Photograph
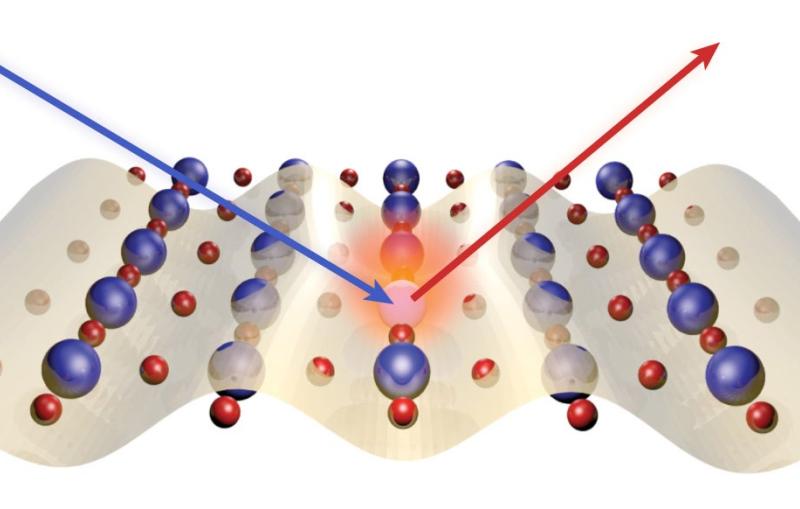
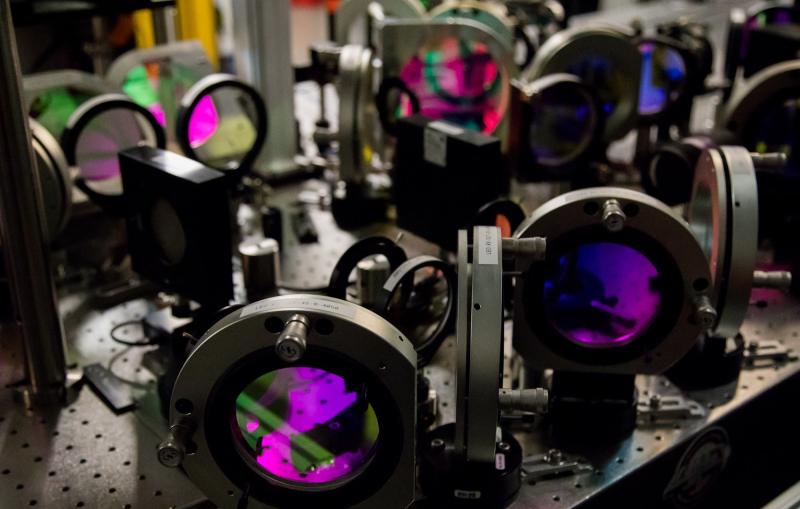
Highly reflective mirrors and telescope lenses in the Matter in Extreme Conditions (MEC) optical laser system are carefully positioned to...

News Feature
VIA Stanford Energy
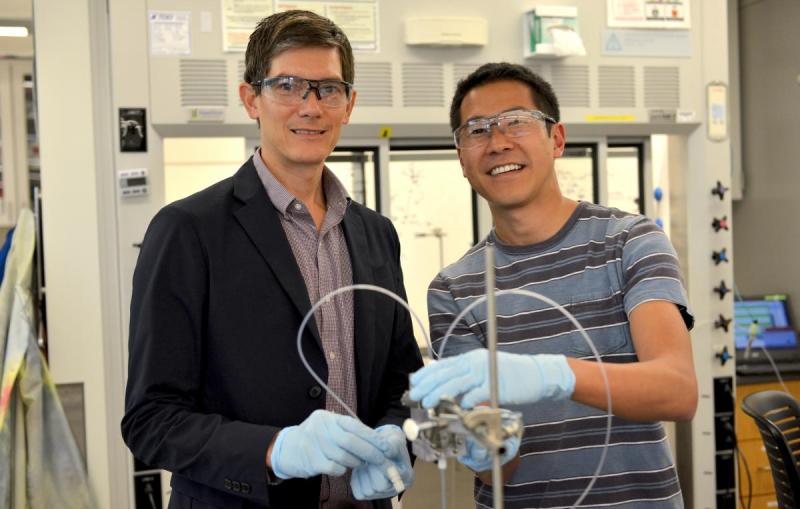
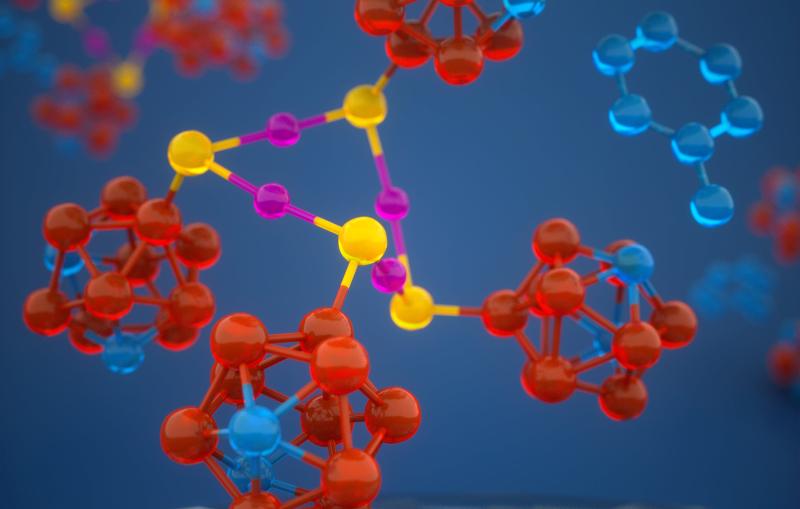
Discovery Could Lead to Sustainable Ethanol Made from Carbon Dioxide