Researchers identify new culprit for Minamata mercury poisoning tragedy
The 1950s and ‘60s poisoning event was long attributed to methylmercury, but studies at SLAC suggest a different compound was to blame. The findings could reshape toxicologists’ understanding of disease related to mercury poisoning.
By Nathan Collins
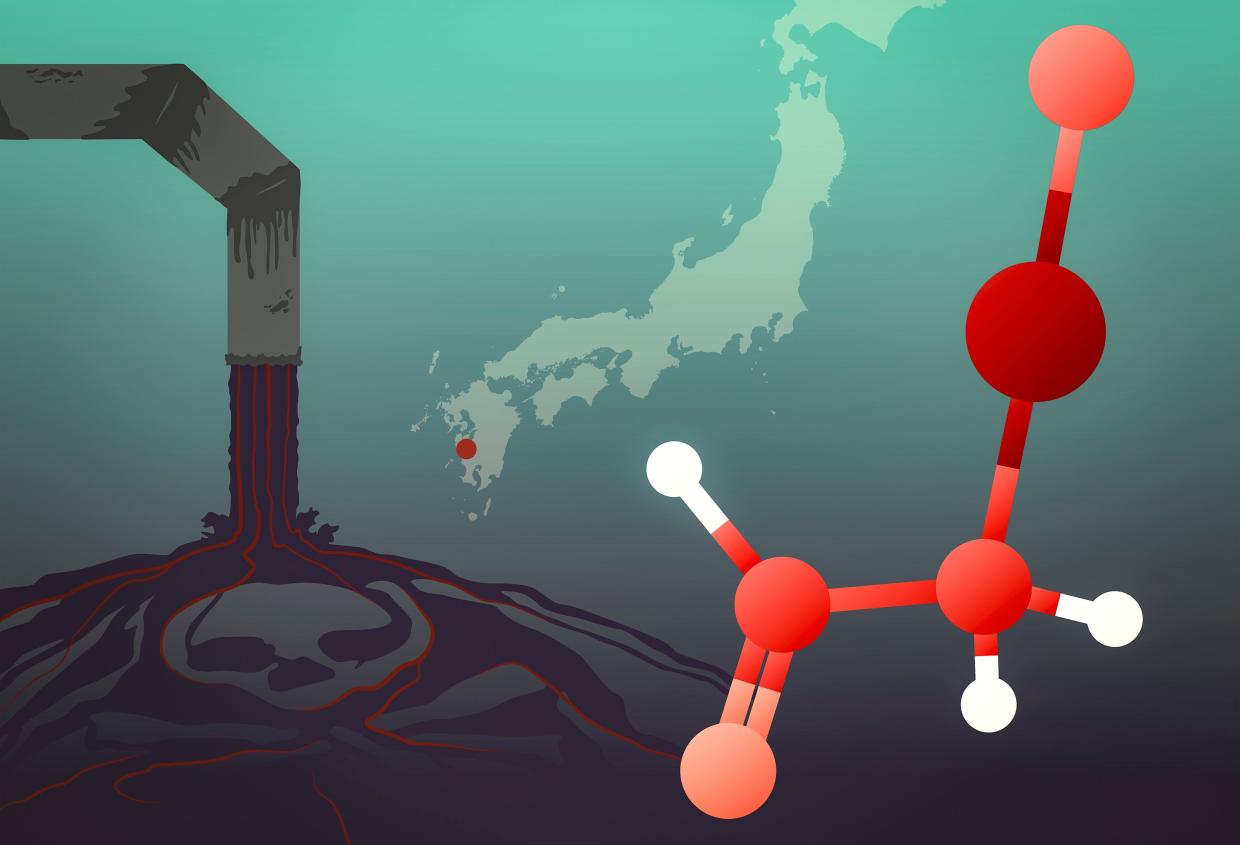
The story of one of history’s worst mercury poisoning events has a new twist. Drawing on sophisticated X-ray spectroscopy techniques, researchers at the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and the University of Saskatchewan have traced the origins of the Minamata tragedy, which unfolded in 1950s and ‘60s Japan, to a little-studied mercury compound dumped into Minamata Bay. Their study was published recently in Environmental Science & Technology.
Minamata disease, which is the subject of a film premiering February 21 at the Berlin International Film Festival, emerged when “dancing cats” developed neurological symptoms, including convulsions. When children and adults in the area also began to get sick and die, doctors took notice. The disease, which at the time sickened more than 2,000 people – most of whom died – was soon attributed to industrial waste from a nearby chemical plant, but the exact nature of the mercury compound involved remained unclear.
At first, it was thought the plant was dumping an inorganic form of mercury, which microorganisms in the bay transformed into a more toxic organic form called methylmercury. More recently, studies of samples from the brains of cats that had been fed plant waste in the late 1950s suggested the plant had dumped that organic form directly, but even then questions remained. For one thing, the levels of methylmercury in the cat samples were relatively low, and no one was quite sure why.
In an effort to resolve lingering questions about the origins of Minamata disease, a team of University of Saskatchewan researchers revisited one of the cat samples in collaboration with Dimosthenis Sokaras and Thomas Kroll, staff scientists at SLAC’s Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource. At SSRL, the team used sophisticated X-ray spectroscopy methods along with computer modelling to make fine distinctions between different mercury compounds and ultimately identify which one resided within the cat tissues.
“These kinds of samples have very low concentrations of mercury, so getting enough of a signal out of them to distinguish the different chemical species is pretty demanding,” Sokaras said. But the team was able to determine that the mercury compound was neither inorganic nor methylmercury. Instead, it was most likely α-mercuri-acetaldehyde, the toxic effects of which have not been studied in great detail.
“It was this species that very likely contaminated Minamata Bay and subsequently gave rise to the tragedy of Minamata disease,” said Graham George, a professor of geological sciences at the University of Saskatchewan and an expert in the spectroscopy of toxic molecules, although the researchers are not yet sure of the implications for public health and the understanding of mercury poisoning. “More work is needed to explore the molecular toxicology of these compounds to understand the ways they could be toxic to humans, animals and the environment,” he said.
Researchers from the Japanese Ministry of the Environment, National Institute for Minamata Disease also contributed to the study. The research was funded by grants from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Canada Foundation for Innovation, and Canada Research Chairs. SSRL is a Department of Energy Office of Science user facility. The researchers used SSRL’s Structural Molecular Biology Program facilities, which are supported by the DOE Office of Science and the National Institutes of Health, National Institute of General Medical Sciences.
Editor’s note: This article is based on a press release from the University of Saskatchewan.
Citation: Ashley K. James, Susan Nehzati, et al., Environmental Science and Technology, January 17, 2020 (10.1021/acs.est.9b06253)
Contact
For questions or comments, contact the SLAC Office of Communications at communications@slac.stanford.edu.
SLAC is a vibrant multiprogram laboratory that explores how the universe works at the biggest, smallest and fastest scales and invents powerful tools used by scientists around the globe. With research spanning particle physics, astrophysics and cosmology, materials, chemistry, bio- and energy sciences and scientific computing, we help solve real-world problems and advance the interests of the nation.
SLAC is operated by Stanford University for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time.




