X-ray Laser Gives Buckyballs a Big Kick
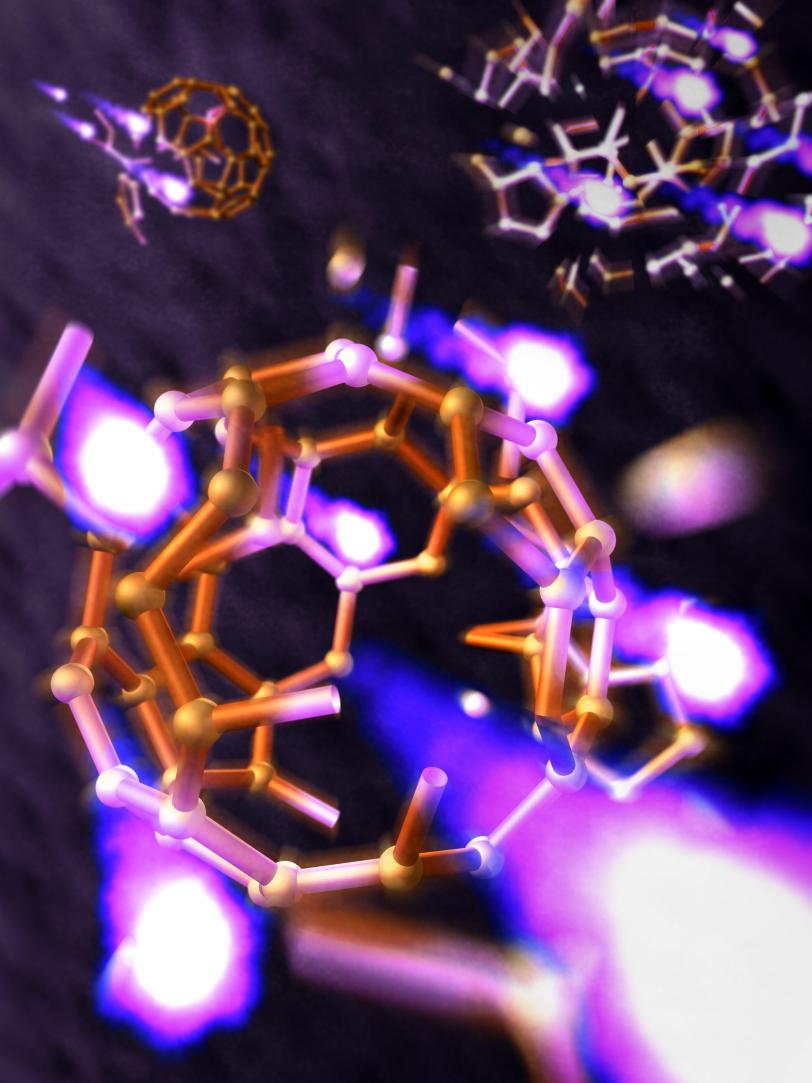
Scientists at SLAC have been blowing up "buckyballs" – soccer-ball-shaped carbon molecules – with an X-ray laser to understand how they fly apart. The results, they say, will help them interpret X-ray images of tiny viruses, individual proteins and other important biomolecules.
By Glenn Roberts Jr.
Scientists at SLAC have been blowing up "buckyballs" – soccer-ball-shaped carbon molecules – with an X-ray laser to understand how they fly apart. The results, they say, will aid biological studies by improving the analysis of X-ray images of tiny viruses, individual proteins and other important biomolecules.
The experiment was carried out at SLAC's Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS) X-ray laser, a DOE Office of Science user facility, and the results appear in the June 27 issue of Nature Communications.
"It's sort of a Catch-22: You need the X-ray laser focus to be extremely intense and bright to get a good picture," says Nora Berrah, an experimental physicist at the University of Connecticut. "But the X-rays also trigger unexpectedly rapid and substantial damage and motion in the atoms, resulting in a blurred image." Berrah led the research with Robin Santra, a theorist from the Center for Free-Electron Laser Science at Germany's DESY lab.
Because buckyballs are composed entirely of carbon – the backbone of all life on Earth – they are a good stand-in for biological molecules, many of which also have strong atomic bonds. They got their formal name, “buckminsterfullerene,” for their resemblance to the geodesic domes invented by R. Buckminster Fuller.
Within 20 femtoseconds, or quadrillionths of a second, after being struck by LCLS X-rays, atoms in the buckyballs had flown apart and traveled a distance about 10 times longer than their own diameters, the researchers reported.
“The bright X-rays knock a large number of electrons out of the molecule, its atoms become more and more positively charged, and the electric repulsion finally lets the molecule explode,” Berrah said.
Just as fast-moving objects can blur conventional photographs, the high speeds of atoms and free-floating electrons in an exploding molecule can obscure X-ray images, so the best way to observe a molecule in its intact state is to use the shortest, brightest pulses available at LCLS to snap images before any damage occurs.
In addition, modeling the details of the damage can help researchers find the best timing and techniques for capturing accurate images that map the 3-D structure and other properties of the samples.
At LCLS, researchers used a specialized oven to create a thin gas beam of buckyballs that passed into the path of LCLS X-ray pulses. They varied the energy and length of the LCLS pulses and used a specialized spectrometer, developed in Sweden, to measure charged fragments of the molecules in the X-ray-driven explosions and their aftermath.
On average, about 180 particles of light, called photons, entered each buckyball struck by an LCLS pulse, and in some cases they stripped all the electrons from the carbon atoms while blowing the molecule apart.
Then the highly charged buckyball bits, known as ions, formed tiny plasmas and began to pull free-floating electrons back toward them – a process known as "secondary ionization."
Without experiments, developing models that simulate and predict the behavior of large, complex molecules is challenging even with powerful computers, Berrah noted. The experiment at LCLS was key in helping to construct and validate a new theoretical model to explain how buckyballs behave under extreme X-ray intensity.
"What's most important, in fact, are the secondary ionization effects that were explained by the model, which we validated," Berrah explained. "These effects were stronger and lasted longer than expected."
The scientists compared the debris of the molecular explosion with a simulation developed by DESY scientist Zoltan Jurek of CFEL. “Such simulation tools were originally developed for things like liquids and polymers that are at or near equilibrium, not for the high energies and strong forces we see here,” explains Jurek. “Nobody knew if this would really work.”
Berrah said, "We needed the experimental data to build and develop the model. At the same time, this powerful model allowed us to interpret the data. This is an important milestone for the investigation of individual, complex biomolecules like proteins with lasers like LCLS."
In addition to the University of Connecticut, the Center for Free-Electron Laser Science and SLAC, other collaborators in the study are from Western Michigan University, The Hamburg Center for Ultrafast Imaging and University of Hamburg in Germany, University of Gothenburg in Sweden, Oxford University in the United Kingdom, the Institute of Inorganic Methodologies and Plasmas in Italy, Stanford PULSE Institute, Imperial College London, University of Turku in Finland, University of Texas at Austin, Synchrotron SOLEIL in France and Tohoku University in Japan.
This work was supported by the DOE Office of Science, the Hamburg Center for Ultrafast Imaging in Germany, the Swedish Research Council, Göran Gustafsson and Knut and Alice Wallenberg foundations in Sweden, and the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council in the U.K.
Citation
B. F. Murphy, T. Osipov, Z. Jurek et al. Nature Communications, 27 June 2014 (10.1038/ncomms5281)
Contact
For questions or comments, contact the SLAC Office of Communications at communications@slac.stanford.edu.
SLAC is a multi-program laboratory exploring frontier questions in photon science, astrophysics, particle physics and accelerator research. Located in Menlo Park, California, SLAC is operated by Stanford University for the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science.
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.