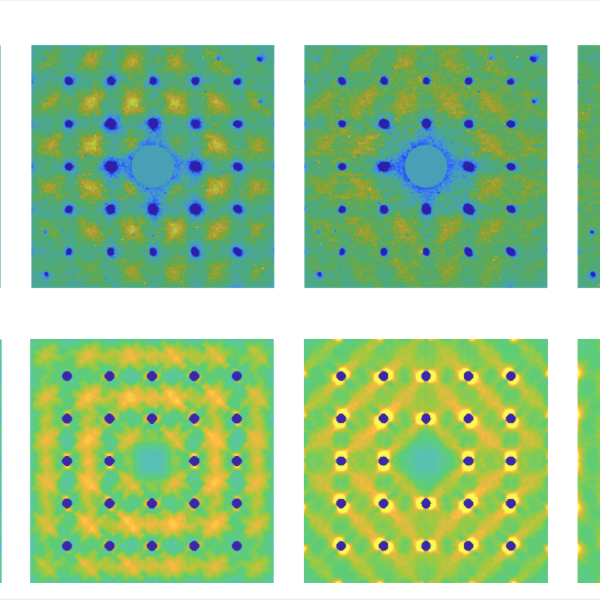
Under extreme conditions – like those in the hearts of planets or in exploding stars – materials can enter other exotic phases with unique characteristics. At SLAC, researchers are studying some of the most extreme and exotic forms of matter ever created, in detail never before possible.
Browse tagged content