Scientists Discover Atomic-resolution Details of Brain Signaling
X-ray Laser Experiment Could Help in Designing New Drugs for Brain Disorders
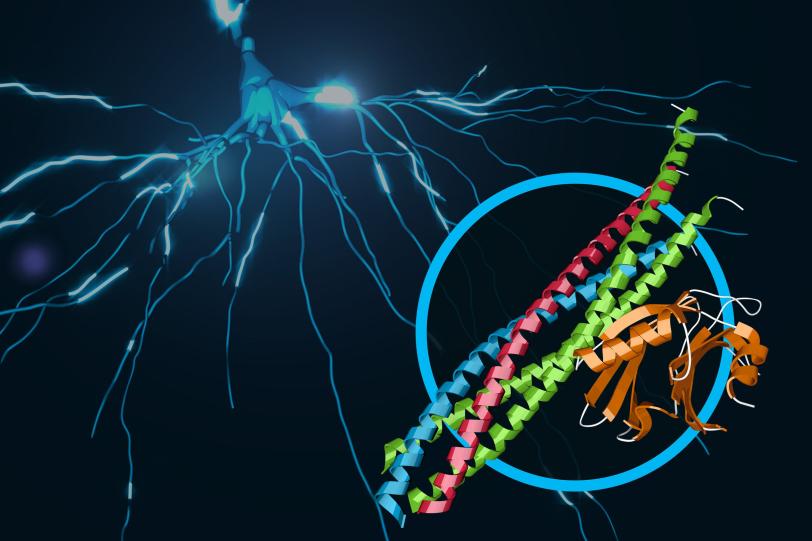
Menlo Park, Calif. — Scientists have revealed never-before-seen details of how our brain sends rapid-fire messages between its cells. They mapped the 3-D atomic structure of a two-part protein complex that controls the release of signaling chemicals, called neurotransmitters, from brain cells. Understanding how cells release those signals in less than one-thousandth of a second could help launch a new wave of research on drugs for treating brain disorders.
The experiments, at the Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS) X-ray laser at the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, build upon decades of previous research at Stanford University, Stanford School of Medicine and SLAC. Researchers reported their latest findings today in the journal Nature.
“This is a very important, exciting advance that may open up possibilities for targeting new drugs to control neurotransmitter release. Many mental disorders, including depression, schizophrenia and anxiety, affect neurotransmitter systems,” said Axel Brunger, the study’s principal investigator. He is a professor at Stanford School of Medicine and SLAC and a Howard Hughes Medical Institute investigator.
“Both parts of this protein complex are essential,” Brunger said, “but until now it was unclear how its two pieces fit and work together.”
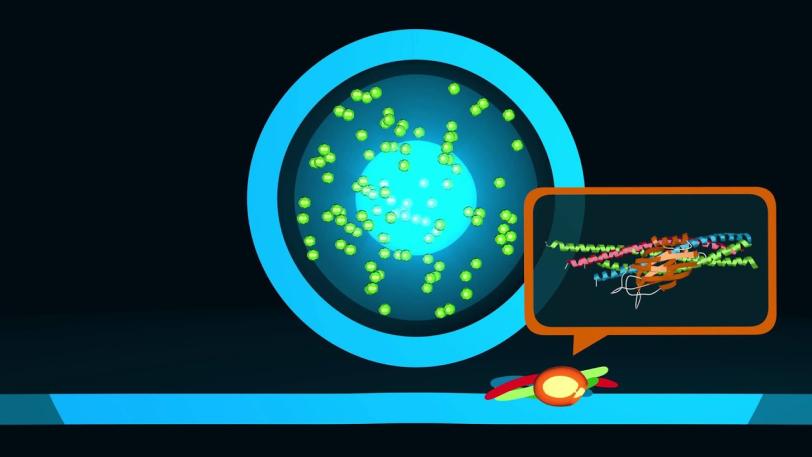
XPP | Unlocking the Secrets of Brain Signals
This video describes the function and 3-D structure of a protein complex that provides the ultrafast trigger for chemical messages sent between nerve cells in our brains. The details of this structure, brought to light in an experiment at SLAC’s Linac Coherent Light Source X-ray laser, provide a new understanding of the molecular machinery driving brain function.
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory
Unraveling the Combined Secrets of Two Proteins
The two protein parts are known as neuronal SNAREs and synaptotagmin-1.
Earlier X-ray studies, including experiments at SLAC’s Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource (SSRL) nearly two decades ago, shed light on the structure of the SNARE complex, a helical protein bundle found in yeasts and mammals. SNAREs play a key role in the brain’s chemical signaling by joining, or “fusing,” little packets of neurotransmitters to the outer edges of neurons, where they are released and then dock with chemical receptors in another neuron to trigger a response.
A ‘Smoking Gun’ for Neurotransmitter Release
In this latest research, the scientists found that when the SNAREs and synaptotagmin-1 join up, they act as an amplifier for a slight increase in calcium concentration, triggering a gunshot-like release of neurotransmitters from one neuron to another. They also learned that the proteins join together before they arrive at a neuron’s membrane, which helps to explain how they trigger brain signaling so rapidly.
“The neuron is not building the ‘gun’ as it sits there on the membrane – it’s already there,” Brunger said.
The team speculates that several of the joined protein complexes may group together and simultaneously interact with the same vesicle to efficiently trigger neurotransmitter release, an exciting area for further studies.
“The structure of the SNARE-synaptotagmin-1 complex is a milestone that the field has awaited for a long time, and it sets the framework for a better understanding of the system,” said James Rothman, a professor at Yale University who discovered the SNARE proteins and shared the 2013 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
Thomas C. Südhof, a professor at the Stanford School of Medicine and Howard Hughes Medical Institute investigator who shared that 2013 Nobel Prize with Rothman, discovered synaptotagmin-1 and showed that it plays an important role as a calcium sensor and calcium-dependent trigger for neurotransmitter release.
“The new structure has identified unanticipated interfaces between synaptotagmin-1 and the neuronal SNARE complex that change how we think about their interaction by revealing, in atomic detail, exactly where they bind together,” Südhof said. “This is a new concept that goes much beyond previous general models of how synaptotagmin-1 functions.”
Using Crystals, Robotics and X-rays to Advance Neuroscience
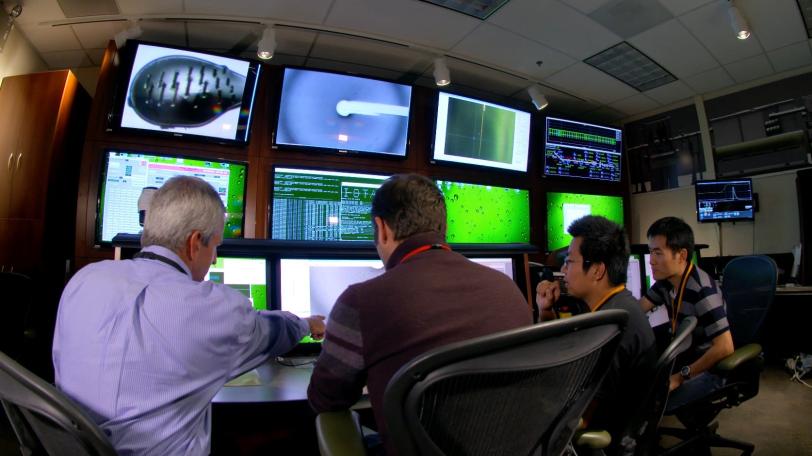
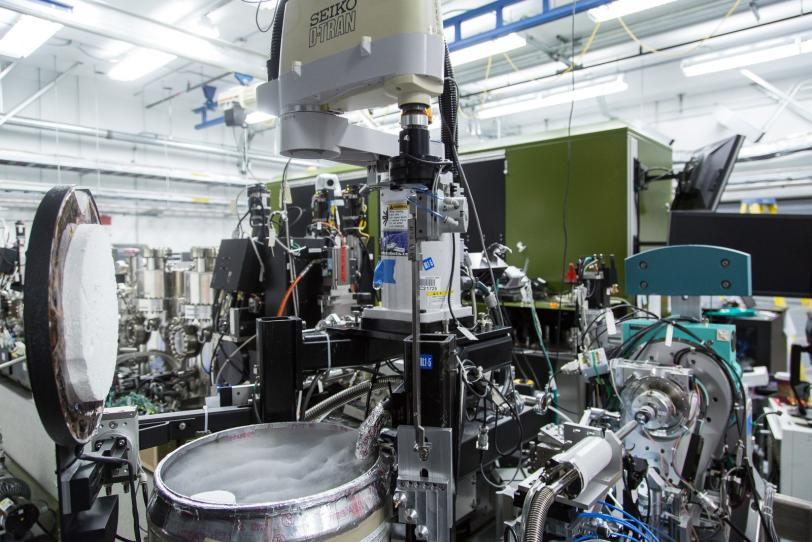
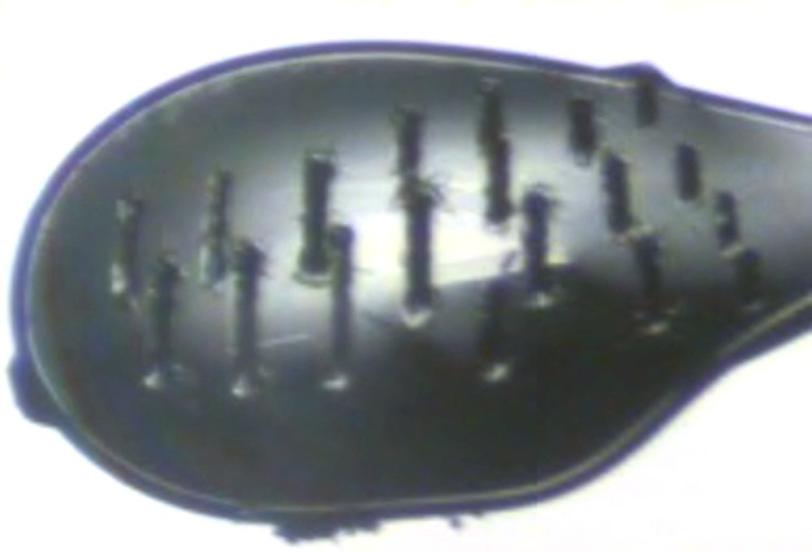
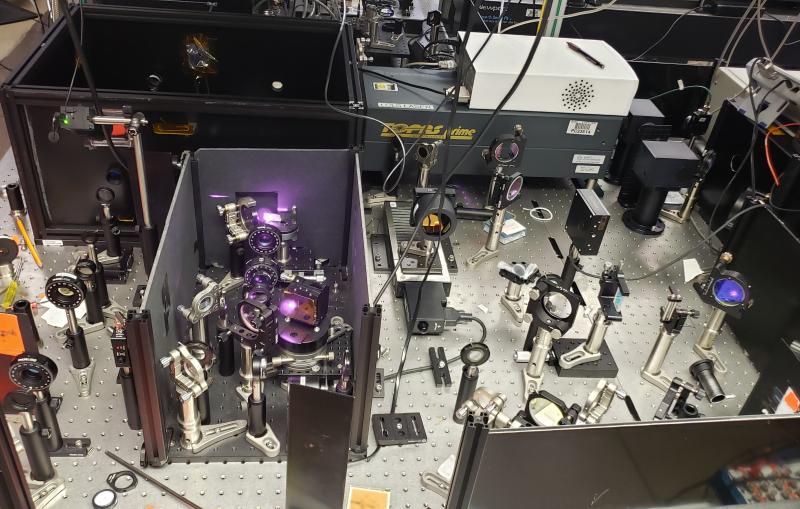
To study the joined protein structure, researchers in Brunger’s laboratory at the Stanford School of Medicine found a way to grow crystals of the complex. They used a robotic system developed at SSRL to study the crystals at SLAC’s LCLS, an X-ray laser that is one of the brightest sources of X-rays on the planet. SSRL and LCLS are DOE Office of Science User Facilities.
The researchers combined and analyzed hundreds of X-ray images from about 150 protein crystals to reveal the atomic-scale details of the joined structure.
SSRL’s Aina Cohen, who oversaw the development of the highly automated platform used for the neuroscience experiment, said, “This experiment was the first to use this robotic platform at LCLS to determine a previously unsolved structure of a large, challenging multi-protein complex.” The study was also supported by X-ray experiments at SSRL and at Argonne National Laboratory’s Advanced Photon Source.
“This is a good example of how advanced tools, instruments and X-ray methods are providing us new insights into what are truly complex mechanisms,” Cohen said.
Brunger said future studies will explore other protein interactions relevant to neurotransmitter release. “What we studied is only a subset,” he said. “There are many other factors interacting with this system and we want to know what these look like. This by no means is the end of the story.”
In addition to researchers at SLAC, Stanford University and the Stanford School of Medicine, other contributing scientists were from Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. The research was supported by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute; the National Institutes of Health (NIH); the DOE Office of Science; and the SSRL Structural Molecular Biology Program, which is also supported by the DOE Office of Science and the NIH’s National Institute of General Medical Sciences.
Citation: Q. Zhou et al., Nature, 17 August 2015 (10.1038/nature14975)
Press Office Contact: Andrew Gordon, agordon@slac.stanford.edu, (650) 926-2282
SLAC is a multi-program laboratory exploring frontier questions in photon science, astrophysics, particle physics and accelerator research. Located in Menlo Park, Calif., SLAC is operated by Stanford University for the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science.
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.