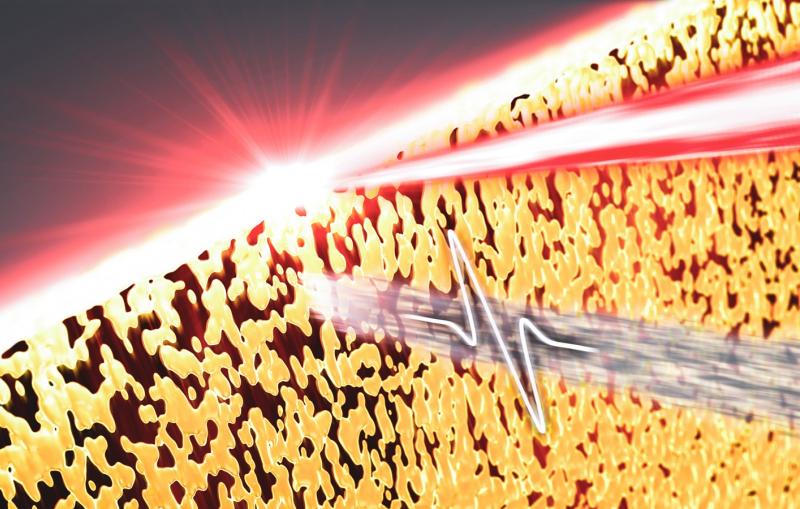
SLAC Study: Light Can Switch On Topological Materials
Computer Simulations Show How Light Pulses Can Create Channels that Conduct Electricity with No Resistance in Atomically Thin Semiconductors
Theoretical physicists at the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory used computer simulations to show how special light pulses could create robust channels where electricity flows without resistance in an atomically thin semiconductor.
If this approach is confirmed by experiments, it could open the door to a new way of creating and controlling this desirable property in a wider range of materials than is possible today.
The result was published in Nature Communications.
Over the past decade, understanding how to create this exotic type of material – known as “topologically protected” because its surface states are impervious to minor distortions – has been a hot research topic in materials science. The best-known examples are topological insulators, which conduct electricity with no resistance in confined channels along their edges or surfaces, but not through their interiors.
SLAC and Stanford University researchers have been at the forefront of discovering such materials and investigating their properties, which could have future applications in microelectronic circuits and devices. This year’s Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to three scientists who first suggested the possibility of topologically protected material properties.
Previous theoretical studies had looked at how light might induce topologically protected phenomena in graphene, a sheet of pure carbon just one atom thick. Unfortunately, it would take an impractically high light energy and intensity to induce that effect in graphene. In this study, SLAC researchers focused on tungsten disulfide and related compounds, which form sheets just one molecule thick and are intrinsically semiconducting.
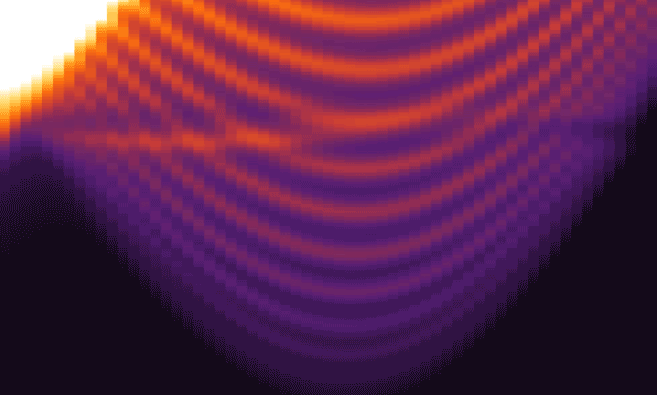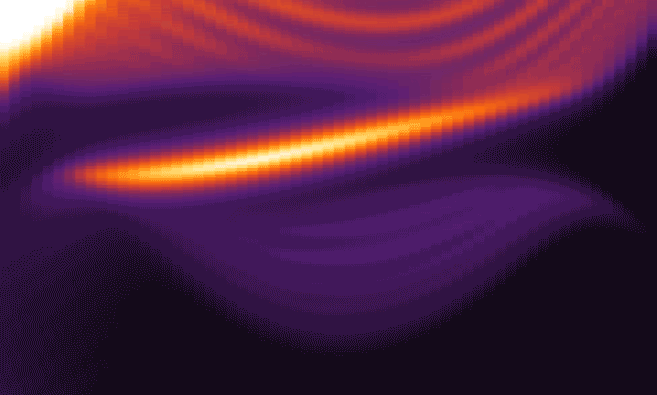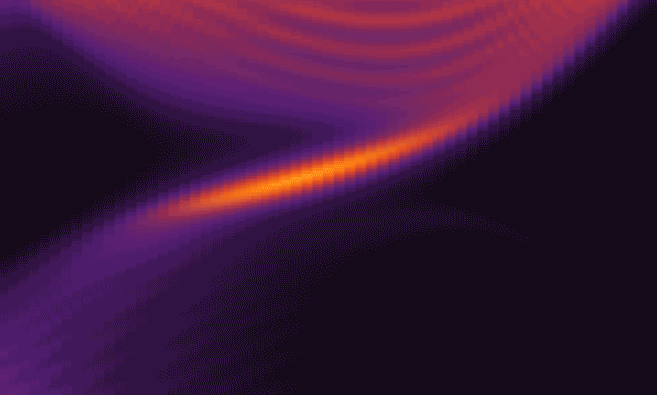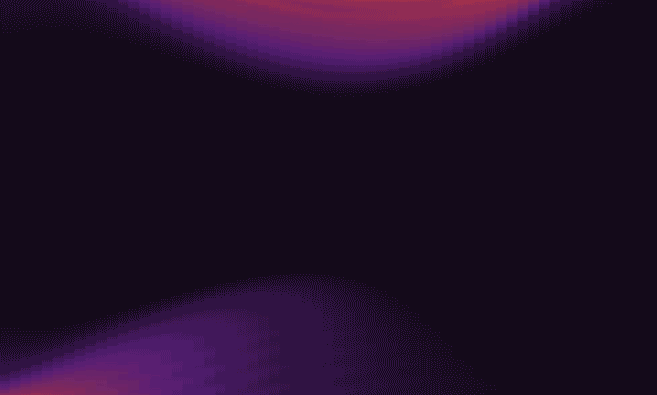
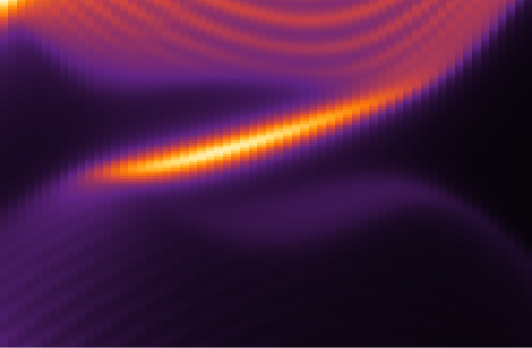
The researchers simulated experiments in which pulses of circularly polarized light, in the red to near-infrared wavelength range, hit a single layer of tungsten disulfide. The results showed that during the time the material was illuminated, its electrons organized themselves in a manner fundamentally different from graphene, creating new paths with absolutely no electrical resistance along the sample’s edges.
To account for the fluctuating interactions between light waves and electrons, the researchers employed a periodically time-varying frame of reference that had roots dating back to the 1880s and French mathematician Gaston Floquet. The approach clearly showed that lower-energy light, to which the material would seem transparent, would create topologically protected, no-resistance edge paths in the tungsten disulfide monolayer.
Moreover, the simulation showed that unwanted heating of the material that would disrupt the paths could be avoided by tuning the light energy to be slightly less than the most-efficient "resonant" energy.
“We are the first to connect first-principles material models with light-induced topologically protected states while mitigating excess material heating,” said Martin Claassen, a Stanford graduate student working at SLAC and lead author of the technical paper.
The researchers are in discussions with other research groups that could lead to experiments that test their theoretical predictions in real materials.
The report’s co-authors are SLAC staff scientists Chunjing Jia and Brian Moritz and Thomas Devereaux, SLAC professor and director of the Stanford Institute for Materials and Energy Sciences.
This research was funded by the DOE Office of Science. Computational resources were provided by the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center, a DOE Office of Science User Facility at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
Citation
Claassen, M. et al., Nature Communications, 10 October 2016 (10.1038/ncomms13074)
Contact
For questions or comments, contact the SLAC Office of Communications at communications@slac.stanford.edu.
SLAC is a multi-program laboratory exploring frontier questions in photon science, astrophysics, particle physics and accelerator research. Located in Menlo Park, Calif., SLAC is operated by Stanford University for the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science.
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.