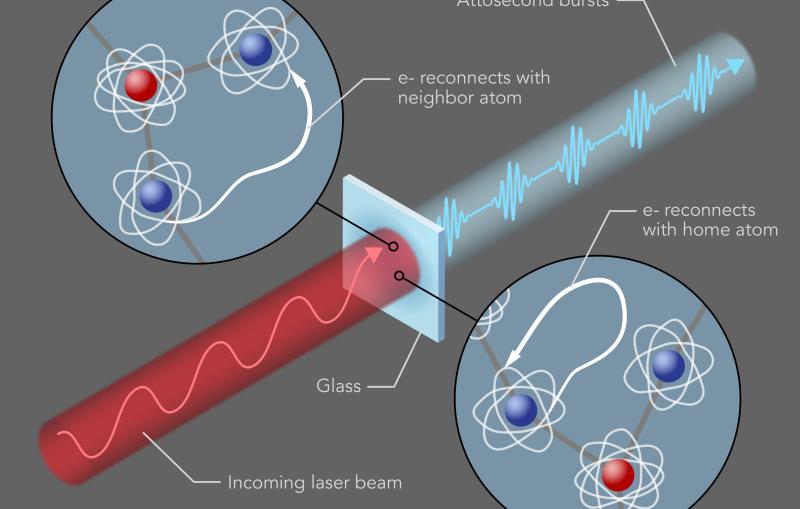
SLAC topics
Stanford PULSE Institute
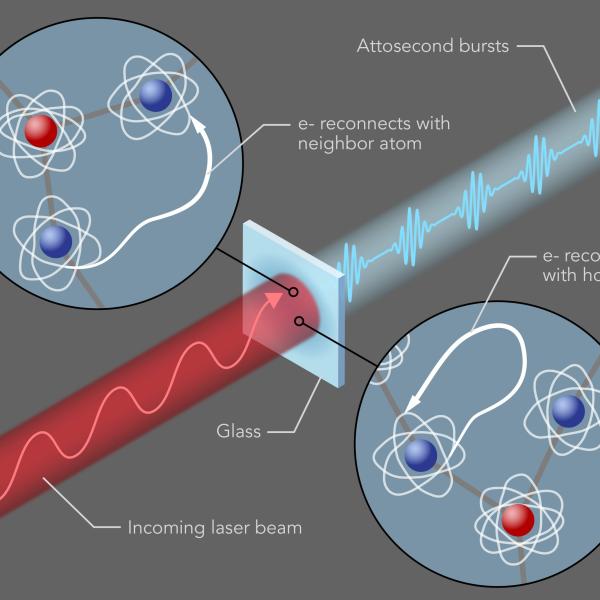
Researchers at the Stanford PULSE Institute watch ultrafast particle motions and chemical reactions to get a deeper understanding of matter in all its forms. Soon we’ll be able to watch even speedier electron movements that underlie all of chemistry, technology and life.