Shining light on the radical production of DNA building blocks
An international team has uncovered details about the formation of DNA's building blocks, paving the way for potential medical and therapeutic applications.
Despite its fundamental role in biology and extensive studies over half a century, many aspects of how DNA's building blocks are formed remain unclear. Now, an international team of scientists has revealed valuable details about this intricate process. The research, published last week in Science, offers insights into the radical enzyme – a highly reactive molecule that initiates the DNA synthesis – and could pave the way for medical and therapeutic applications for cancer and infectious diseases.
The team, which included researchers from Stockholm University, CNRS-University of Toulouse, the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, and several other institutions combined their expertise to crack open the mysteries of ribonucleotide reductases (RNRs), a unique set of enzymes that produce the DNA building blocks.
Paradoxical phenomenon
RNRs have puzzled scientists for decades. They generate free radicals, which are a type of molecule that can cause damage to cells, but which are also essential to several biochemical processes. Solving the mystery of RNRs lies in understanding their active radical state, a seemingly paradoxical phenomenon first discovered 50 years ago in which the protein is itself a radical, and thus has an odd number of electrons.
“Having a background in chemistry, it amazed me when I learned that enzymes used radicals,” said Martin Högbom, a researcher at Stockholm University who led the research. “At that time, the idea of determining what a protein radical looks like seemed even theoretically far-fetched. But this curiosity followed me throughout my scientific career.”
Over the years, many enzyme systems have been recognized to use radical chemistry, but until now it has not been possible to observe the structure of proteins in this reactive state due to their inherent sensitivity to being measured.
“We use X-rays to measure the structure of proteins, but radicals are extremely sensitive to radiation damage induced by these X-ray beams.” said SLAC scientist and collaborator Roberto Alonso-Mori. “The X-rays can generate many electrons and other radicals which can nullify the protein radical state we want to investigate.”
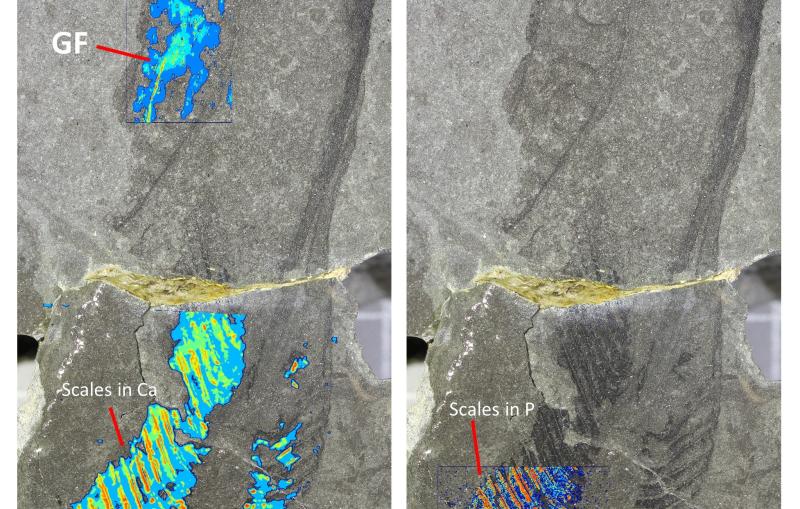
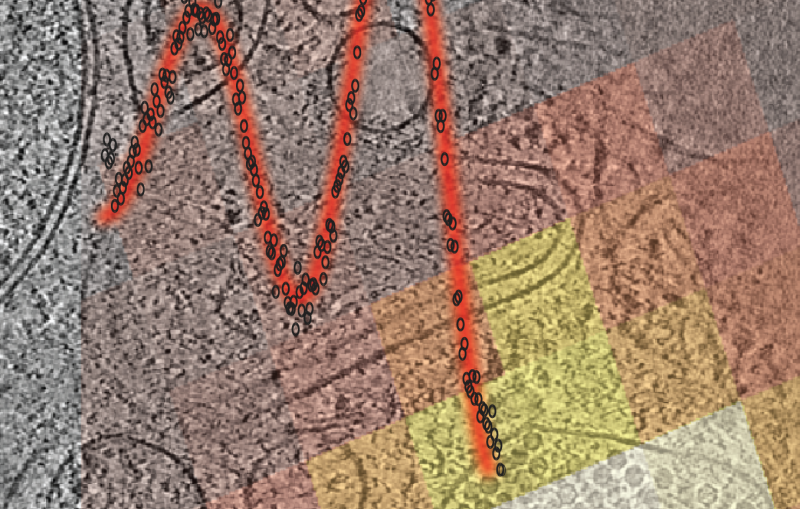
Using SLAC’s Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS) X-ray laser, the team employed a cutting-edge technique called serial femtosecond crystallography, which allows researchers to observe proteins and other molecules at the temperature at which they’re found in nature, coupled to diffraction-before-destruction, which allows researchers to collect precise information from delicate samples in the instant before they’re blown apart by the laser. This allowed them to capture images of the protein in its active radical state for the first time, providing direct insight into how it behaves when it is functional.
Therapeutic potential
Beyond its foundational significance in biology, the discovery has therapeutic potential since RNR is essential for cell division.
Collaborator Jan Kern, a scientist at Berkeley Lab, said “With this new method, we can understand the natural control and utilization of these reactive states, offering potential advancements in treatments, especially for conditions like cancer.”
To follow up, the researchers hope to expand their studies into other forms of this enzyme.
“We aim to study other types of ribonucleotide reductases, expanding our understanding of radical formation in different enzyme types,” said collaborator Hugo Lebrette, a former postdoctoral researcher at Stockholm University and now a research group leader at the CNRS-University of Toulouse.
“Comparing these could provide insights into targeting specific enzymes in relevant organisms,” added collaborator Vivek Srinivas, postdoctoral researcher at Stockholm University. “This would open the door to observing different proteins in their active forms, with the hope that this can reshape disease treatment methods.”
While the data collection itself was executed within an hour, the foundation for this milestone was laid over several decades, marked by meticulous groundwork, identification of suitable model systems, and sample preparation.
“My fascination with protein radicals began nearly 30 years ago during my undergraduate studies,” Högbom said. “The concept of an enzyme generating and maintaining a radical was a revelation. Our goal is to understand this protein family comprehensively, and each experiment, each paper, propels us closer to that objective. This latest result is a major step forward.”
LCLS is a DOE Office of Science user facility. This research was supported by the Office of Science (BES).
Citation: H. Lebrette et al., Science, 6 October 2023 (10.1126/science.adh8160)
Contact
For questions or comments, contact the SLAC Office of Communications at communications@slac.stanford.edu.
About SLAC
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory explores how the universe works at the biggest, smallest and fastest scales and invents powerful tools used by researchers around the globe. As world leaders in ultrafast science and bold explorers of the physics of the universe, we forge new ground in understanding our origins and building a healthier and more sustainable future. Our discovery and innovation help develop new materials and chemical processes and open unprecedented views of the cosmos and life’s most delicate machinery. Building on more than 60 years of visionary research, we help shape the future by advancing areas such as quantum technology, scientific computing and the development of next-generation accelerators.
SLAC is operated by Stanford University for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time.