News Feature
VIA Stanford News
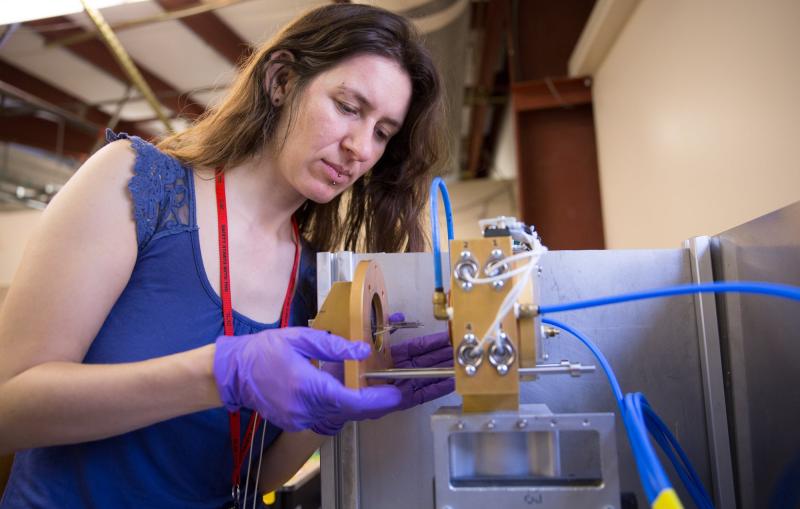
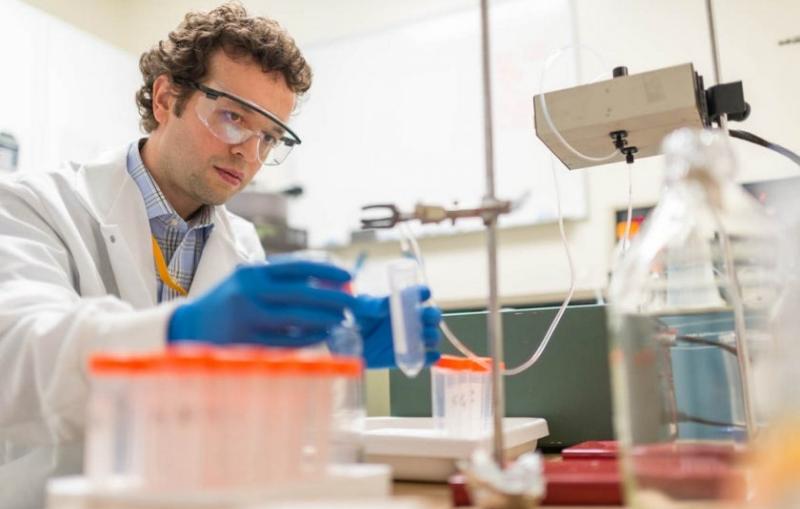
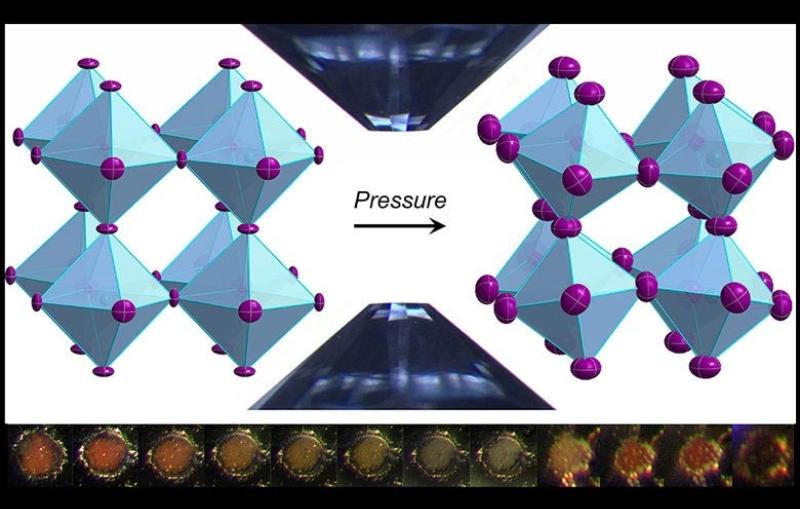
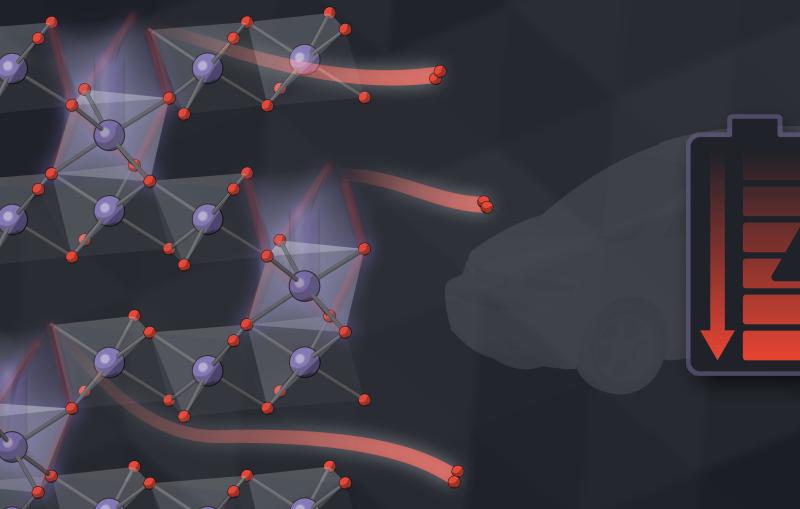
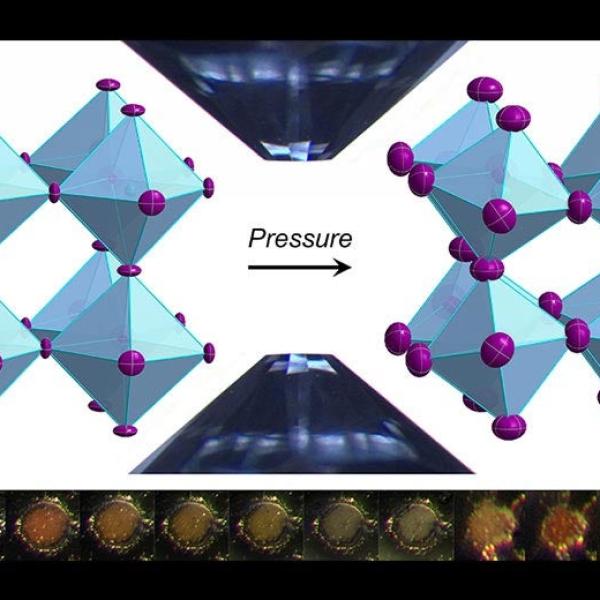
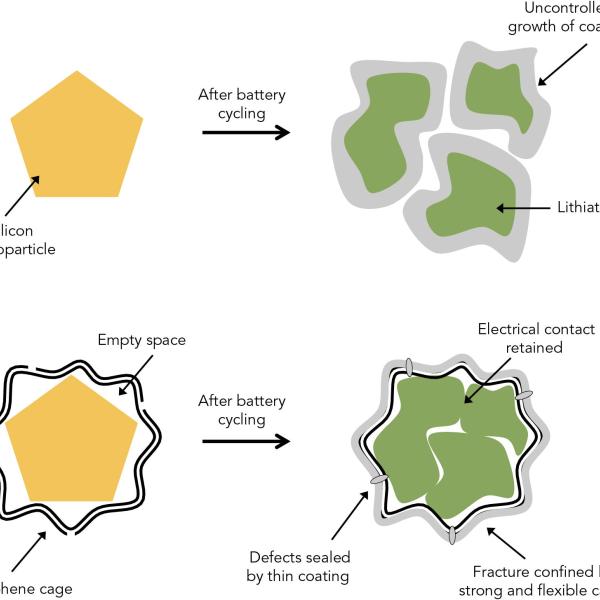
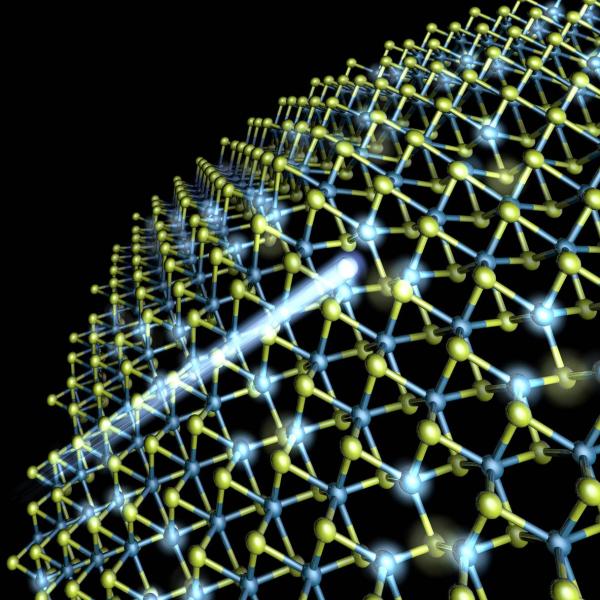
Researchers Find New Way of Making Hydrogen Fuel from Water and Improve Grid-scale Batteries
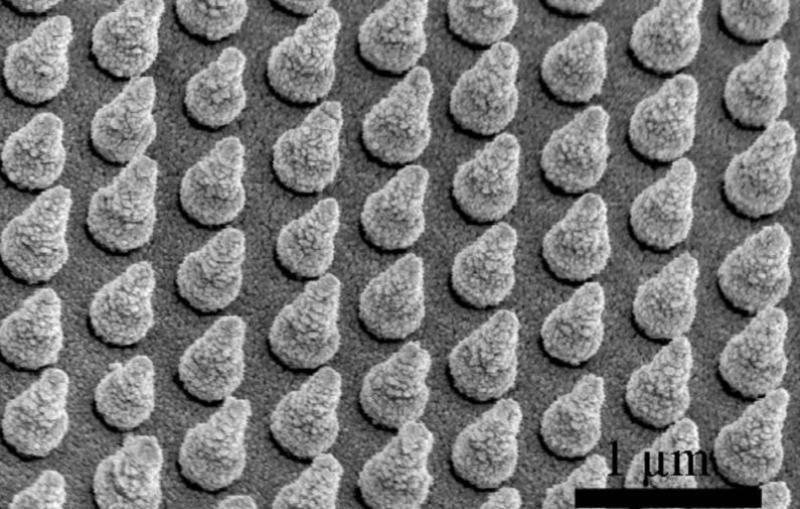
News Feature
VIA Stanford News
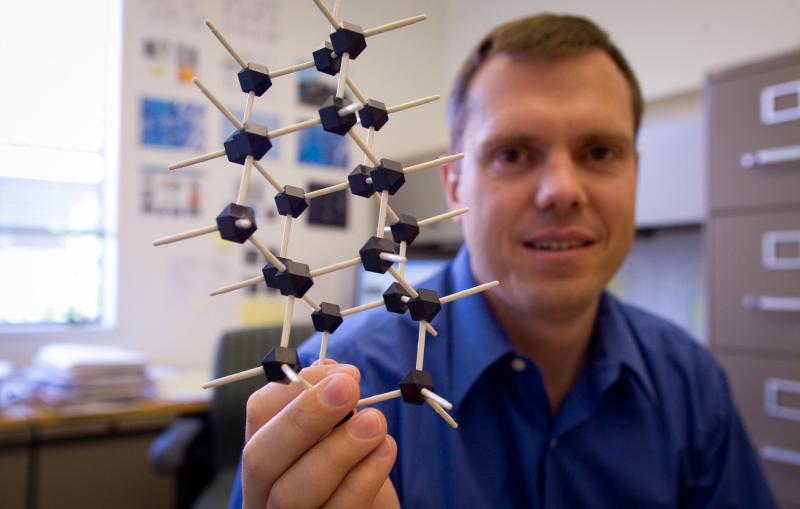
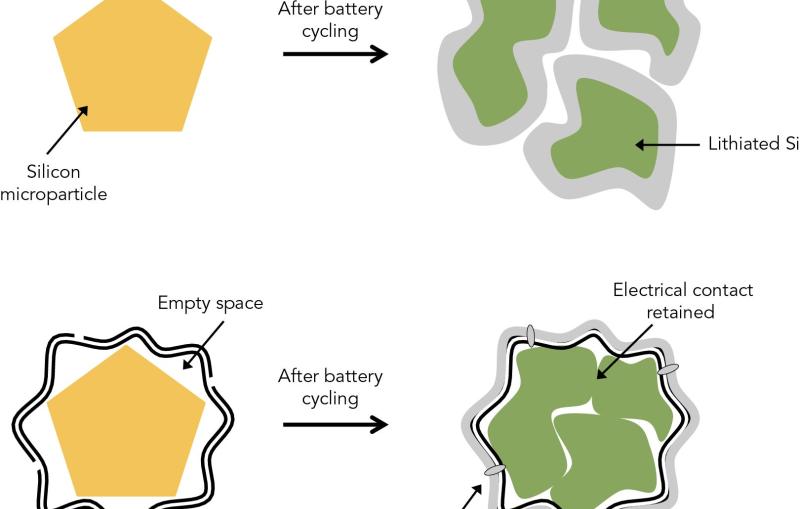
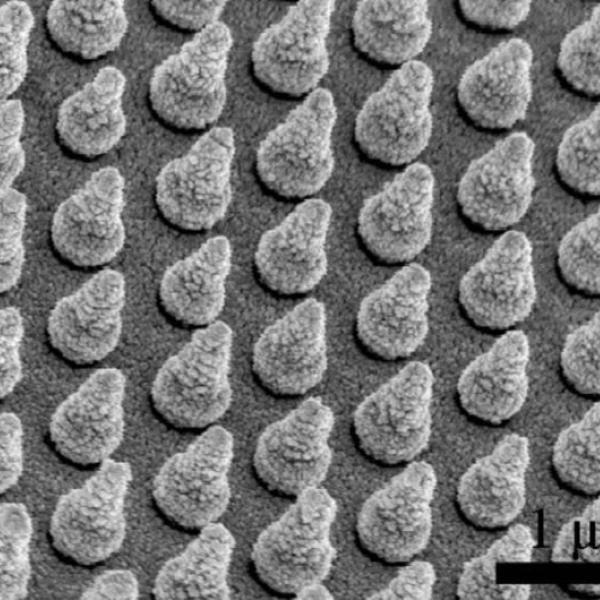
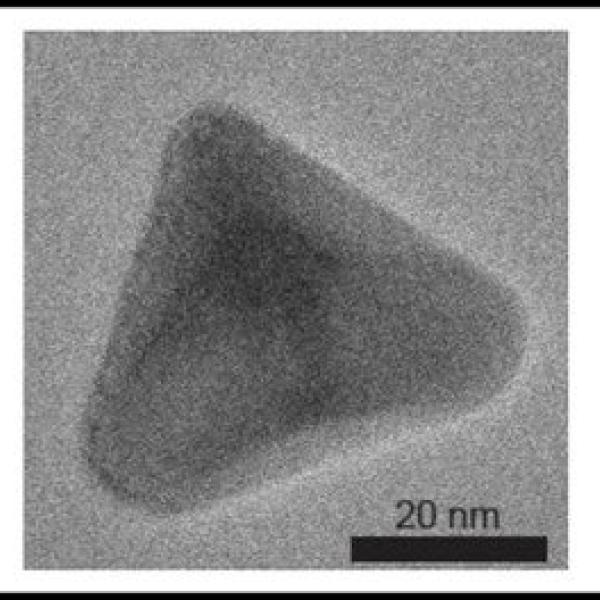
SIMES Engineers Look Inside Nanoparticles to Explore How Their Shape Improves Energy Storage
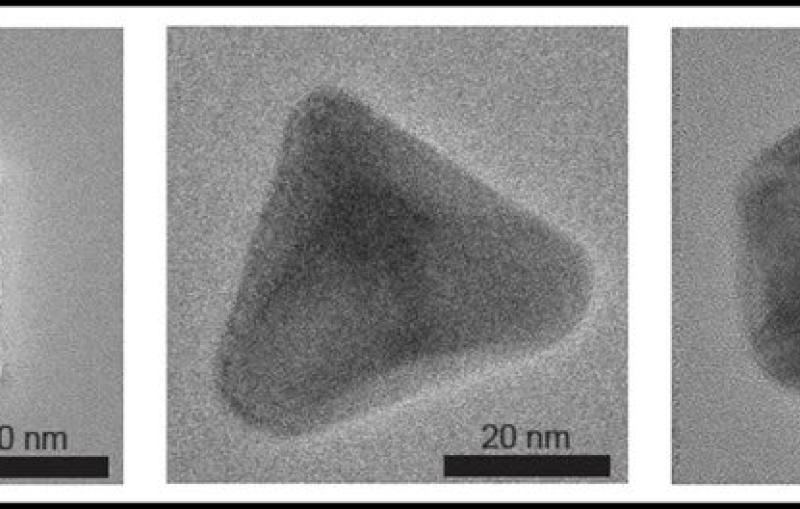
News Feature