Scientists Map Protein in Living Bacterial Cells
Scientists have for the first time mapped the atomic structure of a protein within a living cell. The technique, which peered into cells with an X-ray laser, could allow scientists to explore some components of living cells as never before.
Scientists have for the first time mapped the atomic structure of a protein within a living cell. The technique, which peered into cells with an X-ray laser, could allow scientists to explore some components of living cells as never before.
The research, published Aug. 18 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, was conducted at the Department of Energy's SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory.
"This is a new way to look inside cells," said David S. Eisenberg, a biochemistry professor at University of California, Los Angeles, and Howard Hughes Medical Institute investigator.
"There are a lot of semi-ordered materials in cells where an X-ray laser could provide powerful information," Eisenberg added. They include arrays in white blood cells that help to fight parasites and infections, insulin-containing structures in the pancreas and structures that break fatty acids and other molecules into smaller units to release energy.
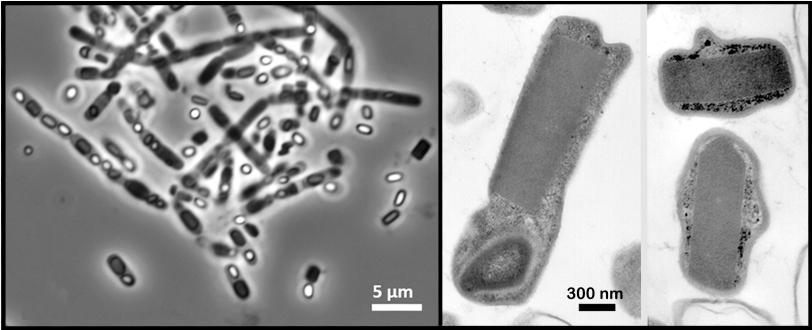
In the experiment at SLAC's Linac Coherent Light Source X-ray laser, a DOE Office of Science User Facility, researchers probed a soil-dwelling bacterium, Bacillus thuringiensis or Bt, that is commonly used as a natural insecticide. Strains of this bacterium produce microscopic protein crystals and spores that kill insects. Normally scientists need to find ways to crystallize proteins in order to get their structures – typically a time-consuming, hit-and-miss process – but these naturally occurring crystals eliminated that step.
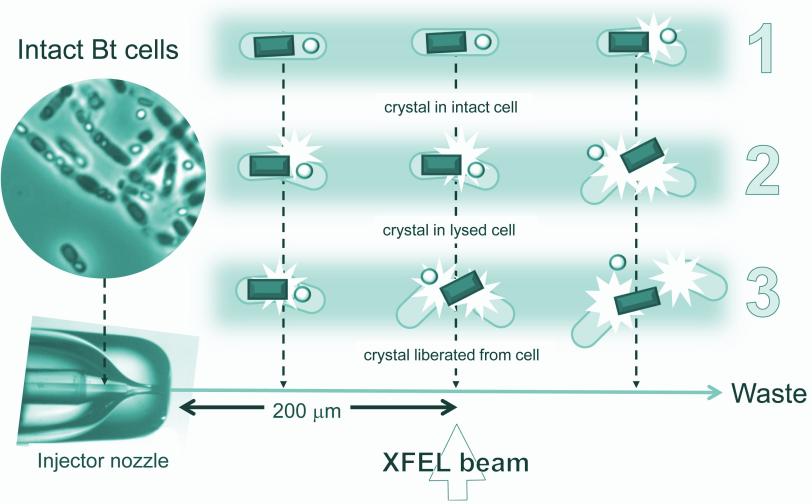
A liquid solution containing the living cells was jetted into the path of the ultrabright LCLS X-ray laser pulses. When a laser pulse struck a crystal, it created a pattern of diffracted X-ray light. More than 30,000 of these patterns were combined and analyzed by sophisticated software to reproduce the detailed 3-D structure of the protein.
Many of the bacterial cells likely ruptured and spewed their crystal contents as they flew at high speed toward the X-rays. But because it took just thousandths of a second for the cells to reach the X-ray pulses, it's very likely that many of the X-ray images showed protein crystals that were still inside the cells, the researchers concluded.
Importantly, Eisenberg said, "The rest of the cell contents don't obscure the results."
In addition, the 3-D structure of proteins obtained from the crystals in living bacteria cells was essentially identical to that obtained through other methods. Earlier studies had already shown that LCLS can be used to study smaller, easier-to-produce crystals than traditional X-ray sources require, although it typically requires a far larger volume of crystals to achieve atomic-scale resolution.
In an LCLS study published in 2012, a separate team of researchers used protein crystals grown inside live insect cells to study a potential weak spot in a parasite responsible for a disease called African sleeping sickness. But in that experiment they extracted the crystals rather than attempting to study them inside cells.
Eisenberg said possible next steps include improving the technique by developing new sample-delivery methods that are gentler to the cells' structure, and producing faster X-ray pulse rates that capture more images and yield even better results.
"I think this whole area of science is going to continue growing," he said.
In addition to UCLA and LCLS, other researchers participating in the study were from Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory; Arizona State University; University of California, Riverside; the Institute of Structural Biology in France; and the Max Planck Institute for Medical Research in Germany. The research was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Max Planck Society, the National Institutes of Health, the Keck Foundation and the National Science Foundation.
Citation
Contact
For questions or comments, contact the SLAC Office of Communications at communications@slac.stanford.edu.
SLAC is a multi-program laboratory exploring frontier questions in photon science, astrophysics, particle physics and accelerator research. Located in Menlo Park, Calif., SLAC is operated by Stanford University for the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science.
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.