Buckyballs and Diamondoids Join Forces in Tiny Electronic Gadget
Scientists have married two unconventional forms of carbon – one shaped like a soccer ball, the other a tiny diamond – to make a hybrid that could channel electron flow in molecular electronic devices.
Menlo Park, Calif. — Scientists have married two unconventional forms of carbon – one shaped like a soccer ball, the other a tiny diamond – to make a molecule that conducts electricity in only one direction. This tiny electronic component, known as a rectifier, could play a key role in shrinking chip components down to the size of molecules to enable faster, more powerful devices.
“We wanted to see what new, emergent properties might come out when you put these two ingredients together to create a ‘buckydiamondoid,’” said Hari Manoharan of the Stanford Institute for Materials and Energy Sciences (SIMES) at the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory. “What we got was a basically a one-way valve for conducting electricity – clearly more than the sum of its parts.”
The research team, which included scientists from Stanford University, Belgium, Germany and Ukraine, reported its results September 9, 2014, in Nature Communications.
Two Offbeat Carbon Characters Meet Up
Many electronic circuits have three basic components: a material that conducts electrons; rectifiers, which commonly take the form of diodes, to steer that flow in a single direction; and transistors to switch the flow on and off. Scientists combined two offbeat ingredients – buckyballs and diamondoids – to create the new diode-like component.
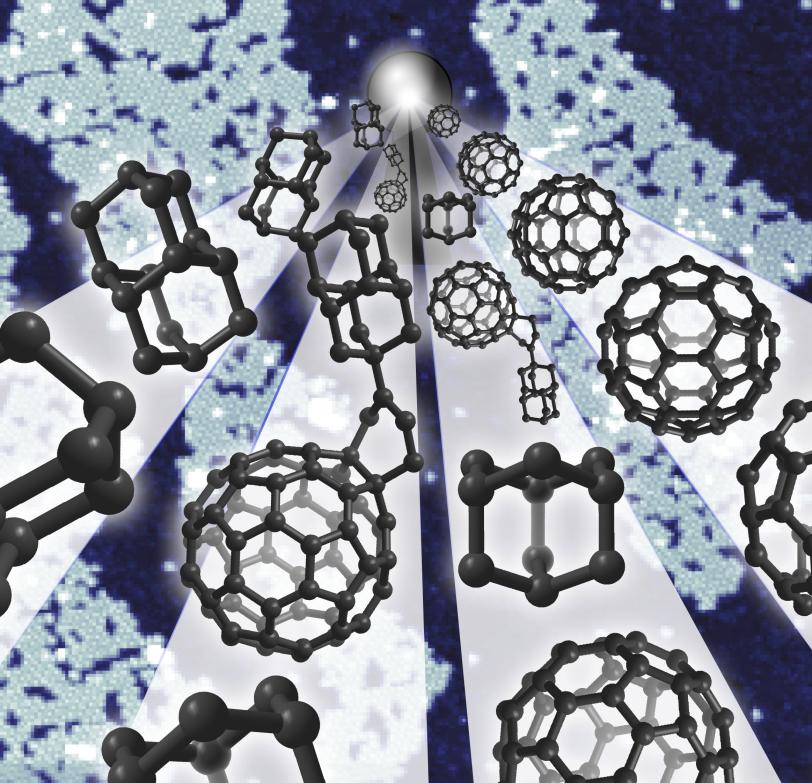
Buckyballs – short for buckminsterfullerenes – are hollow carbon spheres whose 1985 discovery earned three scientists a Nobel Prize in chemistry. Diamondoids are tiny carbon cages bonded together as they are in diamonds, but weighing less than a billionth of a billionth of a carat. Both are subjects of a lot of research aimed at understanding their properties and finding ways to use them.
In 2007, a team led by researchers from SLAC and Stanford discovered that a single layer of diamondoids on a metal surface can efficiently emit a beam of electrons. Manoharan and his colleagues wondered: What would happen if they paired an electron-emitting diamondoid with another molecule that likes to grab electrons? Buckyballs are just that sort of electron-grabbing molecule.
A Very Small Valve for Channeling Electron Flow
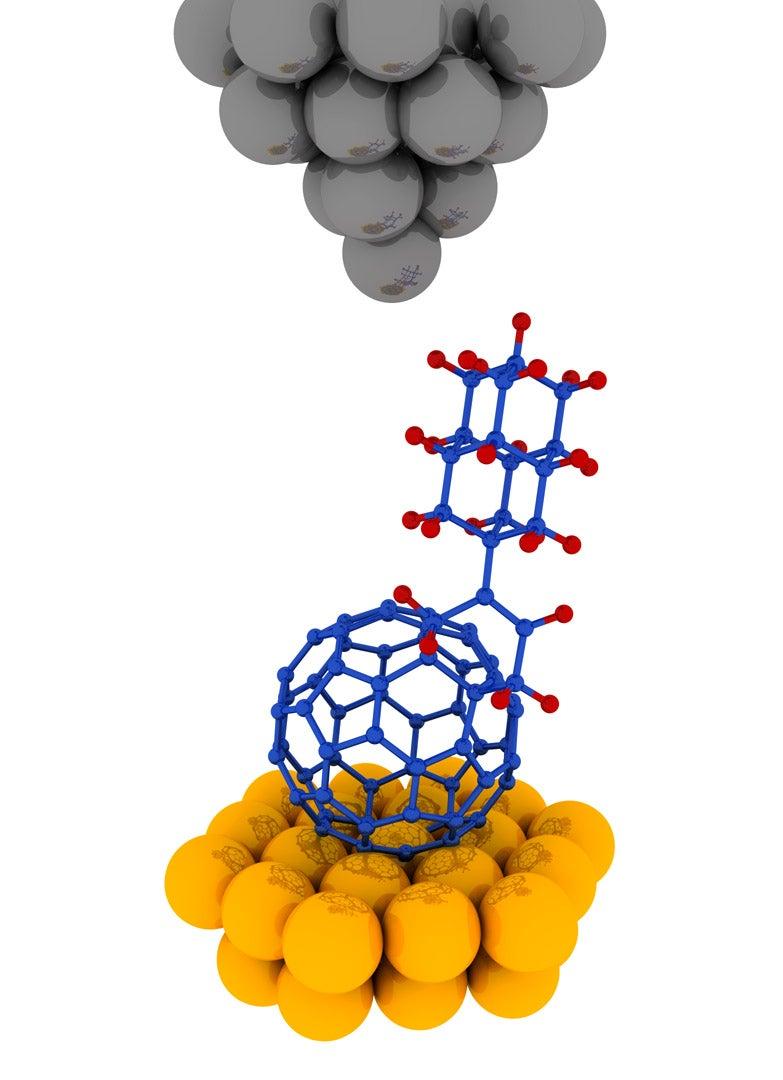
For this study, diamondoids were produced in the SLAC laboratory of SIMES researchers Jeremy Dahl and Robert Carlson, who are world experts in extracting the tiny diamonds from petroleum. They were then shipped to Germany, where chemists at Justus-Liebig University figured out how to attach them to buckyballs.
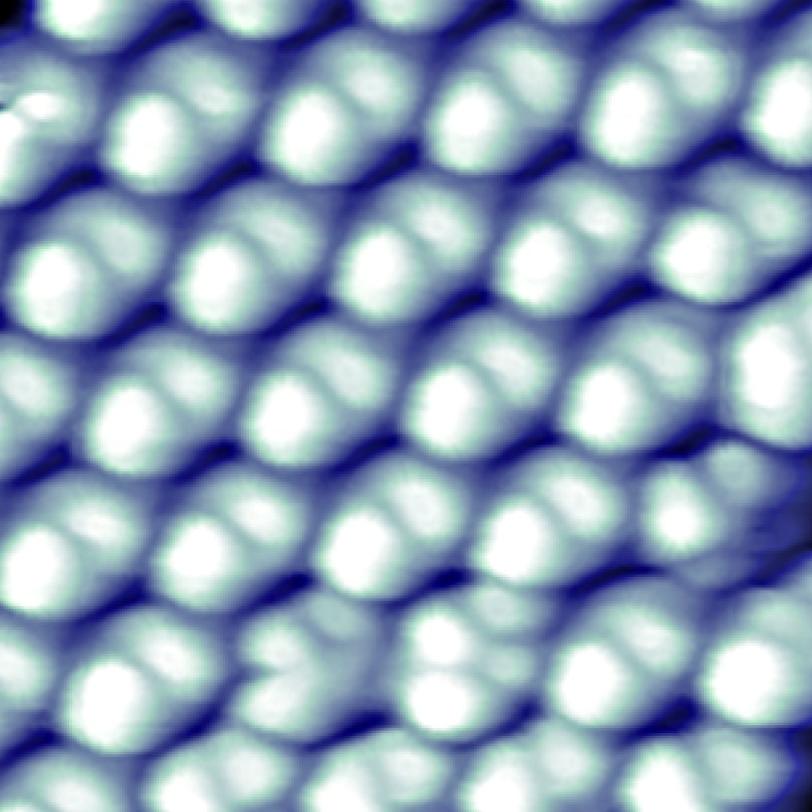
The resulting buckydiamondoids, which are just a few nanometers long, were tested in SIMES laboratories at Stanford. A team led by graduate student Jason Randel and postdoctoral researcher Francis Niestemski used a scanning tunneling microscope to make images of the hybrid molecules and measure their electronic behavior. They discovered the hybrid is an excellent rectifier: The electrical current flowing through the molecule was up to 50 times stronger in one direction, from electron-spitting diamondoid to electron-catching buckyball, than in the opposite direction. This is something neither component can do on its own.
While this is not the first molecular rectifier ever invented, it’s the first one made from just carbon and hydrogen, a simplicity researchers find appealing, said Manoharan, who is an associate professor of physics at Stanford. The next step, he said, is to see if transistors can be constructed from the same basic ingredients.
“Buckyballs are easy to make – they can be isolated from soot – and the type of diamondoid we used here, which consists of two tiny cages, can be purchased commercially,” he said. “And now that our colleagues in Germany have figured out how to bind them together, others can follow the recipe. So while our research was aimed at gaining fundamental insights about a novel hybrid molecule, it could lead to advances that help make molecular electronics a reality.”
Other research collaborators came from the Catholic University of Louvain in Belgium and Kiev Polytechnic Institute in Ukraine. The primary funding for the work came from the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science.
Citation: J. C. Randel et al, Nature Communications, 9 September 2014 (10.1038/ncomms5877)
Press Office Contact: Andrew Gordon, agordon@slac.stanford.edu, (650) 926-2282
SLAC is a multi-program laboratory exploring frontier questions in photon science, astrophysics, particle physics and accelerator research. Located in Menlo Park, California, SLAC is operated by Stanford University for the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science.
The Stanford Institute for Materials and Energy Sciences (SIMES) is a joint institute of SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and Stanford University. SIMES studies the nature, properties and synthesis of complex and novel materials in the effort to create clean, renewable energy technologies. For more information, please visit simes.slac.stanford.edu.
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.