Speed Limit Set for Ultrafast Electrical Switch
Researchers from the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory have clocked the fastest-possible electrical switching in magnetite, a naturally magnetic mineral. Their results could drive innovations in the tiny transistors that control the flow of electricity across silicon chips, enabling faster, more powerful computing devices.
Menlo Park, Calif. — Researchers from the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory have clocked the fastest-possible electrical switching in magnetite, a naturally magnetic mineral. Their results could drive innovations in the tiny transistors that control the flow of electricity across silicon chips, enabling faster, more powerful computing devices.
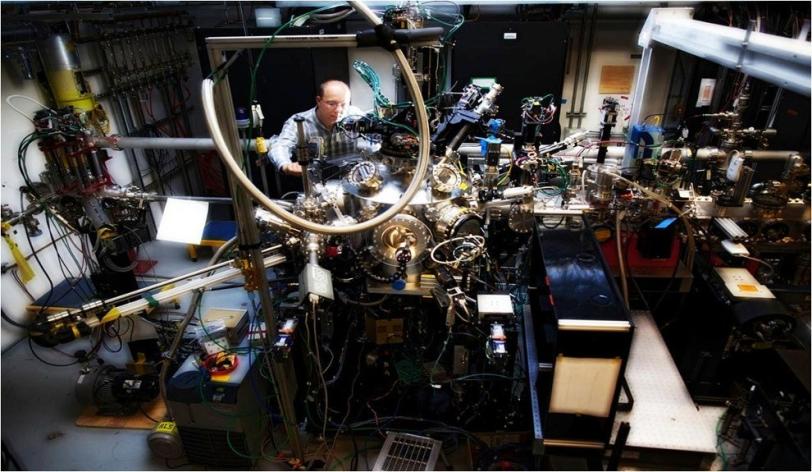
Scientists using SLAC's Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS) X-ray laser found that it takes only 1 trillionth of a second to flip the on-off electrical switch in samples of magnetite, which is thousands of times faster than in transistors now in use. The results were published July 28 in Nature Materials.
"This breakthrough research reveals for the first time the 'speed limit' for electrical switching in this material," said Roopali Kukreja, a materials science researcher at SLAC and Stanford University who is a lead author of the study.
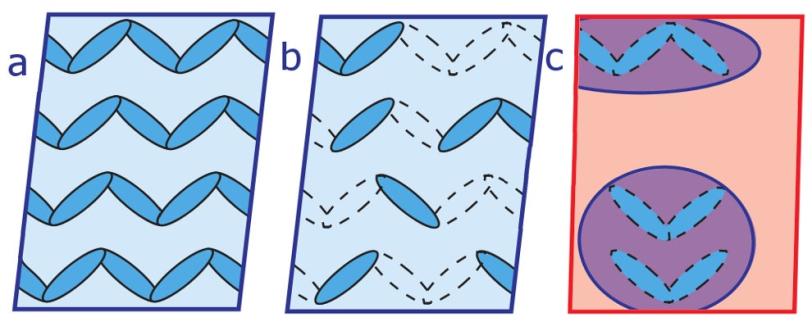
The LCLS experiment also showed researchers how the electronic structure of the sample rearranged into non-conducting "islands" surrounded by electrically conducting regions, which began to form just hundreds of quadrillionths of a second after a laser pulse struck the sample. The study shows how such conducting and non-conducting states can coexist and create electrical pathways in next-generation transistors.
Scientists first hit each sample with a visible-light laser, which fragmented the material's electronic structure at an atomic scale, rearranging it to form the islands. The laser blast was followed closely by an ultrabright, ultrashort X-ray pulse that allowed researchers to study, for the first time, the timing and details of changes in the sample excited by the initial laser strike.
By slightly adjusting the interval of the X-ray pulses, they precisely measured how long it took the material to shift from a non-conducting to an electrically conducting state, and observed the structural changes during this switch.
Scientists had worked for decades to resolve this electrical structure at the atomic level, and just last year another research team had identified its building blocks as "trimerons" – formed by three iron atoms that lock in the charges. That finding provided key insights in interpreting results from the LCLS experiment.
The magnetite had to be cooled to minus 190 degrees Celsius to lock its electrical charges in place, so the next step is to study more complex materials and room-temperature applications, Kukreja said. Future experiments will aim to identify exotic compounds and test new techniques to induce the switching and tap into other properties that are superior to modern-day silicon transistors. The researchers have already conducted follow-up studies focusing on a hybrid material that exhibits similar ultrafast switching properties at near room temperature, which makes it a better candidate for commercial use than magnetite.
Hermann Dürr, the principal investigator of the LCLS experiment and senior staff scientist for the Stanford Institute for Materials and Energy Sciences (SIMES), said there is a major global effort underway to go beyond modern semiconductor transistors using new materials to satisfy demands for smaller and faster computers, and LCLS has the unique ability to home in on processes that occur at the scale of atoms in trillionths and quadrillionths of a second.
While magnetite's basic magnetic properties have been known for thousands of years, the experiment shows how much still can be learned about the more exotic electronic properties of magnetite and other more complex materials using LCLS, Dürr said.
Other collaborating scientists on this research were from Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin for Materials and Energy; Hamburg University/Center for Free Electron Laser Science (CFEL); University of Amsterdam; the T-REX laboratory at the ELETTRA-Sincrotrone Trieste and University of Trieste; Cologne, Potsdam Regensburg and Purdue universities; the Advanced Light Source at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory; and SwissFEL.
Research at Stanford University was supported through SIMES and LCLS by the DOE Office of Science. Portions of this research were carried out on the Soft X-ray (SXR) instrument at the LCLS, a user facility operated by Stanford University for the DOE. SXR is funded by a consortium including LCLS, Stanford, Berkeley Lab, CFEL, University of Hamburg and several other research organizations in Europe.
SLAC is a multi-program laboratory exploring frontier questions in photon science, astrophysics, particle physics and accelerator research. Located in Menlo Park, California, SLAC is operated by Stanford University for the DOE Office of Science. To learn more, please visit www.slac.stanford.edu.
DOE’s Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.
Citation
S. de Jong et al., Nature Materials, 28 July 2013 (10.1038/NMAT3718)
Press Office Contact
Andy Freeberg, SLAC, afreeberg@slac.stanford.edu, (650) 926-4359
Scientist Contact
Hermann A Dürr, SLAC / Stanford University, hdurr@slac.stanford.edu, (650) 926 3239
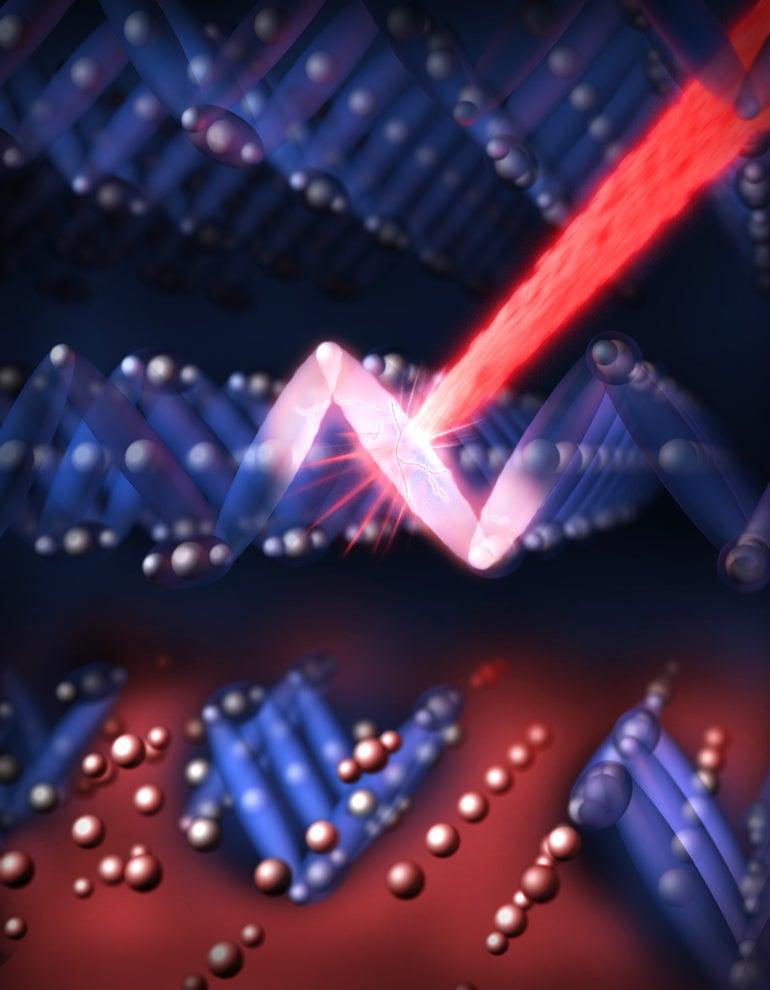
(Greg Stewart/SLAC)