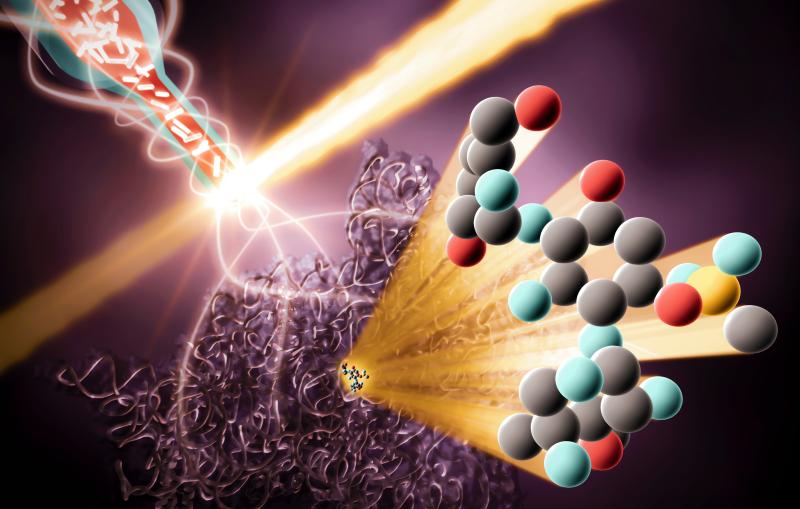
Researchers will use FACET-II to develop the plasma wakefield acceleration method, in which researchers send a bunch of very energetic particles through a hot...
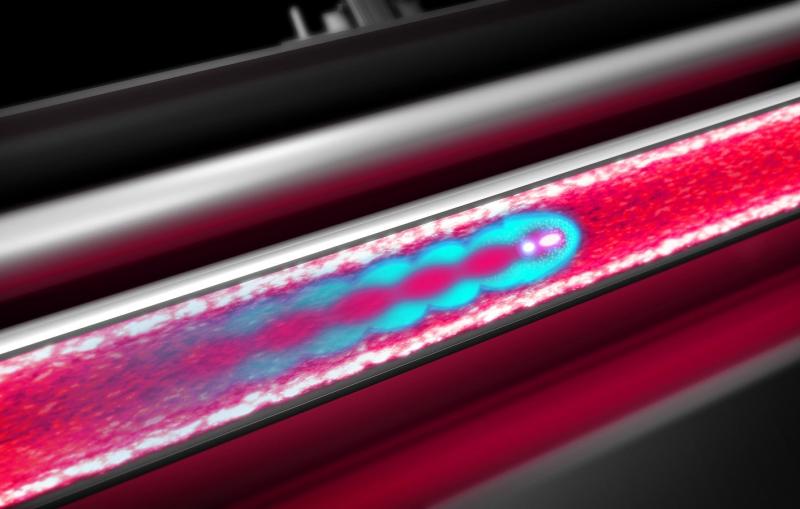
An animation shows how an infrared laser beam (orange) triggers atomic vibrations in a thin layer of iron selenide, which are then recorded by...
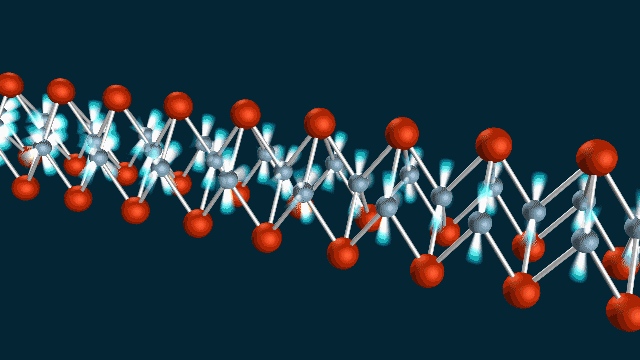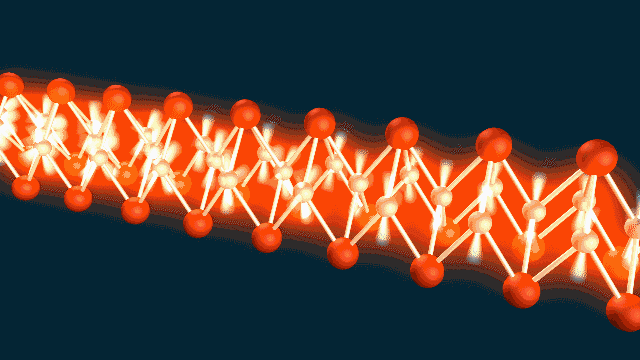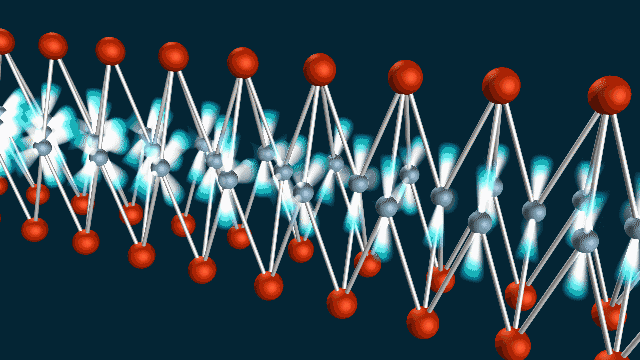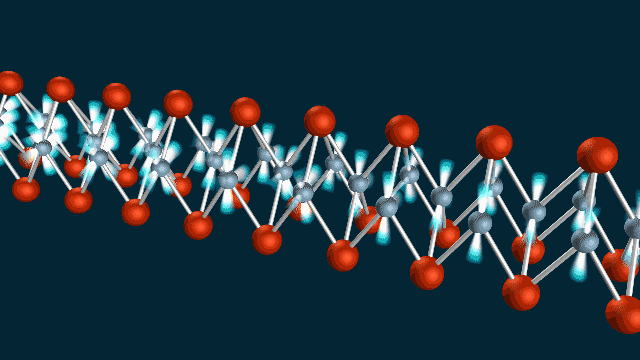


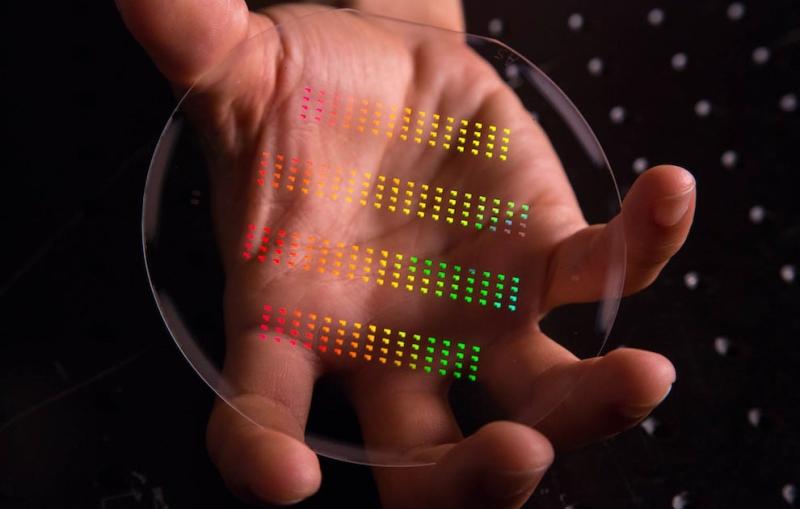
The nanoscale patterns of SLAC and Stanford’s accelerator on a chip gleam in rainbow colors prior to being assembled and cut into their final...
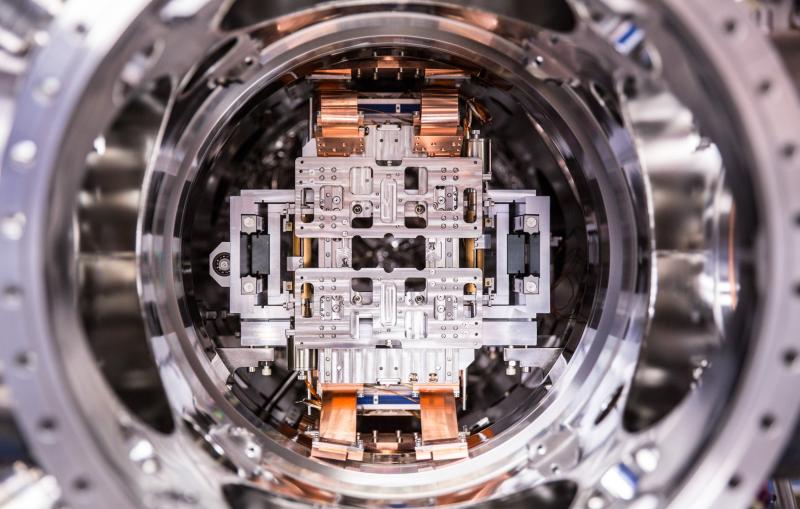
A view of a chamber inside the LAMP instrument during its installation at SLAC’s Linac Coherent Light Source X-ray laser.

X-ray laser pulses probe water droplets like these to discover water’s hidden (and sometimes bizarre) properties.
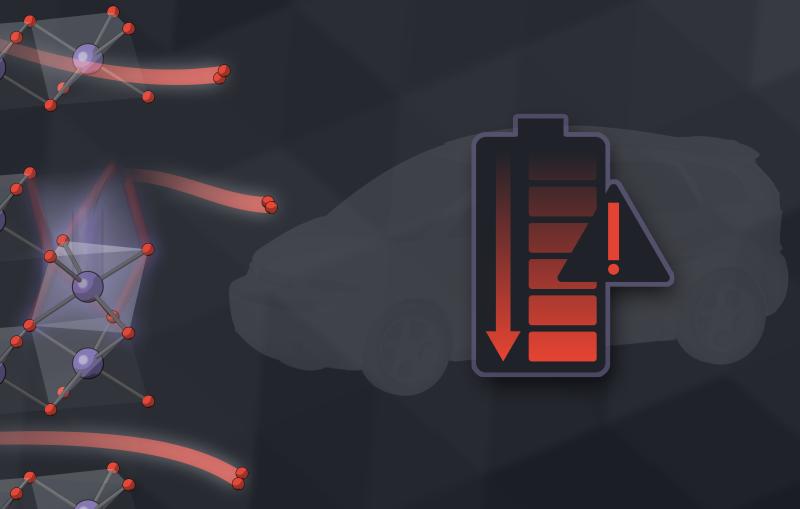
Studies of atomic-level processes that drain battery life and efficiency help improve battery performance.
Ultra-bright X-ray laser pulses can be used to strip electrons away from atoms, creating ions with strong charges.
At LCLS, crystallized ribosomes travel through a capillary into the interaction region, where they are zapped with a beam of X-rays.