SLAC topics
LCLS Coherent X-ray Imaging (CXI)
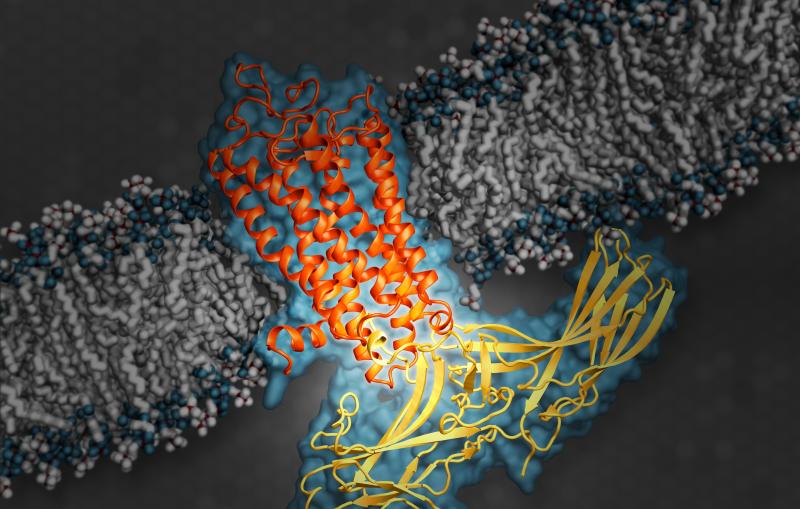
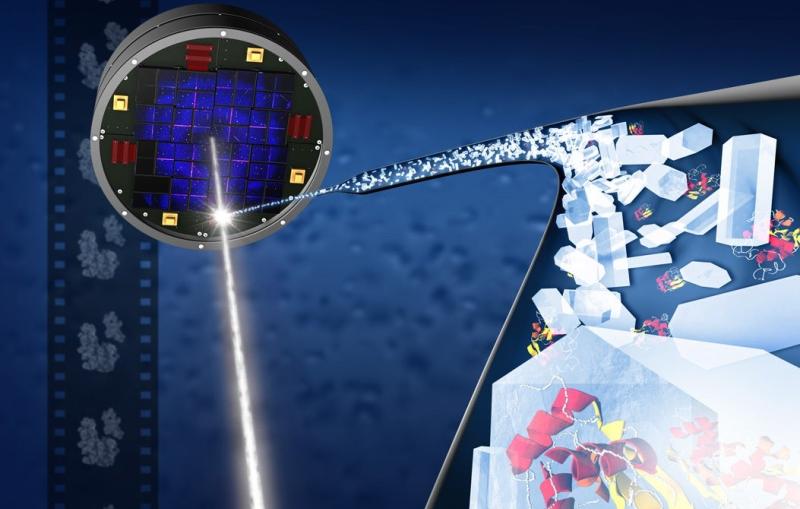
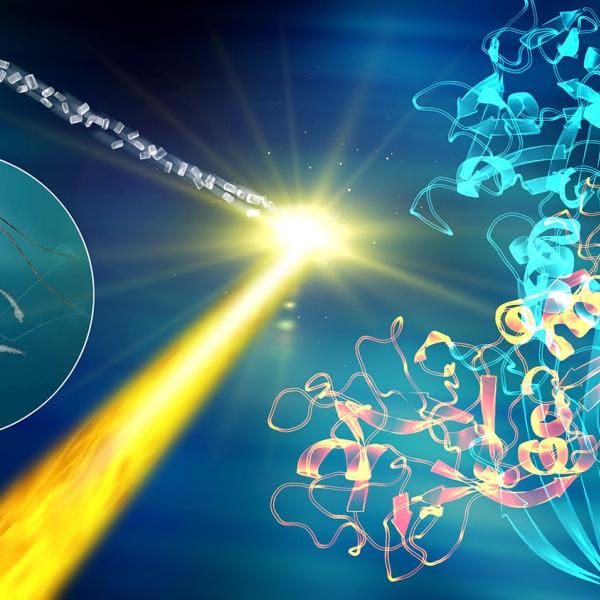
The Coherent X-ray Imaging (CXI) instrument makes use of the unique brilliant hard X-ray pulses from LCLS to perform a wide variety of experiments utilizing various techniques. The primary capability of CXI is to make use of the high peak power of the focused X-ray beam using the “diffraction-before-destruction” method.