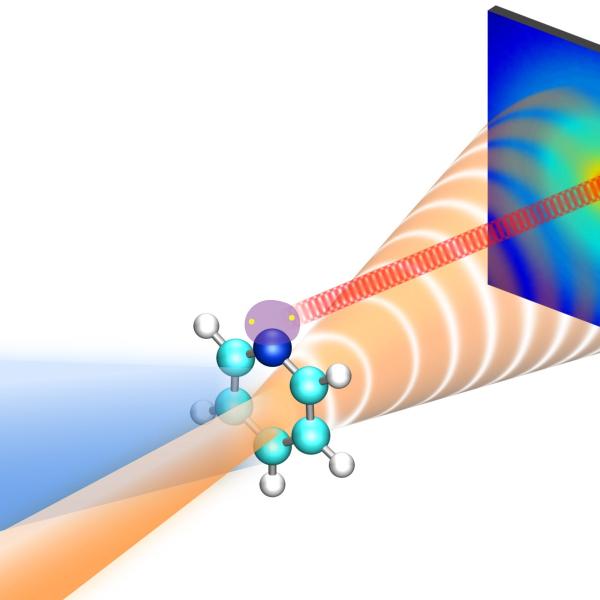
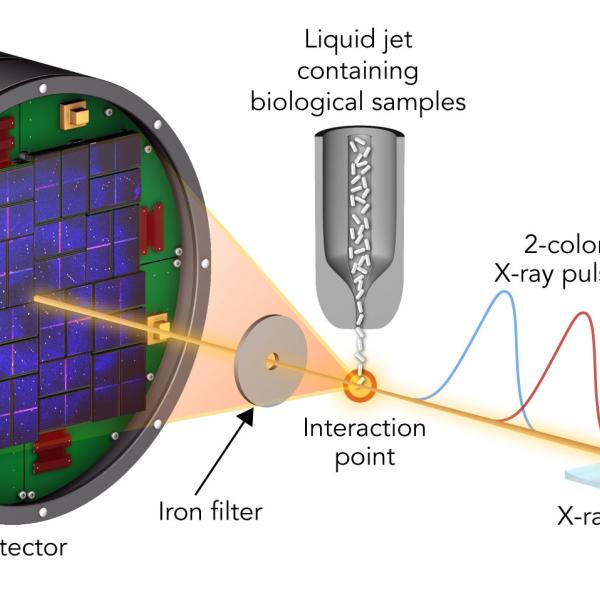
News Feature
VIA Stanford Energy
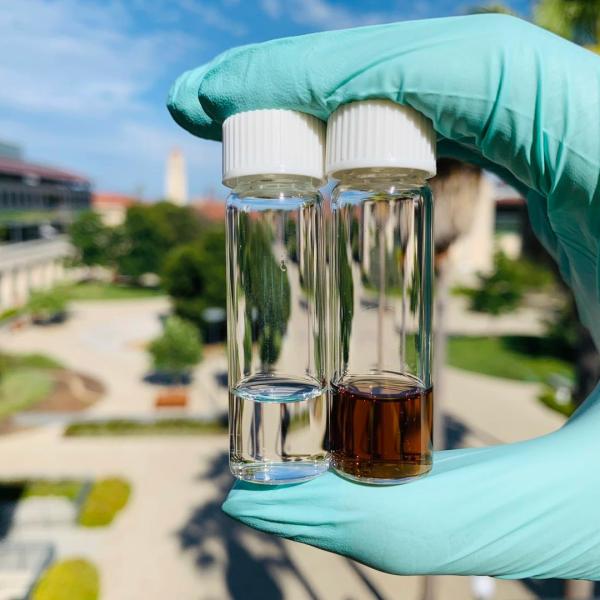
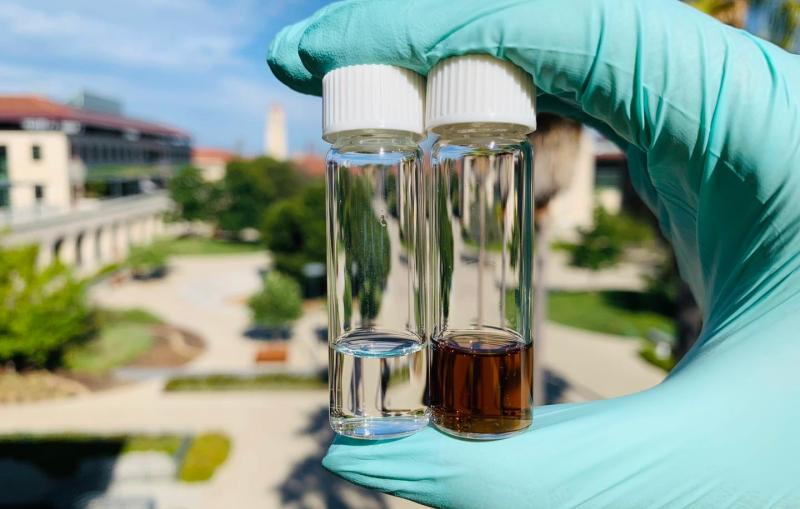
New battery electrolyte may boost the performance of electric vehicles

Animation
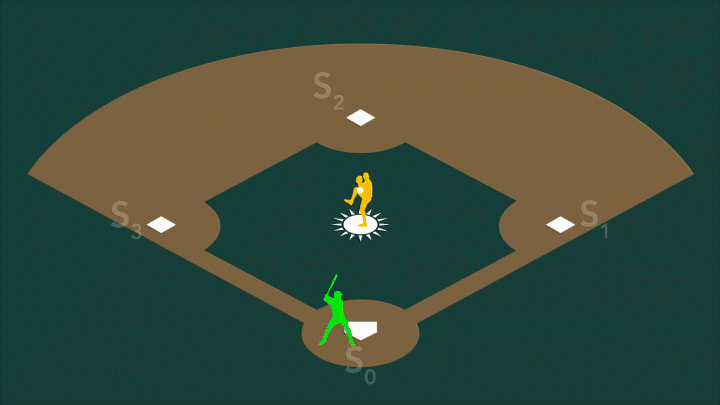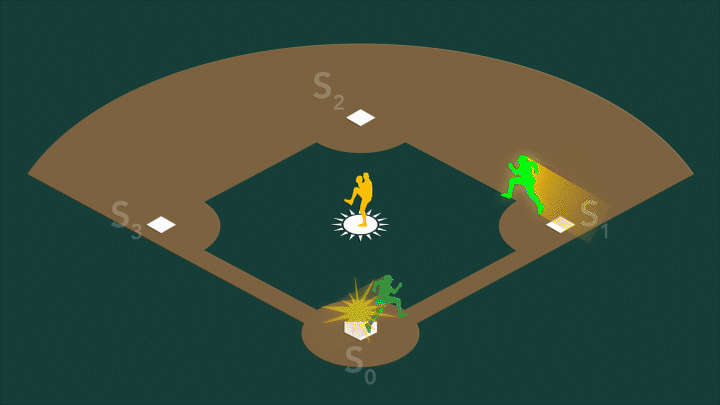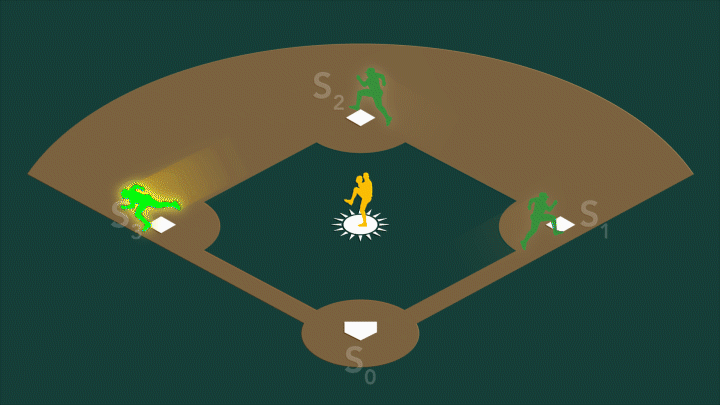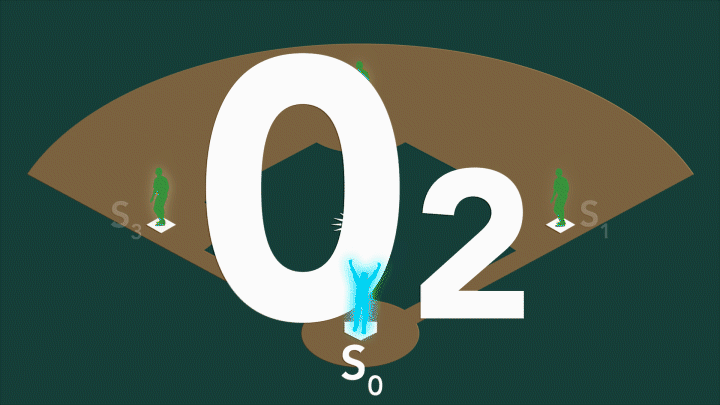
In photosystem II, the water-splitting center cycles through four stable states, S0-S3. On a baseball field, S0 would be...