San Jose State students study nanodiamonds at SLAC’s synchrotron
A physical chemist and a diverse group of his students are working on applications with nanoscopic diamonds.
By Stephanie Melchor

To Abraham Wolcott, diamonds are so much more than sparkly rocks and status symbols. The San Jose State University physical chemist works with nanodiamonds – that is, nanoscale diamonds made from breaking up larger synthetic diamonds. These nanodiamonds are so small, it takes a row of about 8,000 of them to span the width of a human hair.
A scientist's best friend
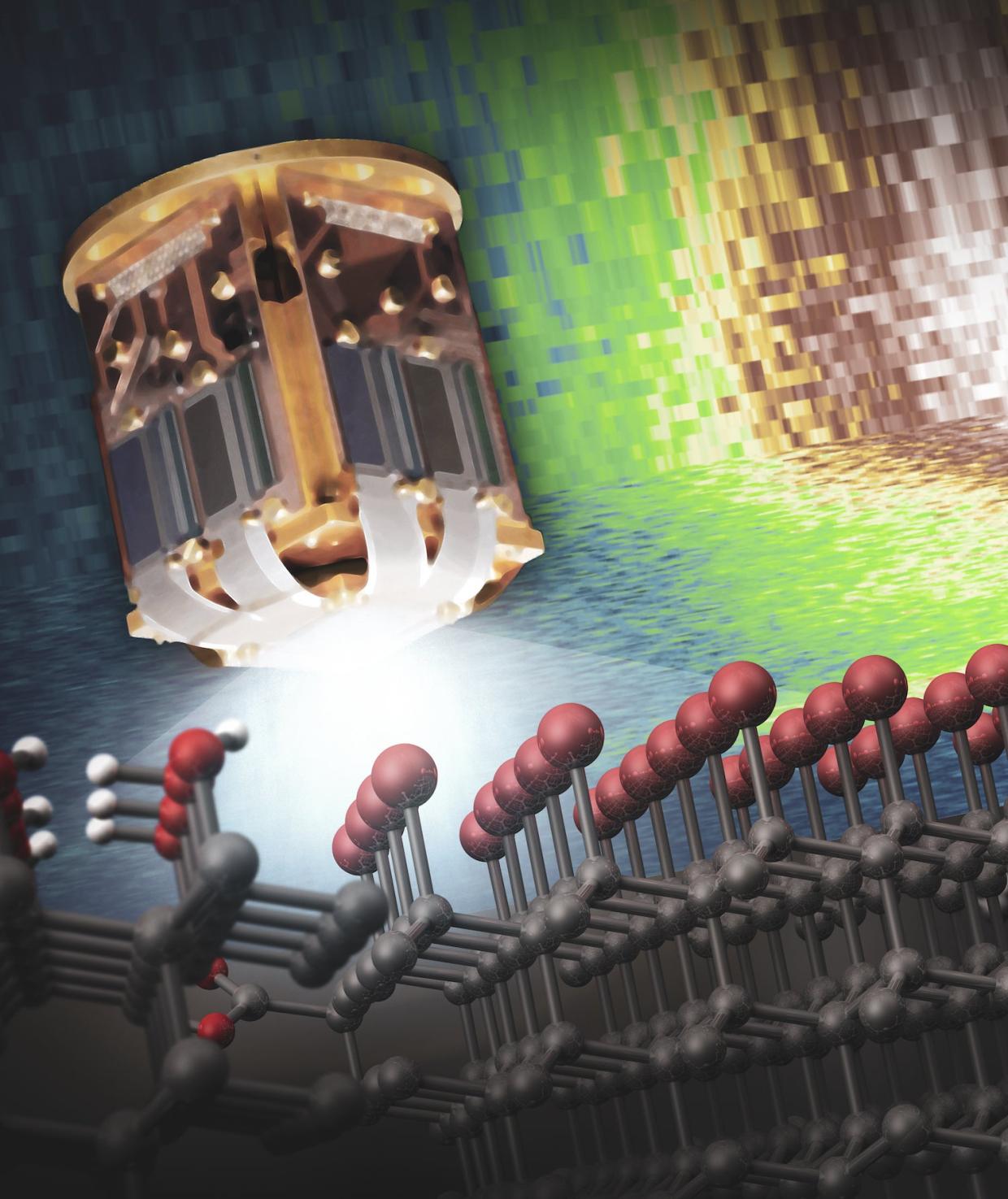
Wolcott’s research group in San Jose is working to attach different chemical groups to the surface of the nanodiamonds. Earlier this year, they published a paper in The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters on developing a stable chemical reaction to attach nitrogen-containing chemical groups called amines to the surface of the nanodiamonds by first chemically coaxing bromine atoms onto the surface. The discoveries, which the researchers say could be useful for studying biological systems or in quantum sensors, are also being patented for their potential applications in nanotechnology.
This development was the product of lots of work, and Wolcott is quick to credit students like SJSU senior Tsz “Megan” Cheung, who has been in the lab since her freshman year. Cheung says she was initially interested in Wolcott’s lab because she had heard he allowed freshmen to join his group—and she really wanted to join a lab. Upon joining, she assumed she’d be washing dishes or restocking chemicals but was put to work on a research project almost right away. In fact, according to his students, jumping into experiments soon after joining is often the standard protocol in the Wolcott lab.
Cheung says some of her group’s chemical procedures can take up to five days to complete, which poses a potential logistical challenge since undergrads are generally busy with classes and aren’t expected to be in lab full-time. However, she says clear communication is key on the team. The students coordinate their schedules with one another and work through the reaction like a multi-day assembly line until the reaction is complete.
Nanodiamonds at the beamline
After trying to chemically attach different molecules to the surface of the nanodiamonds, Wolcott’s students need a way to test whether their reactions were successful. For this, they take their chemically-treated nanodiamonds to the Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource (SSRL) at the Department of Energy's SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory.
The synchrotron acts as a “big factory to produce intense X-ray beams,” says staff engineer Sang-Jun Lee. As electrons hurtle through the synchrotron's storage ring, super-strong magnets cause the beam of particles to wiggle, generating powerful X-rays that are funneled into experimental stations at each beamline. At Beam Line 10-1, an instrument called a transition edge sensor (TES) measures the X-rays coming out of the experimental sample with such fine resolution they can reveal the electronic structure of a substance – that is, patterns in the way its electrons are energetically arranged – says Lee. In the case of the nanodiamonds, TES can detect which chemical groups are present on the surface of the diamond.
Wolcott was among the first pilot users of TES when it was commissioned in 2016 – it was like the “science version of test-driving a Ferrari,” he recalls – and his students have been consistent users ever since, coming a few times a year, says Lee.
For many of Wolcott’s students, even just setting foot on SLAC’s campus is memorable. But they also get hands-on time at the beamline.
“It wasn’t that we were just shadowing and seeing other scientists do the chemistry,” says Cynthia Melendrez, a recent SJSU chemical engineering graduate and first author of the lab's latest study. “It was incredible to be able to go into SSRL and actually do the experiments.”
Cheung agrees: “It’s hard to describe. You have to physically be there to feel the feeling of what a national lab is like.”
According to Lee, who has worked with Wolcott and his students at the beamline, learning the ropes isn’t easy for first-time users, and training undergraduates to use the beamline is especially rare. But, Lee says, Wolcott’s students have been able to do it – whether by writing programs to run the beamline automatically or by taking eight-hour-long night shifts to maximize the work they can get done during their long-awaited beamtime.
Camron Stokes, who recently graduated from SJSU with a degree in physics, was one of the students working the beamline’s graveyard shift. As a physics major, Stokes admits he was initially apprehensive about joining Wolcott’s chemistry lab.
But getting to work at SSRL was “like a dream come true,” he says. After getting a crash course in TES troubleshooting and working through the night to keep things running smoothly, he still got a sense of the magical feeling of being alone with TES at night. “I felt like it belonged to me,” he remembers. “It was really cool.”
‘You actually get a chance’
Stokes credits his confidence and sense of ownership over his research to Wolcott’s mentorship. “It’s not just that the research is good,” he says. “You actually get a chance.”
In recognition of his nanodiamond work, Stokes was recently given an award from the American Chemical Society’s Division of Colloids and Surface Science and will give an invited talk at the national meeting of the ACS in Chicago in August 2022.
Many people assume undergraduates don’t know enough or aren’t experienced enough to do research, says Meléndrez, who is now a science and engineering associate at SLAC’s LCLS. “But the leap of faith that Dr. Wolcott had [when I was] a freshman was pretty neat.”
Wolcott notes that many SJSU students are first-generation college students and deal with a host of difficult life circumstances while continuing to support their families and attend school. For many, the effort of trying to keep a unified research program running while juggling undergraduate schedules and these extra challenges might not be worth it.
“You could have lowered expectations, and assume, ‘You know, what, I'm going to make the project simple, because that's what they can handle,’” says Wolcott. “I would consider that to be deficit thinking.”
“To do good science – to do real science – with those types of challenges,” he says, “that's really what makes it special.”
SSRL is a DOE Office of Science user facility.
Citation: Cynthia Melendrez et al., Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 27 January 2022 (10.1021/acs.jpclett.1c04090)
For questions or comments, contact the SLAC Office of Communications at communications@slac.stanford.edu.
SLAC is a vibrant multiprogram laboratory that explores how the universe works at the biggest, smallest and fastest scales and invents powerful tools used by scientists around the globe. With research spanning particle physics, astrophysics and cosmology, materials, chemistry, bio- and energy sciences and scientific computing, we help solve real-world problems and advance the interests of the nation.
SLAC is operated by Stanford University for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time.