Research Begins at SLAC’s Newest X-ray Laser Experimental Station
The new MFX station expands the X-ray laser’s capability and flexibility for biological studies, which are increasingly in demand at SLAC's Linac Coherent Light Source.
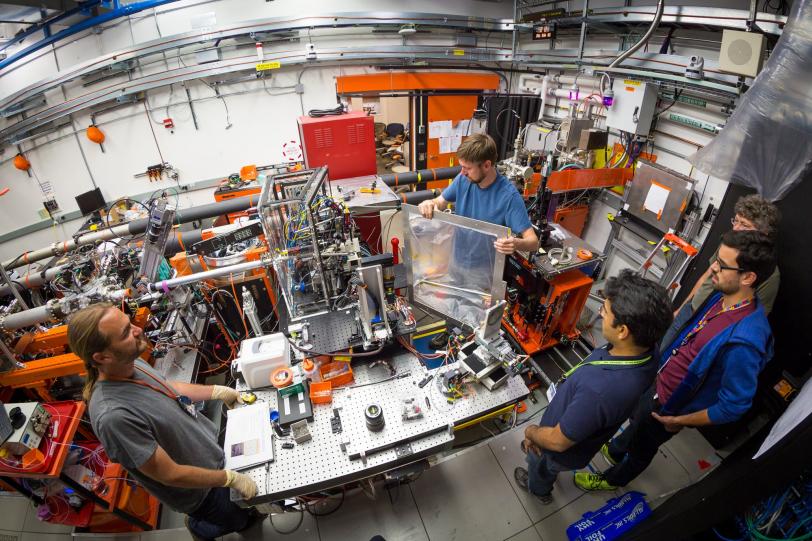
A new X-ray laser experimental station at the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory recently welcomed its first research group, scientists from Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
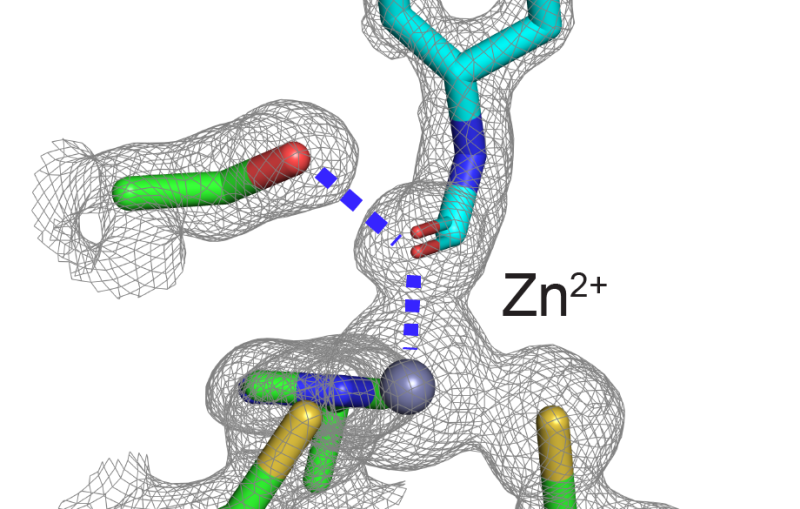
Members of the Berkeley Lab’s Yachandra/Yano research team ran the inaugural experiment from July 1 to 4. They used the X-ray laser to develop new spectroscopic tools, with an initial focus on studying an enzyme in blood known as hemoglobin. Hemoglobin allows oxygen to be carried around our bodies and gives red blood cells their distinctive color.
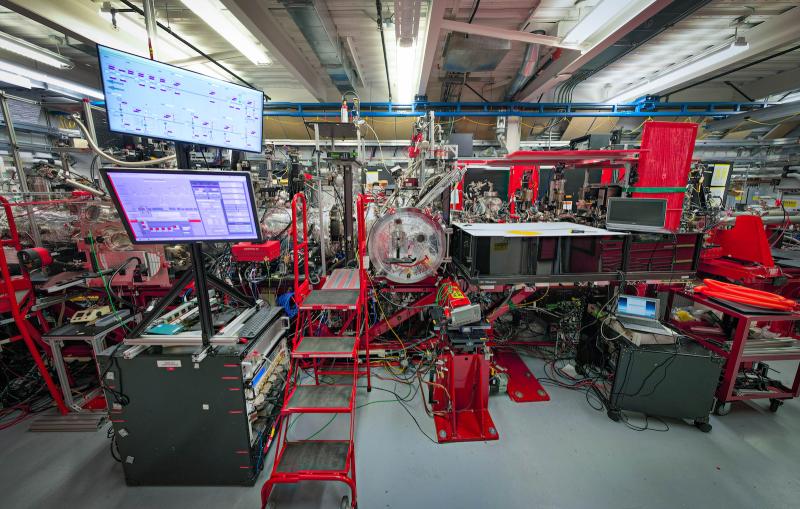
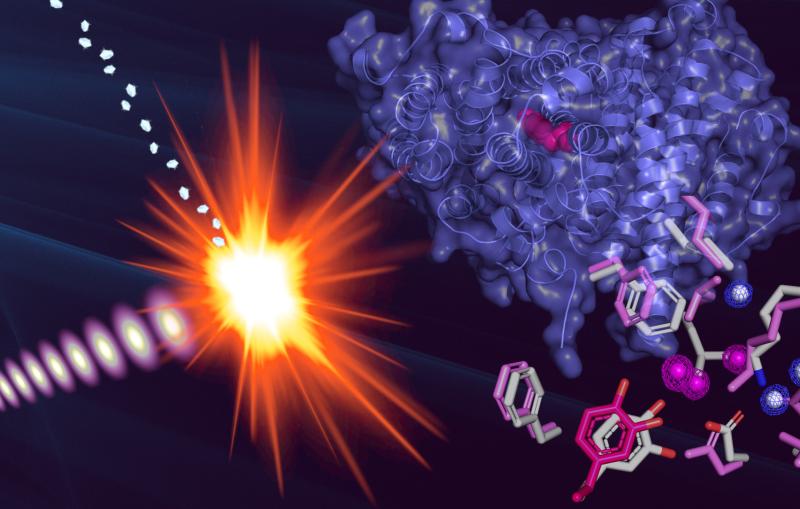
In contrast, Macromolecular Femtosecond Crystallography (MFX) is blaze orange, following the LCLS tradition of personalizing each instrument at SLAC’s Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS), a DOE Office of Science User Facility. LCLS is a hard X-ray free-electron laser that fires in pulses just a few millionths of a billionth of a second in length, offering a look at chemistry on the natural timescales of reactions.
MFX is the seventh instrument at LCLS, and is designed to optimize the facility’s ability to investigate the innermost workings of the chemistry and biology that underpin the living world. MFX allows scientists to study complex molecules such as proteins with atomic resolution using a variety of experimental techniques.
Scientists can take advantage of short X-ray pulses at MFX to limit sample damage during exposure. This can be particularly important, for example, when looking at metal-containing molecules that are more sensitive to damage by radiation.

LCLS MFX Construction Timelapse
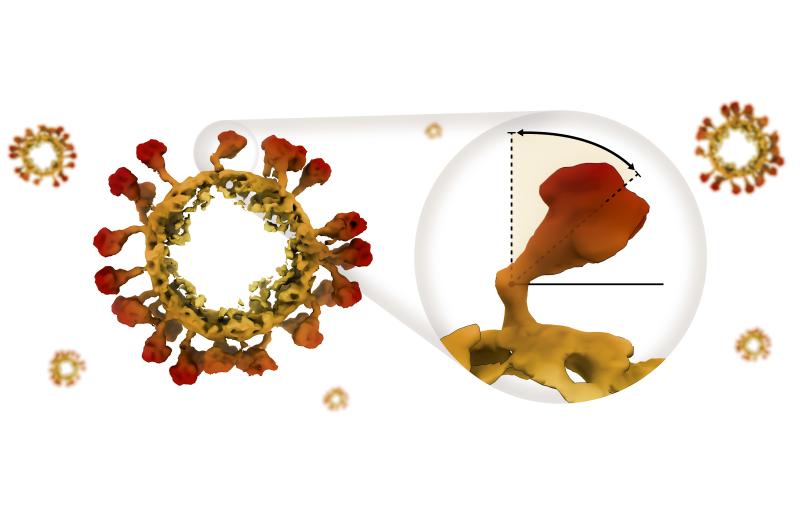
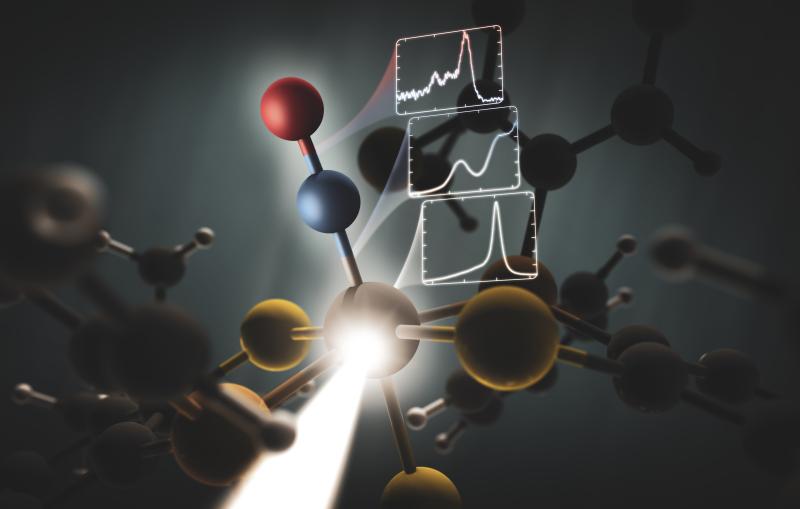
During the first experiment at MFX, the Berkeley Lab group studied the distribution of electrons and the bonds between iron and the surrounding atoms within hemoglobin. Many iron-containing enzymes transfer electrons from the iron to an oxygen molecule. This makes both the metal and the oxygen highly active, leading to other important biological reactions, said Franklin Fuller, a postdoctoral researcher at Berkeley Lab.
“We want to know where these electrons travel throughout the course of the reactions,” said Fuller. “At MFX, we can use an experimental technique – called X-ray emission spectroscopy – that is sensitive to that.”
Using the capabilities of the X-ray laser, they could look at the chemical changes as the reactions progress. The information collected from hemoglobin experiments can also be useful when examining other iron and metal-containing proteins that are important to both energy production and health.
Fuller said it can be difficult to measure signals from these proteins, because they exist at very low concentrations. The signals tend to be weak.
“The goal is to push our ability to examine low concentration samples that represent real-world situations, and that requires the high brilliance, high flux of LCLS,” Fuller said.
The group was able to collect data with excellent quality, said Jan Kern, a scientist at Berkeley Lab and LCLS. They were able to examine the relationship between the many energies in the X-ray laser beam in each shot and the X-ray spectrum from the iron-containing hemoglobin, as well as some simpler iron compounds.
“For a first experiment using a brand new beam line, instrument and hutch, data collection went remarkably smoothly,” said Kern. “Although we were nervous about being the first users, everything worked really well. We really appreciate the work done by the LCLS scientists and engineers."
The number of proposals for biology experiments at LCLS has rapidly increased during the past few years. MFX will help meet this growing demand by complementing the suite of LCLS instruments already in use for structural biology studies.
The Berkeley Lab researchers will return to MFX later in July for another experiment, designed to look closely at water splitting during photosynthesis. Learning how water is ‘split’ into protons and oxygen in photosynthetic organisms by using light is critical for designing artificial systems that are important for solar-based renewable energy. The Berkeley Lab researchers are trying to understand the mechanism using simultaneous data collection for X-ray crystallography and X-ray emission spectroscopy. To do this, the researchers built a small conveyor belt to deliver droplets of the liquid samples into the beam line at MFX.
The new experimental station is designed to handle challenging biological samples that are fundamentally important for medicine, chemistry and energy research. MFX aims to achieve higher throughput and user access with a versatile system that supports a few standard configurations compatible with a broad range of samples.
Scientists from across SLAC (including LCLS, the Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource (SSRL) and the Bioscience Division) designed the MFX experimental station in close consultation with the user community. The project is supported by the DOE’s Office of Biological and Environmental Research and Office of Basic Energy Sciences, both part of the DOE Office of Science, in addition to Stanford University and the NIH National Institute of General Medical Sciences.
For questions or comments, contact the SLAC Office of Communications at communications@slac.stanford.edu.

SLAC is a vibrant multiprogram laboratory that explores how the universe works at the biggest, smallest and fastest scales and invents powerful tools used by scientists around the globe. With research spanning particle physics, astrophysics and cosmology, materials, chemistry, bio- and energy sciences and scientific computing, we help solve real-world problems and advance the interests of the nation.
SLAC is operated by Stanford University for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time.