Shedding light on stellar evolution
Researchers developed a way to measure the basic properties of matter at the highest pressures thus far achieved in a controlled laboratory experiment.
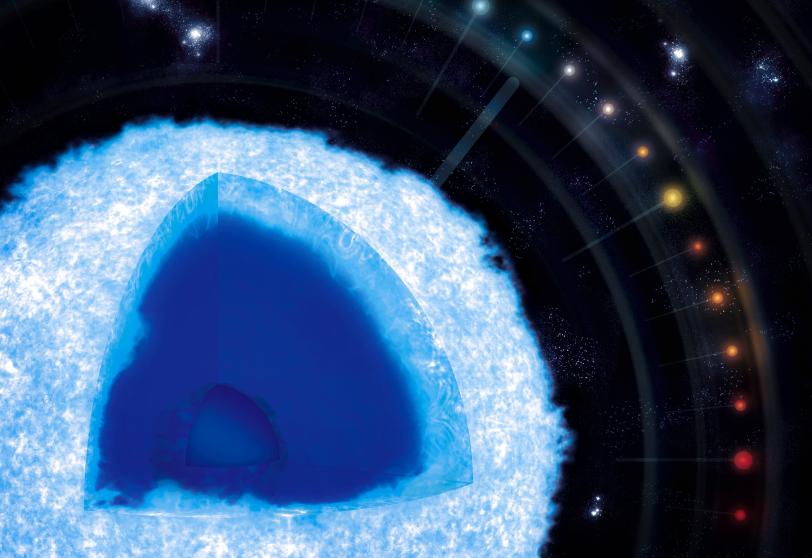
Using the power of the National Ignition Facility (NIF), the world’s highest-energy laser system, an international team developed a way to measure the basic properties of matter, such as the equation of state (EOS), at the highest pressures thus far achieved in a controlled laboratory experiment. The results are relevant to the conditions at the cores of giant planets, the interiors of brown dwarfs (failed stars), the carbon envelopes of white dwarf stars and many applied science programs.
The team, led by researchers at the Department of Energy's Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, included scientists from the DOE's SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory. Their paper was published today in Nature.
According to the authors, the overlap with white dwarf envelopes is particularly significant – this new research enables experimental benchmarks of the basic properties of matter in this regime. The results should ultimately lead to improved models of white dwarfs, which represent the final stage of evolution for most stars in the universe. They are among the most ancient stellar objects, so their temperatures and predictable lifecycles enable them to work as "cosmic clocks" that can help determine the age of the universe and nearby stars and galaxies.
After billions of years, the sun and other medium- and low-mass stars will undergo a sequence of expansions and contractions that results in the formation of white dwarfs – the fate of stars that have exhausted their nuclear fuel and collapsed into hot, super-dense mixtures of carbon and oxygen.
“For the first time, we’re able to take data at the extreme conditions found in these stars, which were not accessible in the lab until now," says co-author Siegfried Glenzer, director of the High Energy Density Division at SLAC, who was involved in the early proposal for this research. "By combining our expertise in various fields, we can construct equation of state models that agree with the data. It narrows down the models used to describe how white dwarfs behave, opening up a whole new area of work that has to be done.”
In an effort to resolve disagreements in EOS models at extreme pressures that are relevant to white dwarf stars and various laboratory research projects, scientists conducted the first laboratory studies of matter at the conditions in the outer carbon layer of an unusual class of white dwarf called a “hot DQ.”
The research subjected solid hydrocarbon samples to pressures ranging from 100 to 450 megabars (100 to 450 million times Earth’s atmospheric pressure) to determine the EOS – the relationship between pressure and compression – in the convection layer of a hot DQ. These were the highest pressures ever achieved in laboratory EOS measurements.
“White dwarf stars provide important tests of stellar physics models, but EOS models at these extreme conditions are largely untested,” said LLNL physicist Annie Kritcher, the paper’s lead author.
“NIF can duplicate conditions ranging from the cores of planets and brown dwarfs to those in the center of the sun,” Kritcher added. “We’re also able in NIF experiments to deduce the opacity along the shock Hugoniot (the Hugoniot curve is a plot of the increase in a material’s pressure and density under strong shock compression). This is a necessary component in studies of stellar structure and evolution.”
Hot DQs have atmospheres primarily composed of carbon – instead of hydrogen and helium as in most white dwarfs – and are unusually hot and bright. Some also pulsate as they rotate because of magnetic spots on their surface, providing observable variations in brightness. Analyzing these variations “provides stringent tests of white dwarf models and a detailed picture of the outcome of the late stages of stellar evolution,” the researchers said.
They added, however, that current EOS models relevant to white dwarf envelopes at pressures in the hundreds of millions of atmospheres can vary by nearly 10 percent, “a significant uncertainty for stellar evolution models.” Previous researchers have called this the “weakest link in the constitutive physics” that inform white dwarf modeling, Kritcher said.
The NIF research could help resolve the differences by providing the first EOS data that reach conditions deep in the convection zone of a hot DQ – the region where models show the greatest variability. Results of the experiments agree with EOS models that recognize the extent to which extreme pressures can strip inner-shell electrons from their carbon atoms, decreasing the opacity and increasing the compressibility of the resulting ionized plasma.
The EOS research is an outgrowth of the NIF Discovery Science “Gbar (gigabar, or one billion atmospheres) Campaign," initiated by Roger Falcone and his students and postdocs at University of California, Berkeley and other NIF academic users and early career scientists from LLNL. It was supported by the LLNL Laboratory Directed Research and Development Program, the University of California Office of the President, the National Nuclear Security Administration and the Department of Energy Office of Science.
“The NIF Discovery Science Program enabled our diverse team of researchers – from universities, national labs and industry – to work together on a long-term effort to fundamentally understand the behavior of matter under the most extreme pressures and temperatures,” Falcone said. “NIF is the only facility in the world capable of creating and probing those conditions, and its expert support teams were key to our success. This paper highlights the strength of that collaboration and is evidence for how basic research can find applications in many fields, including astrophysics.
In the EOS experiments, NIF’s lasers delivered 1.1 million joules of ultraviolet light to the inside of a pencil-eraser-size hollow gold cylinder called a hohlraum, creating a uniform X-ray “bath” with a peak radiation temperature of nearly 3.5 million degrees. The X-rays were absorbed by a solid plastic sphere mounted in the center of the hohlraum.
The plastic was heated and ablated, or blown off like rocket exhaust, by the X-rays, creating ablation pressure that launched converging shock waves at 150 to 220 kilometers a second toward the center of the target capsule. The shocks coalesced into a single stronger shock that reached pressures approaching a billion times Earth’s atmosphere.

Researchers determined the Hugoniot – the density and pressure at the shock front – using temporally and spatially resolved streaked X-ray radiography. The studies showed consistent results for experiments fielded at both cryogenic and ambient temperatures – which produced different initial starting densities – and with varying laser pulse shapes. They also measured the bulk shocked material’s electron temperature and degree of ionization with X-ray Thomson scattering.
“We measured a reduction in opacity at high pressures, which is associated with a significant ionization of the carbon inner shell,” Kritcher said. “This pressure range along the Hugoniot corresponds to the conditions in the carbon envelope of white dwarf stars. Our data agree with equation-of-state models that include the detailed electronic shell structure.”
Those models “show a sharper bend in the Hugoniot and higher maximum compression than models that lack electronic shells,” she said, suggesting a “softening” of the EOS. This leads to increased compression resulting from this “pressure ionization.”
The experimental data can contribute to better models of pulsating hot DQ stars and a more accurate determination of their internal structures, pulsation properties, spectral evolution, and complex origin, the researchers concluded.
This research was supported by the DOE Office of Science.Kritcher, Falcone and Glenzer were joined on the paper by LLNL researchers Damian Swift, Tilo Döppner, Benjamin Bachmann, Lorin Benedict, Jonathan DuBois, Jim Gaffney, Sebastien Hamel, Amy Jenei, Natalie Kostinski, Mike MacDonald, Brian Maddox, Madison Martin, Abbas Nikroo, Joe Nilsen, Bruce Remington, Phillip Sterne, Alfredo Correa Tedesco and Heather Whitley; Rip Collins, Laboratory for Laser Energetics at the University of Rochester; Wendi Sweet and Fred Elsner, General Atomics; Gilles Fontaine, University of Montreal; Walter Johnson, University of Notre Dame; Dominik Kraus, Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf and Institute of Solid State and Materials Physics at the Technische Universität Dresden in Dresden, Germany; Paul Neumayer, GSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion Research in Darmstadt, Germany; Didier Saumon, Los Alamos National Laboratory; and Siegfried Glenzer, SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory.
This article is based on a press release from Livermore.
Citation: A. Kritcher et al., Nature 5 June 2020 (10.1126/sciadv.aaz5132)
Contact
For questions or comments, contact the SLAC Office of Communications at communications@slac.stanford.edu.
SLAC is a vibrant multiprogram laboratory that explores how the universe works at the biggest, smallest and fastest scales and invents powerful tools used by scientists around the globe. With research spanning particle physics, astrophysics and cosmology, materials, chemistry, bio- and energy sciences and scientific computing, we help solve real-world problems and advance the interests of the nation.
SLAC is operated by Stanford University for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time.