World's Most Powerful X-ray Laser Beam Refined to Scalpel Precision
With a thin sliver of diamond, scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory have transformed the Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS) into an even more precise tool for exploring the nanoworld.
Menlo Park, Calif. — With a thin sliver of diamond, scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory have transformed the Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS) into an even more precise tool for exploring the nanoworld. The improvements yield laser pulses focused to higher intensity in a much narrower band of X-ray wavelengths, and may enable experiments that have never before been possible.
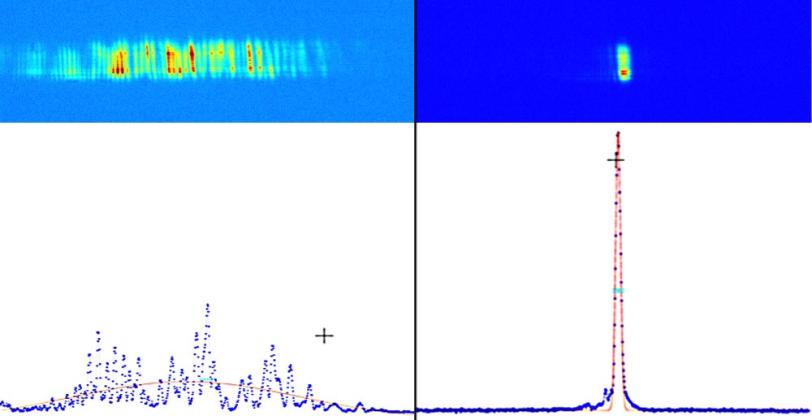
In a process called “self-seeding,” the diamond filters the laser beam to a single X-ray color, which is then amplified. Like trading a hatchet for a scalpel, the advance will give researchers more control in studying and manipulating matter at the atomic level and will deliver sharper images of materials, molecules and chemical reactions.
“The more control you have, the finer the details you can see,” said Jerry Hastings, a SLAC scientist and co-author on the research, published this week in Nature Photonics. “People have been talking about self-seeding for nearly 15 years. The method we incorporated at SLAC was proposed in 2010 by Gianluca Geloni, Vitali Kocharyan and Evgeni Saldin of the European XFEL and DESY research centers in Germany. When our team from SLAC and Argonne National Laboratory built it, we were surprised by how simple, robust and cost-effective the engineering turned out to be.” Hastings added that laboratories around the world are already planning to incorporate this important advance into their own X-ray laser facilities.
Self-seeding has the potential to produce X-ray pulses with significantly higher intensity than the current LCLS performance. The increased intensity in each pulse could be used to probe deep into complex materials to help answer questions about exotic substances like high-temperature superconductors or intricate electronic states like those found in topological insulators.
The LCLS generates its laser beam by accelerating bunches of electrons to nearly the speed of light and setting them on a zigzag path with a series of magnets. This forces the electrons to emit X-rays, which are gathered into laser pulses that are a billion times brighter than any available before, and fast enough to scan samples in quadrillionths of a second.
Without self-seeding these X-ray laser pulses contain a range of wavelengths (or colors) in an unpredictable pattern, not all of which experimenters can use. Until now, creating a narrower wavelength band at LCLS meant subtracting the unwanted wavelengths, resulting in a substantial loss of intensity.
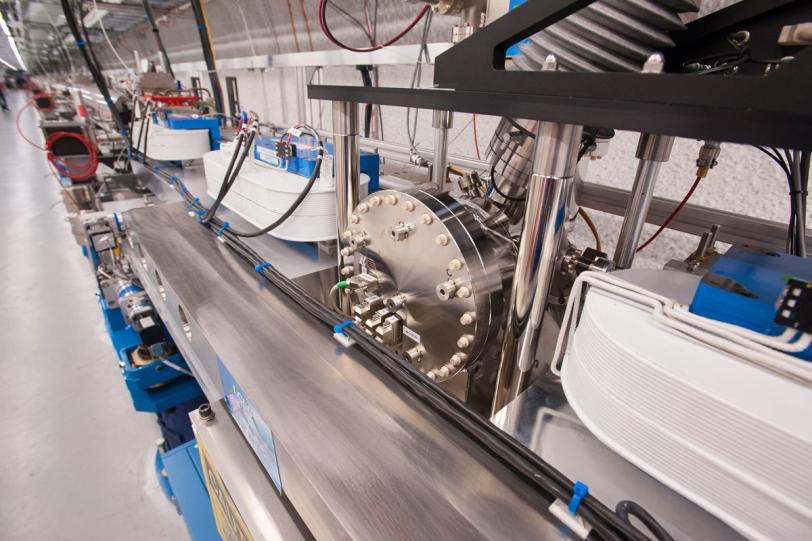
To create a precise X-ray wavelength band and make the LCLS even more “laser-like,” researchers installed a slice of diamond crystal halfway down the 130-meter bank of magnets where the X-rays are generated.
Producing the narrower wavelength band is just the beginning. “The resulting pulses could pack up to 10 times more intensity when we finish optimizing the system and add more undulators," said Zhirong Huang, a SLAC accelerator physicist and co-author, who has been a major contributor to the project.
LCLS has already begun accepting proposals to use self-seeding for future experiments.
The first tests of the LCLS self-seeding system have generated intense excitement among scientists the world over. Representatives from other X-ray laser facilities, including Swiss FEL, SACLA in Japan and the European XFEL, came to help, and also learn how to implement it at their own sites.
According to Paul Emma, a co-author who was a key figure in the original commissioning of the LCLS and in implementing self-seeding, “the entire group of observers was smiling from ear to ear." Emma, now working at Lawrence Berkeley National Lab, has a history of making tough jobs look easy, but he would only say, "I was very happy to see it work."
The team included collaborators from the Technical Institute for Superhard and Novel Carbon Materials in Troitsk, Russia, which supplied the diamond filter, and Argonne National Laboratory, which designed the vacuum chamber to house it and the precision motion controls to adjust it. The research was supported by the DOE’s Office of Science.
To read more, see the paper from Nature Photonics: http://www.nature.com/nphoton/journal/vaop/ncurrent/pdf/nphoton.2012.180.pdf
Contact
For questions or comments, contact the SLAC Office of Communications at communications@slac.stanford.edu.
SLAC is a multi-program laboratory exploring frontier questions in photon science, astrophysics, particle physics and accelerator research. Located in Menlo Park, California, SLAC is operated by Stanford University for the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science. To learn more, please visit www.slac.stanford.edu.
DOE’s Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.