New X-ray Laser Technique Measures Atomic Vibrations Faster, More Accurately
An international team led by scientists from two SLAC/Stanford institutes has devised a much faster and more accurate way of measuring subtle atomic vibrations that underlie important hidden properties of materials.
By Mike Ross
An international team led by scientists from two SLAC/Stanford institutes has devised a much faster and more accurate way of measuring subtle atomic vibrations that underlie important hidden properties of materials.
This advance will help researchers design new materials with desirable but elusive traits, such as room-temperature superconductivity or the ability to efficiently convert heat into electricity.
The team led by David Reis and Mariano Trigo, who are members of the Stanford PULSE Institute and the Stanford Institute for Materials and Energy Sciences, published its results in the December issue of Nature Physics.
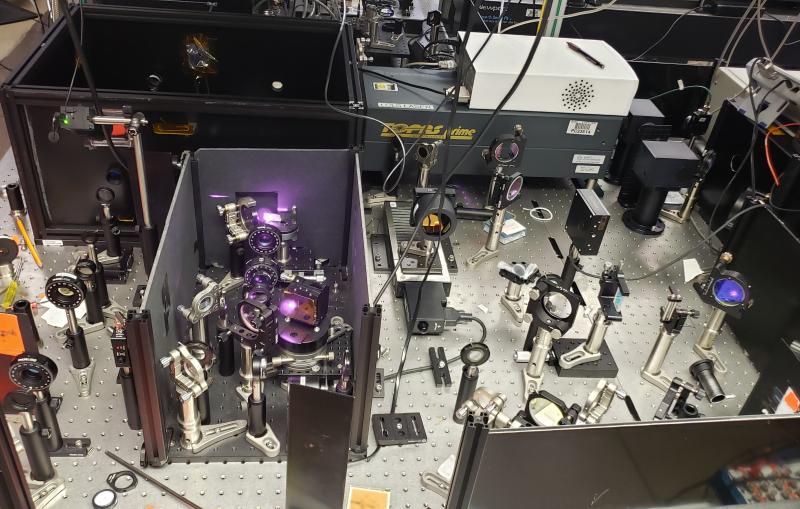
The new method, called Fourier Transform Inelastic X-ray Scattering, hits a sample of material – in this case the semiconductor germanium – with two intense, ultrashort laser pulses of different colors. The first pulse, of infrared light, jars the sample's atoms into a rich, coherent vibration pattern. Next, a burst of X-rays from SLAC's Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS) flashes onto the material and scatters onto sensitive detectors in a way that reveals the atoms' positions at that instant. By varying the time between the two pulses, scientists can capture with unprecedented precision the vibrating atoms' motion. They use this information to calculate forces between the atoms that are critical in determining how electrons, heat and light pass through the material.
With LCLS's 120-pulses-per-second repetition rate, the team gathered in just a few minutes information that would take weeks to accumulate with conventional techniques, said Peter Abbamonte of the University of Illinois in a commentary published in the same issue of Nature Physics.
"Traditional methods have only been able to measure the frequency of the atomic vibrations one wavelength at a time, and from exceedingly faint signals," said Reis. "As a result, they take a very long time to gather enough data to be sure of the result."
By comparison, Trigo said, the new method "is like hitting the side of a piano and measuring the vibrations of all the strings at once, versus listening for the faint sound from just one string at a time.”
Reis added, "Our new technique requires the extreme peak brightness of an X-ray free-electron laser such as the LCLS. Because of the large fluctuations in these sources, it currently also requires exquisite detectors, and extensive data processing on large data sets. Even so, these tools enable us to make these measurements much faster and with much greater precision than had been possible before, and things will only get better with expected equipment improvements and as we gain more experience."
This initial proof-of-principle demonstration correctly determined the already-known vibration pattern and interatomic forces for germanium. Future experiments will examine materials with desirable properties that are not yet well understood, such as cuprate high-temperature superconductors or thermoelectric materials such as lead telluride that convert heat directly into electricity.
"Several groups using a variety of techniques have conflicting explanations for the internal atomic forces that give lead telluride its special properties," Reis said. "The situation is ripe for someone to come in and find the truth, which we intend to do soon."
SLAC is a multi-program laboratory exploring frontier questions in photon science, astrophysics, particle physics and accelerator research. Located in Menlo Park, California, SLAC is operated by Stanford University for the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science. To learn more, please visit www.slac.stanford.edu.
DOE’s Office of Science is the largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.
SLAC's LCLS is the world's most powerful X-ray free-electron laser. A DOE national user facility, its highly focused beam shines a billion times brighter than previous X-ray sources to shed light on fundamental processes of chemistry, materials and energy science, technology and life itself. For more information, visit lcls.slac.stanford.edu.