A new way to shape a material’s atomic structure with ultrafast laser light
X-ray laser experiments show that intense light distorts the structure of a thermoelectric material in a unique way, opening a new avenue for controlling the properties of materials.
By Glennda Chui
Thermoelectric materials convert heat to electricity and vice versa, and their atomic structures are closely related to how well they perform.
Now researchers have discovered how to change the atomic structure of a highly efficient thermoelectric material, tin selenide, with intense pulses of laser light. This result opens a new way to improve thermoelectrics and a host of other materials by controlling their structure, creating materials with dramatic new properties that may not exist in nature.
“For this class of materials that’s extremely important, because their functional properties are associated with their structure,” said Yijing Huang, a Stanford University graduate student who played an important role in the experiments at the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory. “By changing the nature of the light you put in, you can tailor the nature of the material you create.”
The experiments took place at SLAC’s X-ray free-electron laser, the Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS). The results were reported today in Physical Review X and will be highlighted in a special collection devoted to ultrafast science.
Heat versus light
Because thermoelectrics convert waste heat to electricity, they’re considered a form of green energy. Thermoelectric generators provided electricity for the Apollo moon landing project, and researchers have been pursuing ways to use them to convert human body heat into electricity for charging gadgets, among other things. Run in reverse, they create a heat gradient that can be used to chill wine in refrigerators with no moving parts.
Tin selenide is considered one of the most promising thermoelectric materials that are grown as individual crystals, which are relatively cheap and easy to manufacture. Unlike many other thermoelectric materials, tin selenide is lead-free, Huang said, and it’s a much more efficient heat converter. Since it consists of regular cube-like crystals, similar to those of rock salt, it’s also relatively easy to make and tinker with.
To explore how those crystals respond to light, the team hit tin selenide with intense pulses of near-infrared laser light to change its structure. The light excited electrons in the sample’s atoms and shifted the positions of some of those atoms, distorting their arrangement.
Then the researchers tracked and measured those atomic movements and the resulting changes in the crystals’ structure with pulses of X-ray laser light from LCLS, which are fast enough to capture changes that happen in just millionths of a billionths of a second.
“You need the ultrafast pulses and atomic resolution that LCLS gives us to reconstruct where the atoms are moving,” said study co-author David Reis, a professor at SLAC and Stanford and director of the Stanford PULSE Institute. “Without that we would have gotten the story wrong.”
A startling result
This result was quite unexpected, and when Huang told the rest of the team what she had seen in the experiments, they had a hard time believing her.
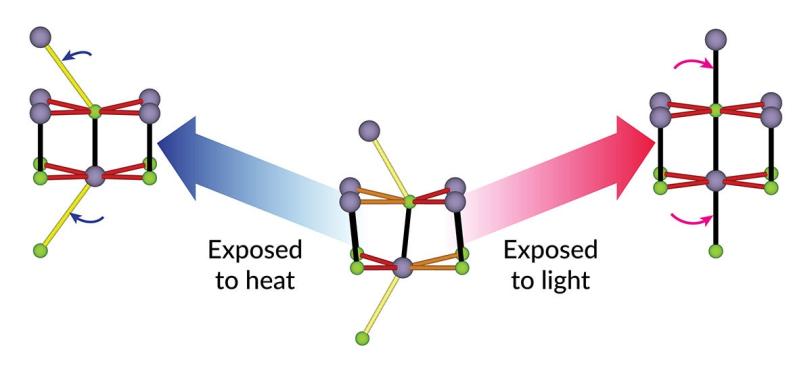
One tried-and-true way of changing the atomic structure of tin selenide is to apply heat, which changes the material in a predictable way and actually makes this particular material perform better. The conventional wisdom was that applying laser light would produce much the same result as heating.
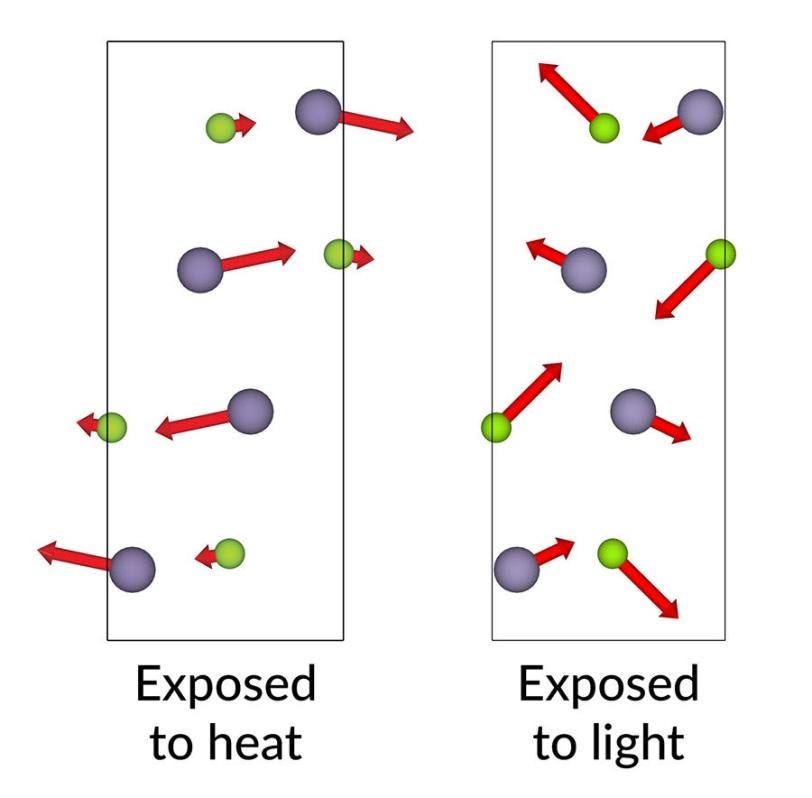
“That’s what we initially thought would happen,” said SLAC staff scientist Mariano Trigo, an investigator with the Stanford Institute for Materials and Energy Sciences (SIMES) at SLAC.
“But after almost two years of discussion, Yijing finally convinced the rest of the team that no, we were driving the material towards an entirely different structure. I think this result goes against most people's intuition about what happens when you excite electrons to higher energy levels.”
Theoretical calculations by Shan Yang, a graduate student at Duke University, confirmed that this interpretation of the experimental data was the right one.
“This material and its class are certainly very interesting, because it’s a system where small changes could lead to very different results,” Reis said. “But the ability to make entirely new structures with light – structures we don’t know how to make any other way – is presumably more universal than that.”
One area where it might be useful, he added, is in the decades-old quest to make superconductors – materials that conduct electricity with no loss – that operate at close to room temperature.
Researchers from DOE’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory also contributed to the study, which was funded by the DOE Office of Science. Preliminary work was performed at SLAC’s Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource (SSRL). SSRL and LCLS are DOE Office of Science user facilities.
Citation: Yijing Huang et al., Physical Review X, 14 February 2022, (10.1103/PhysRevX.12.011029)
For questions or comments, contact the SLAC Office of Communications at communications@slac.stanford.edu.
SLAC is a vibrant multiprogram laboratory that explores how the universe works at the biggest, smallest and fastest scales and invents powerful tools used by scientists around the globe. With research spanning particle physics, astrophysics and cosmology, materials, chemistry, bio- and energy sciences and scientific computing, we help solve real-world problems and advance the interests of the nation.
SLAC is operated by Stanford University for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time.