Shaken, Not Heated: the Ideal Recipe for Manipulating Magnetism
Scientists have found a way to distort the atomic arrangement and change the magnetic properties of an important class of electronic materials with ultra-short pulses of terahertz (mid-infrared) laser light without heating the material up.
By Mike Ross
Scientists have found a way to distort the atomic arrangement and change the magnetic properties of an important class of electronic materials with ultra-short pulses of terahertz (mid-infrared) laser light without heating the material up. While the achievement is currently of purely scientific interest, the researchers say this new approach control could ultimately lead to extremely fast, low-energy, non-volatile computer memory chips or data-switching devices.
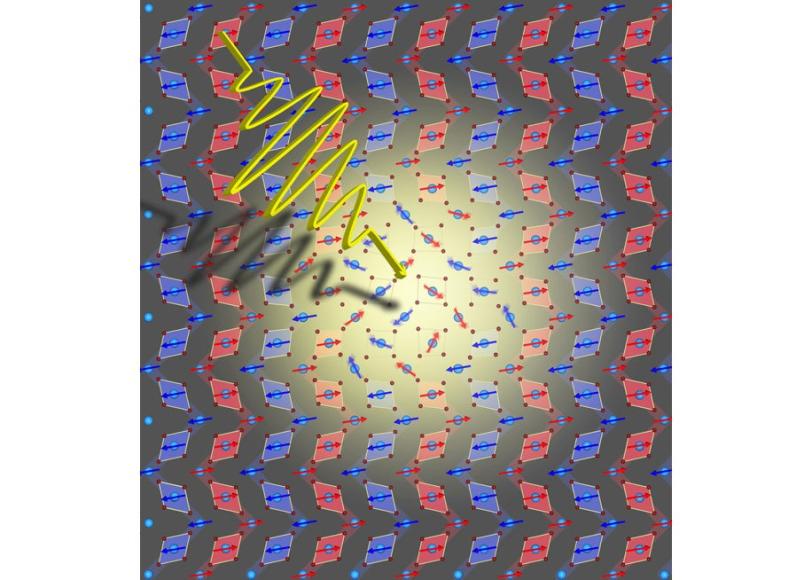
Working at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory’s Linear Coherent Light Source (LCLS), the scientists aimed intense, 130-femtosecond-long pulses of terahertz light at samples of manganite, a class of complex manganese-oxide compounds that has many desirable electronic and magnetic properties.
With each flash, the material’s atoms shimmied and shifted positions, although the overall temperature of the solid barely changed. The scientists then used X-ray laser pulses from the LCLS's Soft X-ray Materials Science (SXR) instrument to measure the material’s altered magnetism.
Rapid light-induced switching of manganite magnetism has been known for many years, said physicist Michael Först of the Max Planck Department of Structural Dynamics (MPSD) in Hamburg, Germany, one of the leaders of the international research group. However, earlier efforts to trigger this switch with higher-energy, near-visible lasers heated the materials, which greatly limits potential applications.
The latest LCLS experiments confirm that terahertz light only distorts the lattice enough to rearrange the electronic and magnetic properties while not generating extra heat.
The research team was led by scientists from the MPSD (Först and Andrea Cavalleri) and Brookhaven National Laboratory (Ron Tobey and John Hill), and included researchers from England and SLAC. They published their results last month in Physical Review B. SLAC co-authors are Bill Schlotter and Josh Turner, SXR instrument scientists; Wei-Sheng Lee and Rob Moore of the Stanford Institute for Materials & Energy Science (SIMES), and Mariano Trigo of Photon Ultrafast Laser Science and Engineering (PULSE).
“We will come back to LCLS later this year to use the X-ray Pump Probe instrument to measure terahertz-light-driven atomic displacements directly,” said Först. In recent years, his same group of MPSD scientists has also used terahertz light pulses to shake materials into a superconducting state and to change insulators into metals.
Future research aims to explore the phenomenon more deeply and start developing capabilities essential for applications, such as reverse-switching techniques, materials that can switch magnetically at room temperature or higher, and a laser source suitable for using on chips.
Contact
For questions or comments, contact the SLAC Office of Communications at communications@slac.stanford.edu.