Video: Dark Matter Hunt with LUX-ZEPLIN
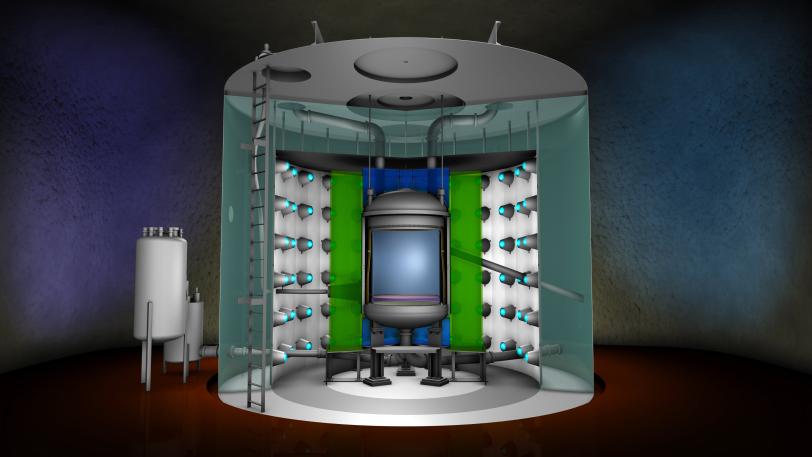
SLAC scientists are helping to build and test one of the biggest and most sensitive detectors ever designed to catch hypothetical WIMP particles.
Researchers at the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory are on a quest to solve one of physics’ biggest mysteries: What exactly is dark matter – the invisible substance that accounts for 85 percent of all the matter in the universe but can’t be seen even with our most advanced scientific instruments?
Most scientists believe it’s made of ghostly particles that rarely bump into their surroundings; that’s why billions of dark matter particles might zip right through our bodies every second without us even noticing. Leading candidates for dark matter particles are WIMPs, or weakly interacting massive particles.
Now SLAC is helping to build and test one of the biggest and most sensitive detectors ever designed to catch a WIMP – the LUX-ZEPLIN or LZ detector. The following video explains how it works.
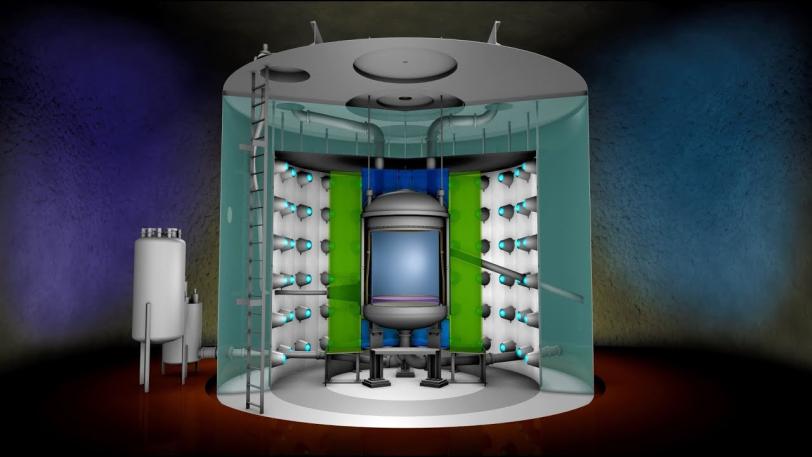

Dark Matter Hunt with LUX-ZEPLIN (LZ)
Contact
For questions or comments, contact the SLAC Office of Communications at communications@slac.stanford.edu.
SLAC is a multi-program laboratory exploring frontier questions in photon science, astrophysics, particle physics and accelerator research. Located in Menlo Park, Calif., SLAC is operated by Stanford University for the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science.
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.