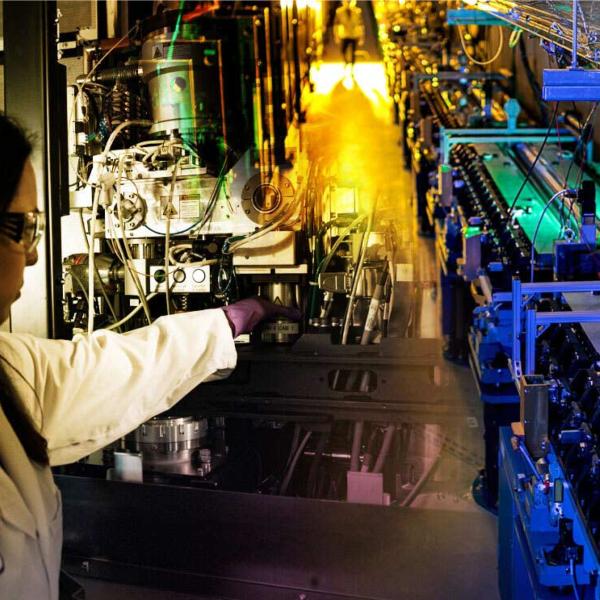
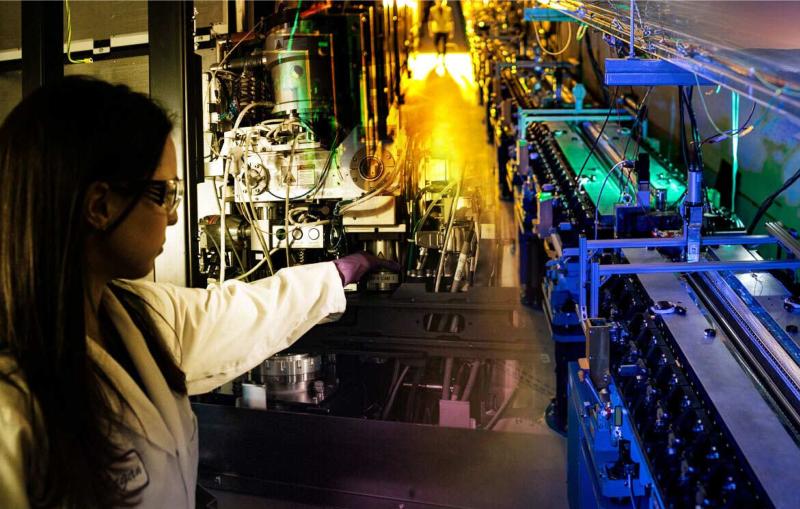
At LCLS, crystallized ribosomes travel through a capillary into the interaction region, where they are zapped with a beam of X-rays.
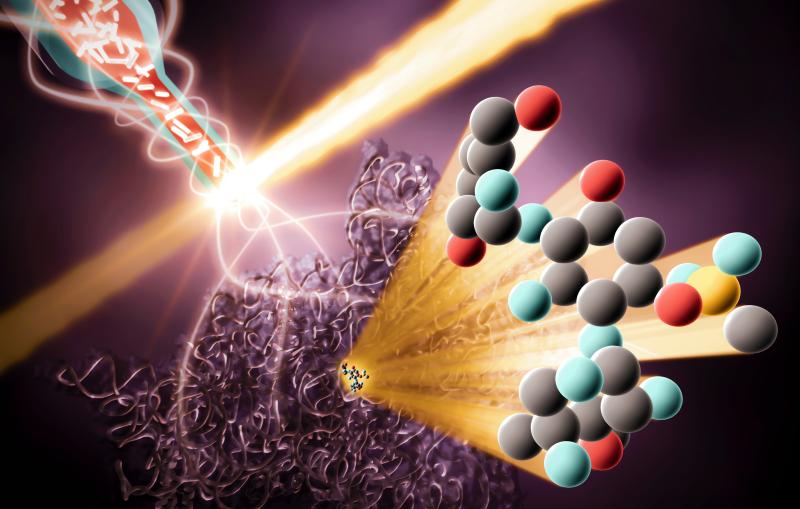
Identifying each tiny chemical step in photosynthesis could aid the development of renewable energy technology.

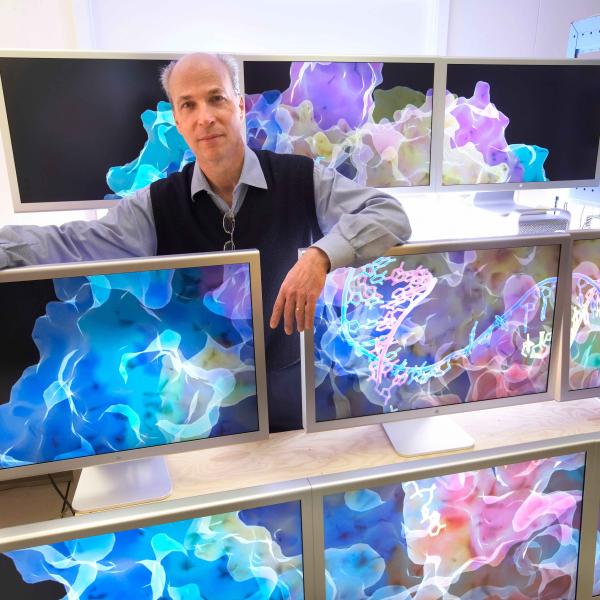
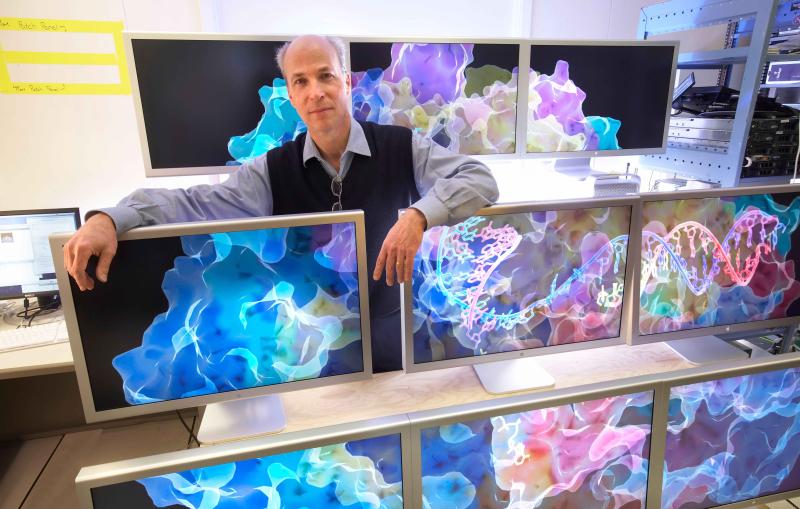
Stanford’s Roger Kornberg received the 2006 chemistry Nobel for work on RNA transcriptase, shown on screens.


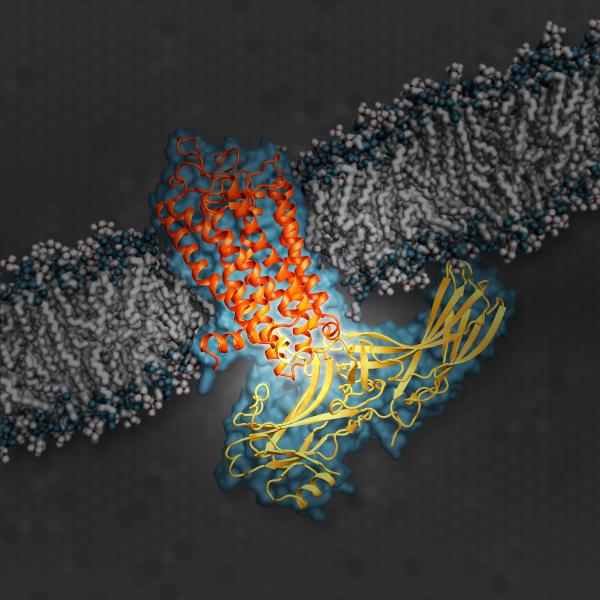
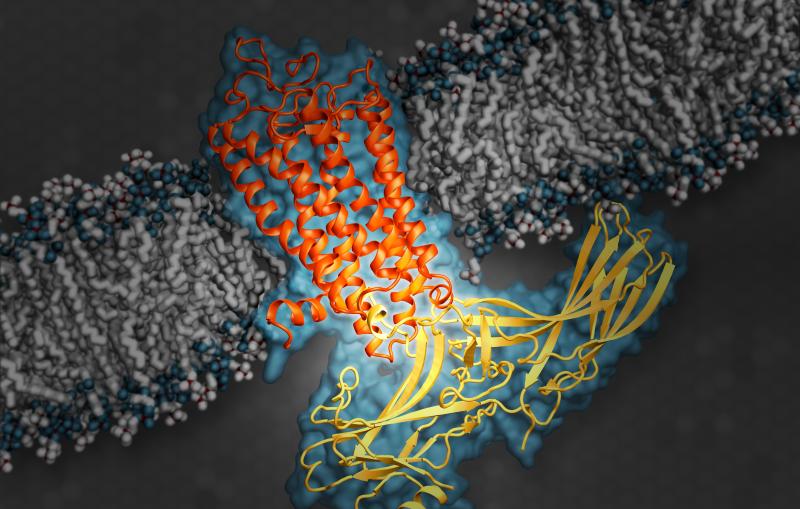
This illustration shows arrestin, an important type of signaling protein, while docked with rhodopsin, a G protein-coupled receptor.
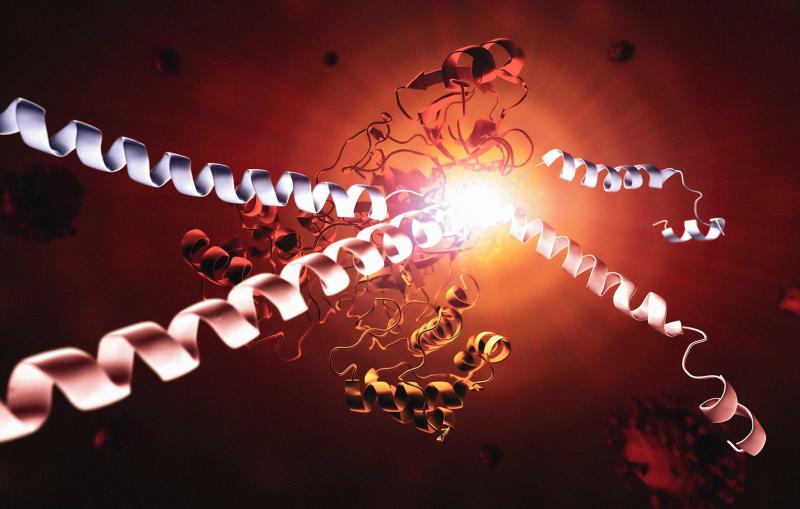
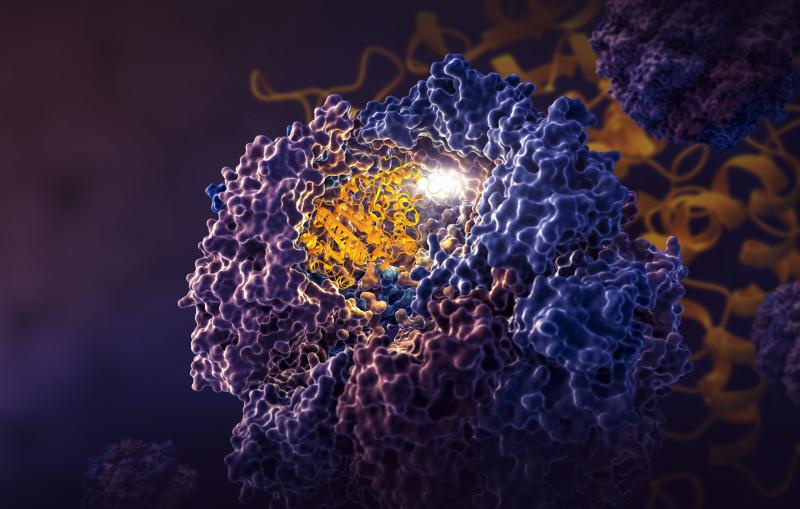
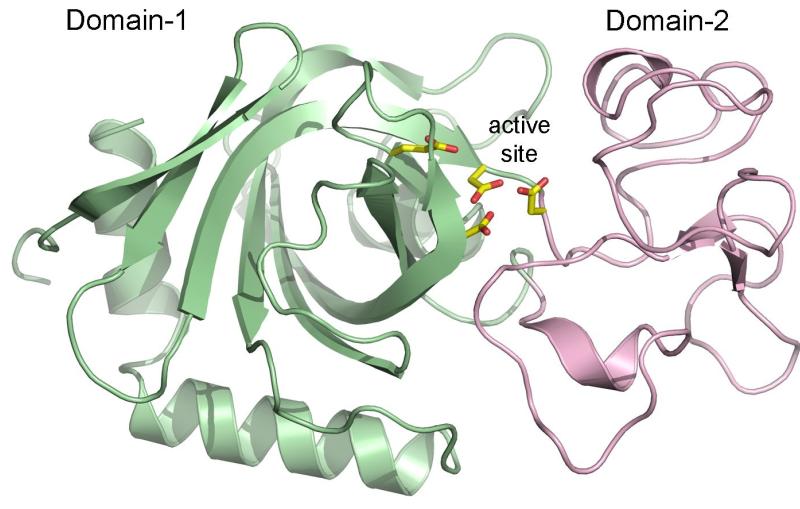
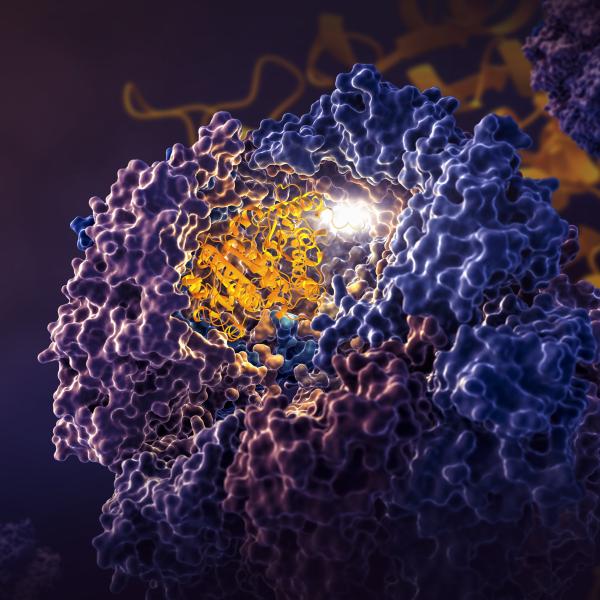
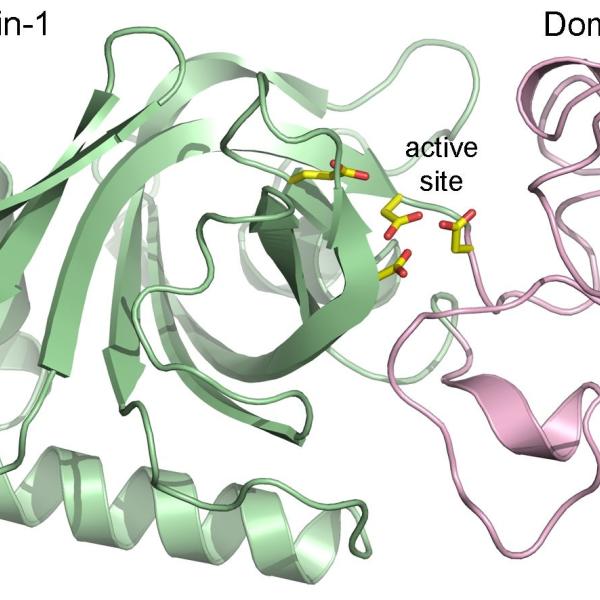
This image shows the SARS-CoV-2 virus's main protease, Mpro, and two strands of a human protein, called NEMO.