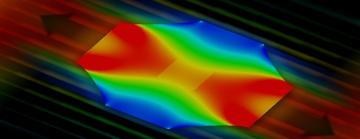
A new way to fine-tune exotic materials: Thin, stretch and clamp
Turning a brittle oxide into a flexible membrane and stretching it on a tiny apparatus flipped it from a conducting to an insulating state and changed its magnetic properties. The technique can be used to study and design a broad range of materials for use in things like sensors and detectors.
By Glennda Chui
One way to change the properties of a material is to stretch it just a wee bit, so its atoms are farther apart but the bonds between them don’t break. This extra distance affects the behavior of electrons, which determine whether the material is an insulator or a conductor of electricity, for instance.
But for an important class of complex oxide materials, stretching doesn’t work so well; they’re as brittle as ceramic coffee cups and would break.
Scientists at the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and Stanford University have now found a way around this problem for a complex oxide known as LCMO. They created a super-thin, flexible membrane from the normally brittle material, used micromanipulators to stretch it on a tiny apparatus and glued it in place to preserve the stretch.
By applying gentle heat to melt the glue, they could release and stretch the same transparent membrane again and again and watch it flip from being an insulator to a conductor and back again. Stretching also changed its magnetic properties.
“We can really stretch and strain these things dramatically, by up to 8%,” said Harold Hwang, a professor at SLAC and Stanford and an investigator with the Stanford Institute for Materials and Energy Sciences (SIMES). “This opens a whole new world of possibilities that will have an impact beyond this particular study.”
The research team reported its findings in Science today.
New ways to float free and stretch
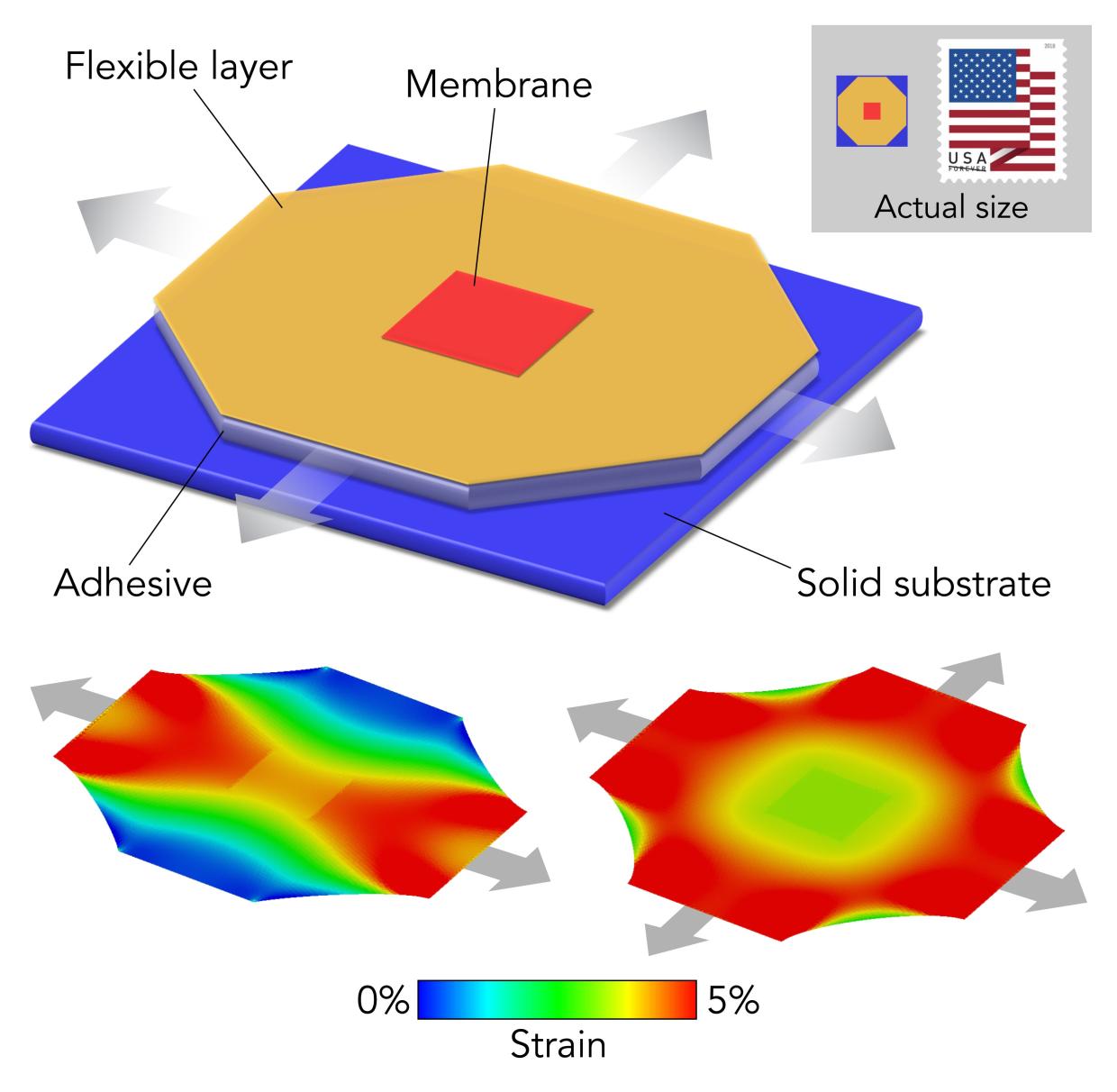
LCMO, or lanthanum calcium manganese oxide, is what’s known as a quantum material because its electrons behave in unconventional and often surprising ways. Scientists want to be able to control and fine-tune this behavior for a new generation of electronics with applications in power transmission, transportation, computing, sensors and detectors.
Thin films of quantum materials are generally grown on the surface of another material. Four years ago, Hwang’s group reported an easy way to detach those delicate layers so they could be studied in new ways.
One of the researchers who worked on that study, Seung Sae Hong, led this one as well. He used the new method to create and free small pieces of LCMO that were thinner than ever before – less than 20 nanometers thick. They were nearly transparent and surprisingly flexible.
Directly stretching such a small, fragile scrap would be difficult, but Hong got around that problem by putting it on a thin polymer film – kind of like a plastic bag from a grocery store – where it stuck of its own volition.
Then he clamped the polymer film on each of its four sides and used a micromanipulator to pull and stretch it – sometimes in one direction, sometimes in both directions at once. Once the LCMO was stretched, its polymer backing could be glued to another surface and taken to another instrument for examination with X-rays.
Flipping electronic states
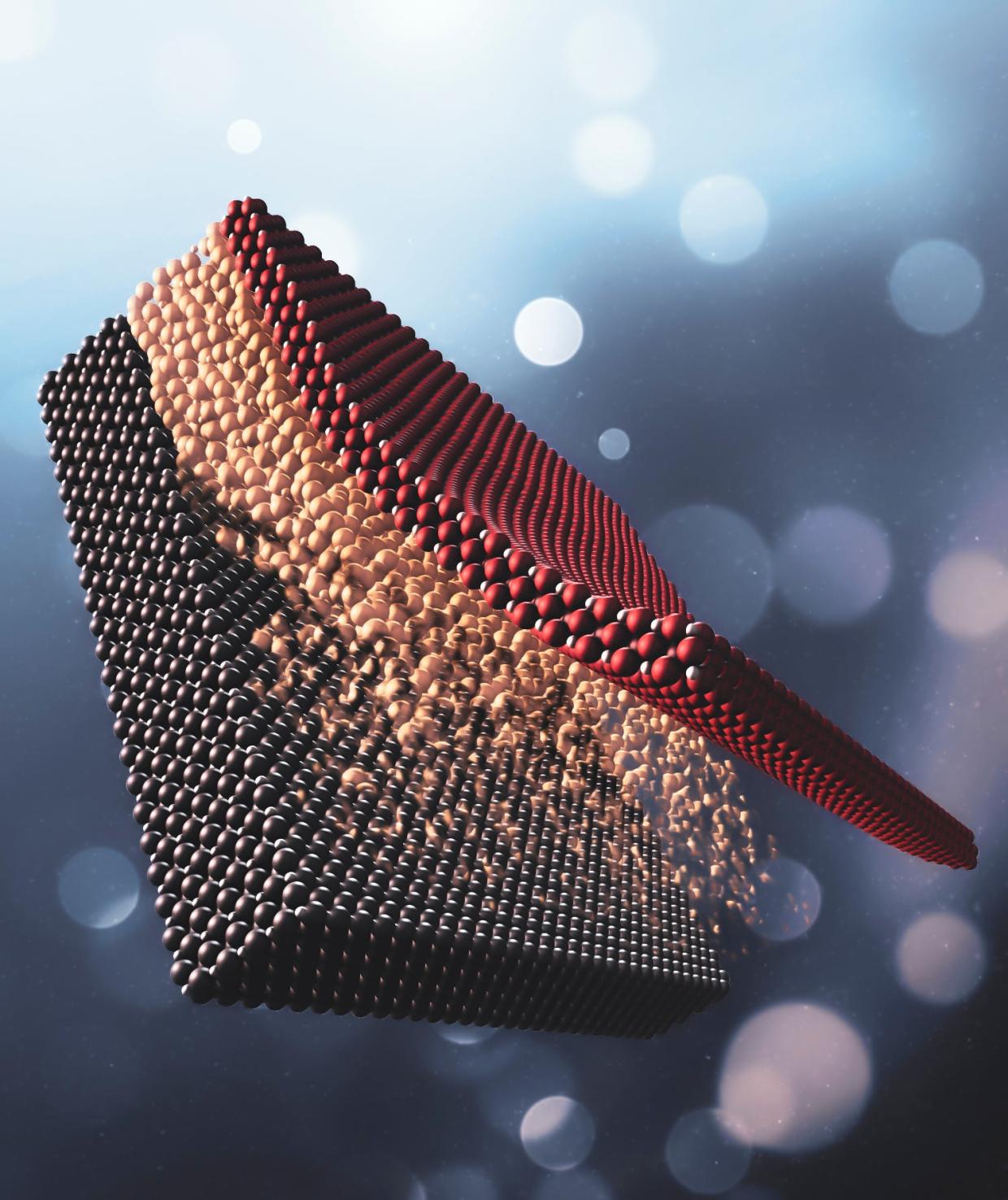
“The experiments were quite tedious and difficult,” said Hong, who is now an assistant professor at the University of California, Davis. “We’d look at the film, warm it to soften the glue and relax the stretch, manipulate it in some other way, freeze it in place and look at it again.”
The researchers were able to directly measure the spacing between atoms and confirm that it increased with stretching. They also measured the electrical resistance of the LMCO and discovered that stretching flipped it from a metallic state that readily conducts electricity to an insulating state, which doesn’t. Applying a strong magnetic field changed the magnetic state of the material and also flipped it back into being a metal.
“As a scientific tool this is really exciting,” Hong said. “It opens opportunities for mechanically manipulating broad classes of materials in ways we couldn’t do before. And it gives us ideas for how we might design flexible materials for electronic devices, including sensors and detectors that measure very small changes.”
Major funding for this study came from the DOE Office of Science and the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation’s Emergent Phenomena in Quantum Systems Initiative. Researchers from Northwestern University and the University of Duisburg-Essen in Germany contributed theoretical modeling for the study. Calculations were performed using the National Extreme Science and Engineering Discovery Environment (XSEDE), which is supported by the National Science Foundation; the CARBON Cluster at DOE’s Argonne National Laboratory; and the MagnitUDE supercomputer at the University of Duisburg-Essen.
Citation: Seung Sae Hong et al., Science, 5 April 2020 (10.1126/science.aax9753)
For questions or comments, contact the SLAC Office of Communications at communications@slac.stanford.edu.
SLAC is a vibrant multiprogram laboratory that explores how the universe works at the biggest, smallest and fastest scales and invents powerful tools used by scientists around the globe. With research spanning particle physics, astrophysics and cosmology, materials, chemistry, bio- and energy sciences and scientific computing, we help solve real-world problems and advance the interests of the nation.
SLAC is operated by Stanford University for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time.