News Brief
Via The University of Manchester
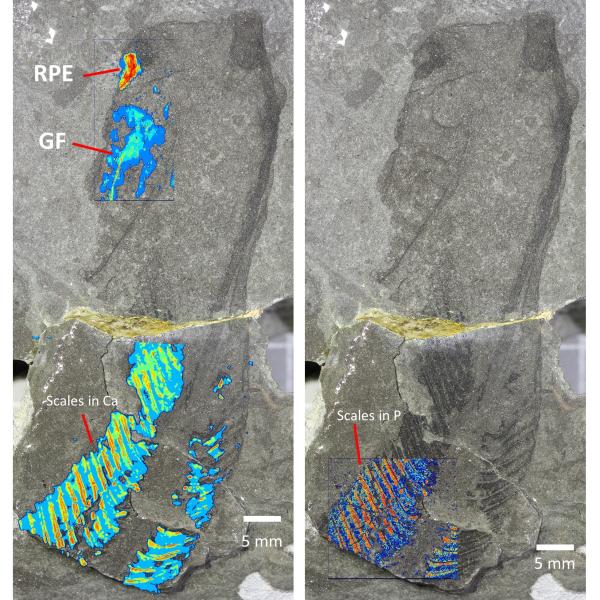
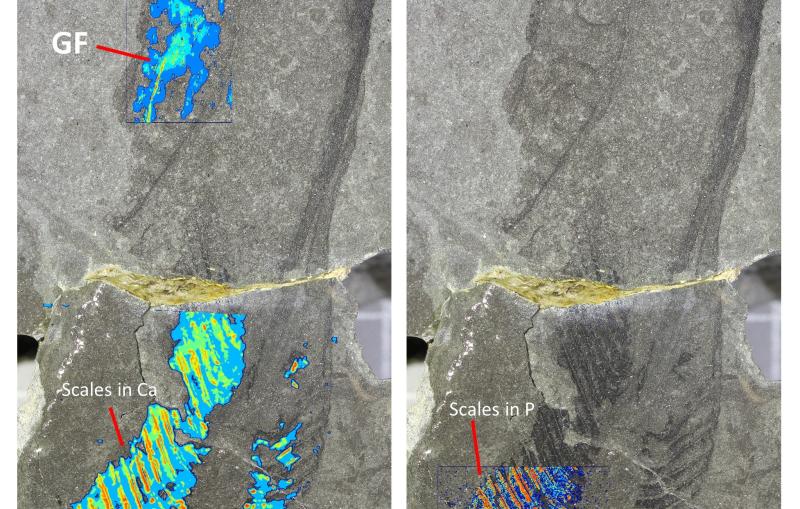
443-million-year-old fossils reveal early vertebrate eyes
News Brief
Via Innovative Genomics Institute
New method uncovers how viruses evade immune responses — and how we might fight back