Research Paints New Picture of 'Dinobird' Feathers
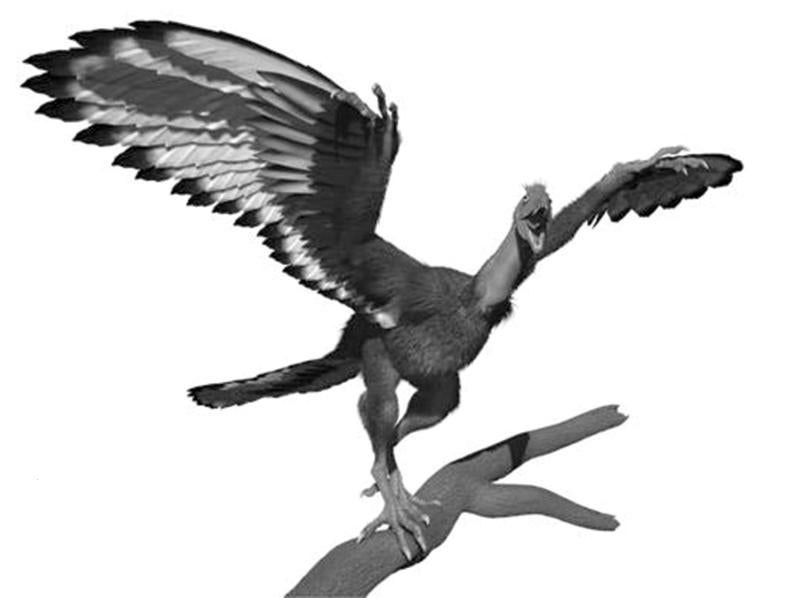
The first complete chemical analysis of feathers from Archaeopteryx, a famous fossil linking dinosaurs and birds, reveals that the feathers were patterned—light in color, with a dark edge and tip—rather than all black, as previously thought.
Menlo Park, Calif. — The first complete chemical analysis of feathers from Archaeopteryx, a famous fossil linking dinosaurs and birds, reveals that the feathers were patterned—light in color, with a dark edge and tip—rather than all black, as previously thought.
The findings came from X-ray experiments at the Department of Energy's (DOE) SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, where scientists were able to find chemical traces of the original dinobird and its pigments in the rock that entombed it 150 million years ago.
"This is a big leap forward in our understanding of the evolution of plumage," said Phillip Manning, a paleontologist at the University of Manchester and lead author of the report in the June 13 issue of the Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry.

Only 11 specimens of Archaeopteryx have been found, the first one consisting of a single feather. Until a few years ago, researchers thought all the bones and tissues of the original animal would have been replaced by minerals during fossilization, leaving no chemical traces behind.
But two recently developed methods have turned up more information about the dinobird and its plumage.
The first is the discovery of melanosomes—microscopic 'paint pot' structures containing pigment—in fossils. A team led by researchers at Brown University announced last year that an analysis of melanosomes in the Archaeopteryx feather specimen showed that the feather was black. They identified the feather as a covert—a type of feather that covers the primary and secondary wing feathers—and said its heavy pigmentation may have strengthened it against the wear and tear of flight, as it does in modern birds.
However, that study examined melanosomes from just a few locations in the fossilized feather, said SLAC’s Uwe Bergmann. "It’s actually quite a beautiful paper," he said, "but they took just tiny samples of the feather, not the whole thing."
The second is a method Bergmann, Manning and Roy Wogelius of the University of Manchester developed for rapidly scanning entire fossils and analyzing their chemistry with an X-ray beam at SLAC’s Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource (SSRL).
Over the past three years, they led a team that used this method to discover chemicals left by the dinobird’s bones and feathers in the surrounding rock, as well as pigments from the fossilized feathers of two of the first known birds. This allowed them to recreate the plumage pattern of a bird that lived more than 120 million years ago.
In the latest study, the team scanned the entire fossil of the first Archaeopteryx feather with the SSRL X-ray beam. They found trace metals associated with pigments and organic sulfur compounds that could only have come from the animal itself. The fact that these compounds have been preserved in the fossil for 150 million years is extraordinary, Manning said.
Together these chemical traces show that the feather was light in color, with areas of darker pigmentation along one edge and on the tip. Scans of a second fossilized Archaeopteryx, known as the Berlin counterpart, revealed that its covert feathers had the same pigmentation pattern, Manning said.
He said the results show that the chemical analysis provided by synchrotron X-ray sources such as SSRL is crucial for understanding these ancient fossils, including plumage patterns that play an important role in the courtship, reproduction and evolution of birds and contain clues to their health, eating habits and environment.
The research team included Dimosthenis Sokaras and Roberto Alonso of SLAC and scientists from the University of Manchester in England, the Black Hills Institute of Geological Research in South Dakota and the Museum für Naturkunde in Berlin, which provided the Archaeopteryx fossils for analysis.
SLAC is a multi-program laboratory exploring frontier questions in photon science, astrophysics, particle physics and accelerator research. Located in Menlo Park, California, SLAC is operated by Stanford University for the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science. To learn more, please visit www.slac.stanford.edu.
SLAC’s Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource is a third-generation light source producing extremely bright X-rays for basic and applied science. A DOE national user facility, SSRL attracts and supports scientists from around the world who use its state-of-the-art capabilities to make discoveries that benefit society. For more information visit http://www-ssrl.slac.stanford.edu.
DOE’s Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.
Citation: Phillip Manning, et al., J. Anal. At. Spectrom., June 13, 2013 ()
Contact
For questions or comments, contact the SLAC Office of Communications at communications@slac.stanford.edu.
Scientist Contact: Uwe Bergmann: bergmann@stanford.edu