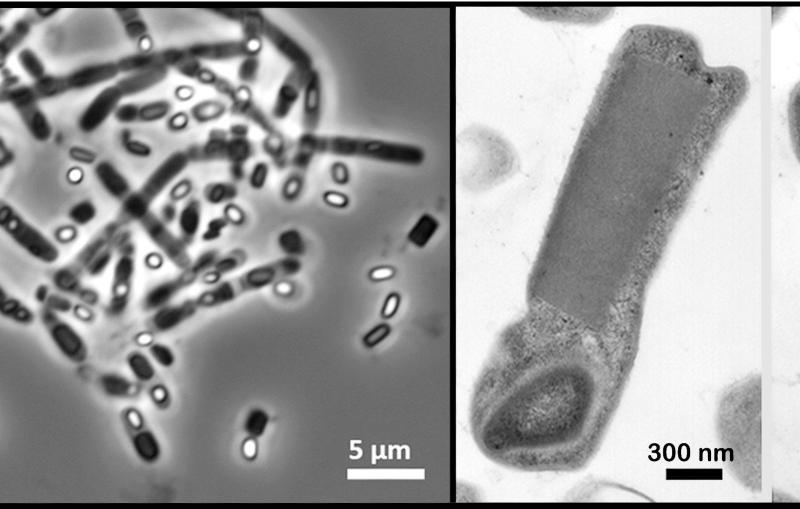

Illustration
X-ray laser pulses probe water droplets like these to discover water’s hidden (and sometimes bizarre) properties.
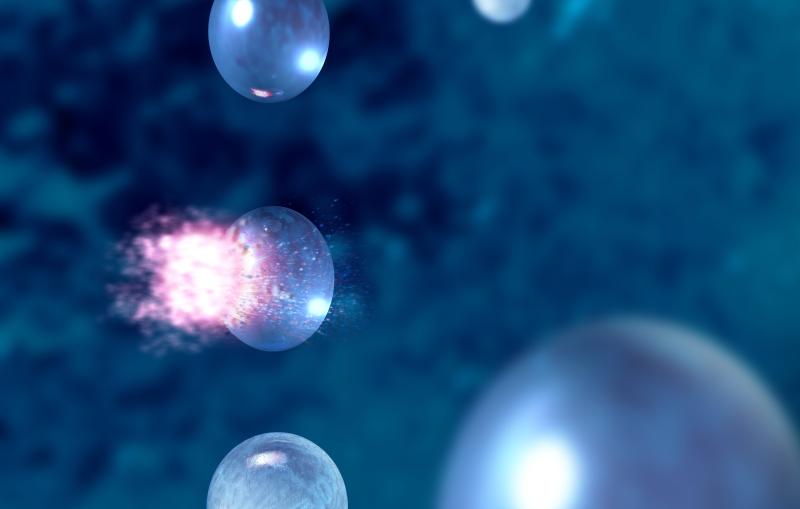
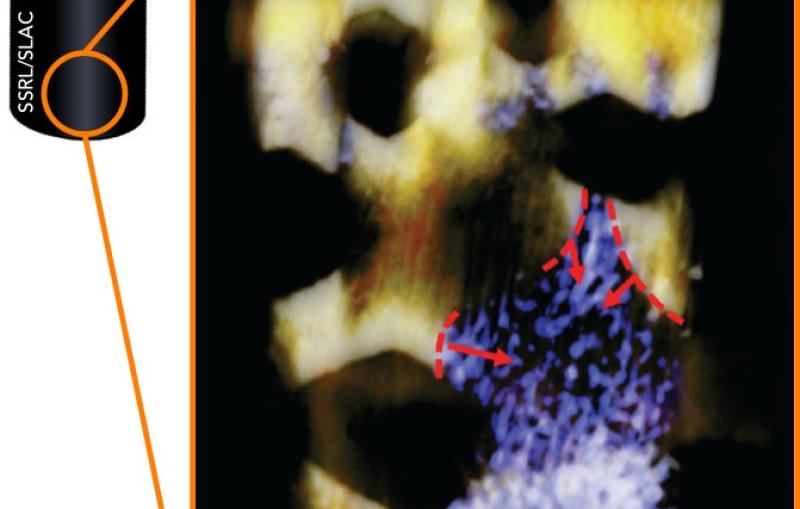


X-ray laser pulses probe water droplets like these to discover water’s hidden (and sometimes bizarre) properties.


