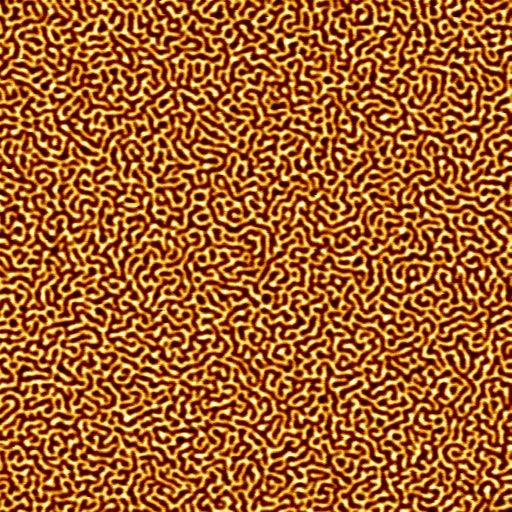
Using Light to Switch Off Magnetism
One way to make magnetic storage drives faster would be to use light to flip the polarity of tiny patches of material, called magnetic domains, back and forth – from 0 to 1 and back again, in computing terms.
By Glenn Roberts Jr.
One way to make magnetic storage drives faster would be to use light to flip the polarity of tiny patches of material, called magnetic domains, back and forth – from 0 to 1 and back again, in computing terms. Now an experiment at a German X-ray laser facility has captured nanoscale, light-induced changes in a material made of layered cobalt and platinum.
Researchers were surprised to find that bombardment with infrared laser light allowed speeding electrons to break through the walls separating one magnetic domain from the next, destroying the local magnetization in the process.
The team used ultrashort pulses of infrared light to trigger changes in the magnetic material and then examined those changes with pulses from the FLASH X-ray laser at DESY in Hamburg. The results were published in the Oct. 2 edition of Nature Communications and are described in a DESY press release.
Led by Stefan Eisebitt, a professor at the Technische Universität Berlin, the experiment included participation by scientists at nearly a dozen research centers, among them Bill Schlotter, an instrument scientist at SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory's Linac Coherent Light Source.
"Ultrafast X-ray pulses are perfect for investigating the role of nanoscale magnetic arrangement on the mechanisms of ultrafast magnetic switching," Schlotter said. LCLS has been used for similar experiments studying nanoscale magnetic switching, and Eisebitt has been involved in experiments at LCLS.
"Optical demagnetization is by far the quickest process to change magnetization locally, and local control of magnetization is the basis of magnetic storage,” Eisebitt said in announcing the results. “Therefore, optical processes could help to make magnetic memories faster in the future.”
The paper's lead author, Bastian Pfau of TU Berlin, said the observations, which line up with theories and simulations, show how electrons speeding through material can destroy magnetization in cobalt-platinum samples by passing across neighboring, nanoscale-sized magnetic domains. The atoms in each domain all have their magnetic fields aligned in the same direction.
“When bombarded with laser light, released electrons that diffuse through the material will break through the domain walls. They go from one domain into the neighboring domain, which is magnetized in the opposite direction, causing the destruction of the local magnetization,” Pfau said, adding that the understanding of this phenomenon may lead towards improved magnetic storage devices.
"In the future we will improve our experiments in a way that we will be able to not only prove the presence of the effect but also quantify its strength," he also said.