March 15, 2019
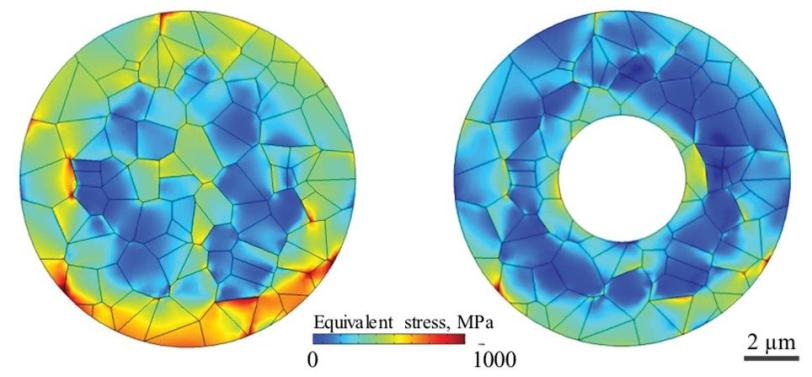
Cause of Cathode Degradation Identified for Nickel-rich Materials
Combination of research methods reveals causes of capacity fading, giving scientists better insight to design advanced batteries for electric vehicles
Dig Deeper