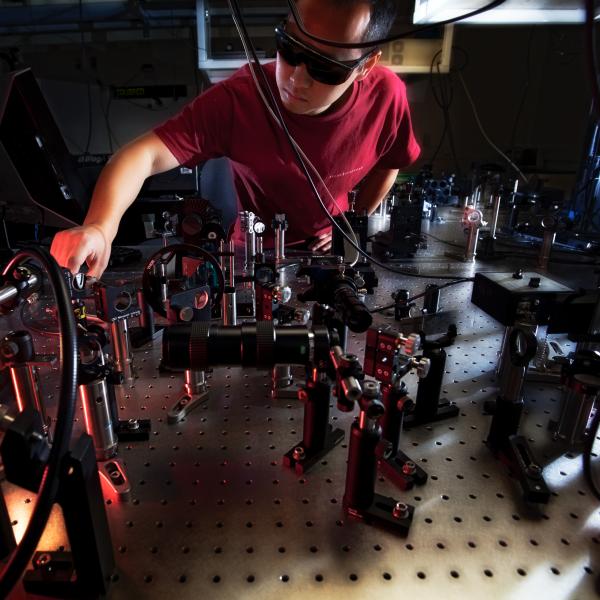
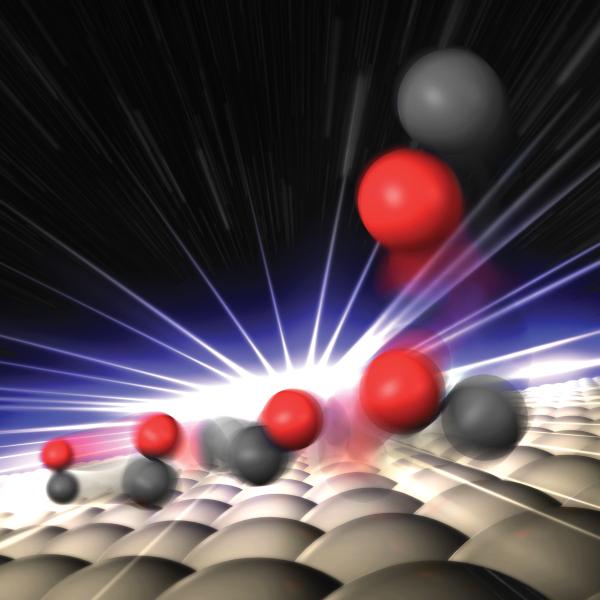
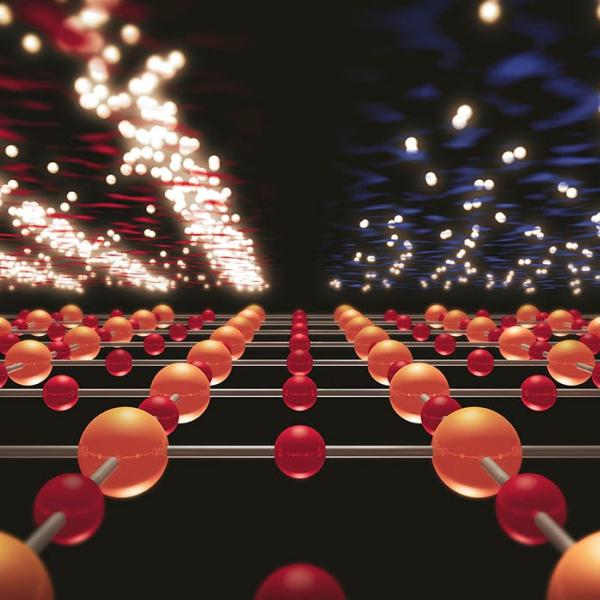
Illustration of how a single crystal sample of silicon deforms during shock compression on nanosecond timescales.

Scientists use a series of magnets to transform an electron bunch into a narrow current spike which then produces a very intense attosecond X-ray...

The ultrafast, ultrabright X-ray pulses of the Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS) have enabled unprecedented views of a catalyst in action, an important step...
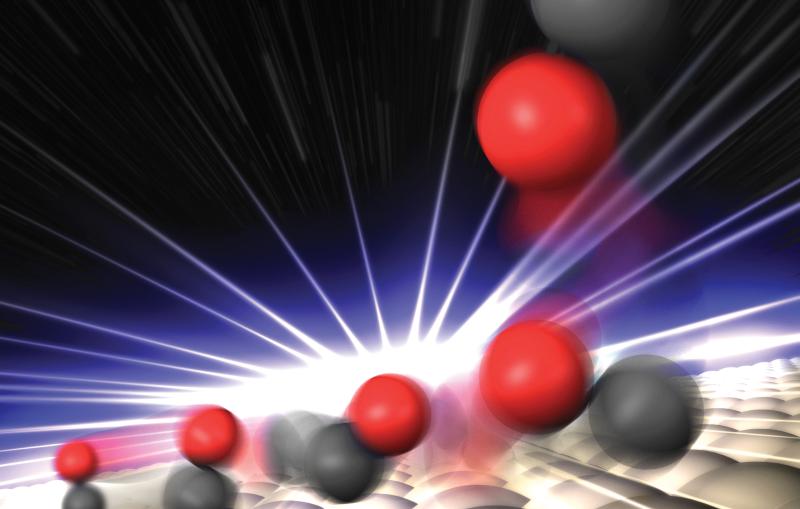
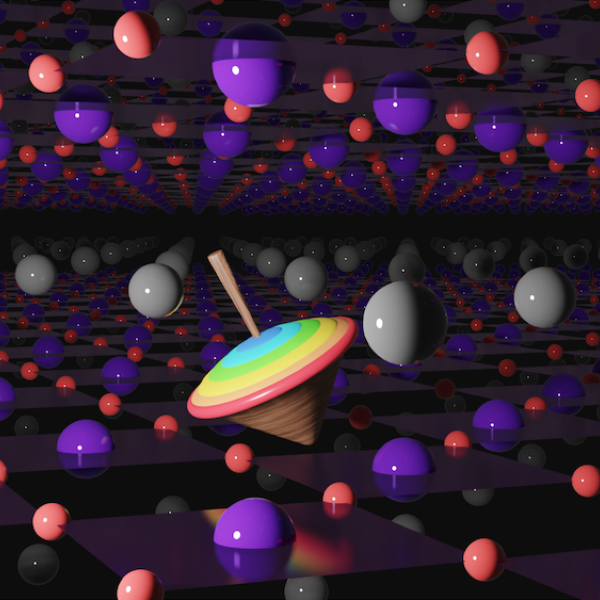
A muon, center, spins like a top within the atomic lattice of a thin film of superconducting nickelate.