New insight into a cancer-shielding protein could guide a new generation of cancer treatments
A better understanding of ‘checkpoint proteins,’ which protect cancer cells against immune system strikes, could lead to the development of more effective drugs.
By Ali Sundermier
In a paper published in Cell Reports, a team of researchers from the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and Stanford University discovered unique characteristics of a protein called VISTA that protects cancer cells against immune system strikes. A better understanding of how this protein works could guide the design of treatments that target these proteins, infiltrating cancer’s first line of defense.
Picking the weeds
The human body is made up of trillions of cells that are constantly created, destroyed and replaced with new ones, like blades of grass on a lawn. But when cells start to grow and divide uncontrollably, like pesky weeds, they can form a solid mass called a tumor. If cancerous, this tumor can deepen its roots and spread to other parts of the body.
The solution seems straightforward enough. Just as one might weed a garden, the immune system can attack these diseased cells and nip the cancer in the bud. But the tumors have a secret weapon: The ability to cloak themselves, using special “checkpoint” proteins such as VISTA, and masquerade as normal, healthy grass.
“When tumor cells arise, they are recognized as foreign and are cleared by the immune system via specialized cells known as T cells,” says Jennifer Cochran, a professor of bioengineering at Stanford University. “But surface markers on the cells surrounding the tumor known as ‘immune checkpoints’ have been shown to act as an invisibility cloak of sorts to shield a tumor from immune system recognition and destruction.”
Stripping the invisibility cloak
FDA-approved antibodies that strip this cloak of invisibility and unleash immune system attacks on tumors have demonstrated remarkable power in treating a variety of cancers because they allow the immune system to find and destroy cancer cells without the toxic effects of chemotherapy. But due to a lack of information about how checkpoint proteins work, these drugs are only effective for about a quarter of patients.
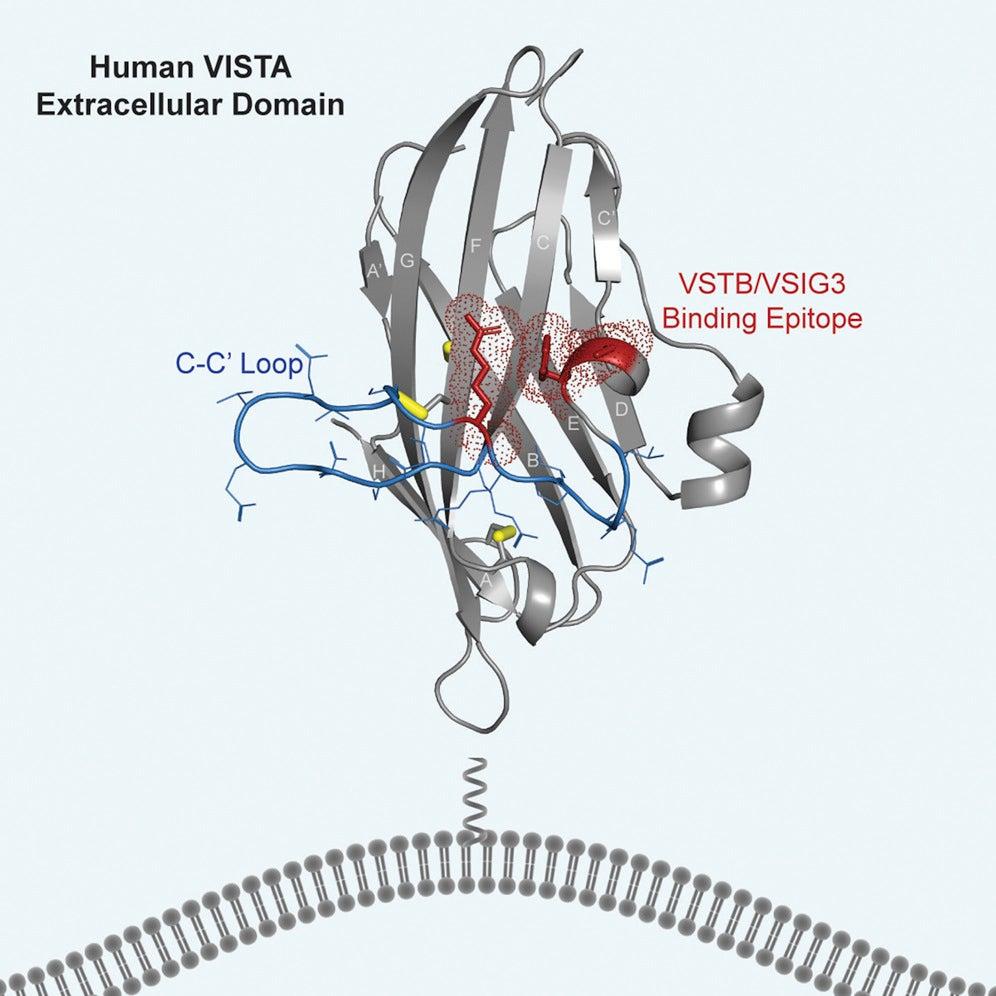
In a first, the team, led by Cochran, Possu Huang, a professor of bioengineering at Stanford, and Nishant Mehta, a Stanford PhD candidate, in collaboration with Irimpan Mathews, a researcher at Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource (SSRL), was able to map the structure of VISTA at high resolution, which required a combination of computational and experimental techniques.
To better understand its structure, the researchers crystallized VISTA molecules, then measured how the crystals diffracted X-rays at one of SSRL’s specialized beamlines. When researchers analyzed the data using computational tools, the patterns formed when the X-rays irradiated the crystals allowed them to map the shape and detailed atomic structure of the protein as well as its epitope, the part of the molecule that the immune system can recognize and target.
“This research was only possible because of the collaboration between experts in molecular engineering, computational protein design and structural biology,” says Mathews.
Breaking down defenses
To follow up on this research, Mehta hopes to use what they learned about the structure and binding region of VISTA to develop drugs that work against it and other checkpoint proteins.
“These proteins keep our immune systems from finding and destroying the cancer cells,” Mehta says. “Until now, researchers didn’t have a detailed picture of what VISTA looks like on a molecular level. What we learned in this study is extremely useful in designing new drugs because it tells us which areas to target to block the checkpoint protein’s function.”
SSRL is a DOE Office of Science user facility. The Structural Molecular Biology Program facilities used in this research were supported by the DOE Office of Science and the National Institutes of Health, National Institute of General Medical Sciences.
For questions or comments, contact the SLAC Office of Communications at communications@slac.stanford.edu.
Citation: N. Mehta et al., Cell Reports, 3 September 2019 (10.1016/j.celrep.2019.07.073)
SLAC is a vibrant multiprogram laboratory that explores how the universe works at the biggest, smallest and fastest scales and invents powerful tools used by scientists around the globe. With research spanning particle physics, astrophysics and cosmology, materials, chemistry, bio- and energy sciences and scientific computing, we help solve real-world problems and advance the interests of the nation.
SLAC is operated by Stanford University for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.




